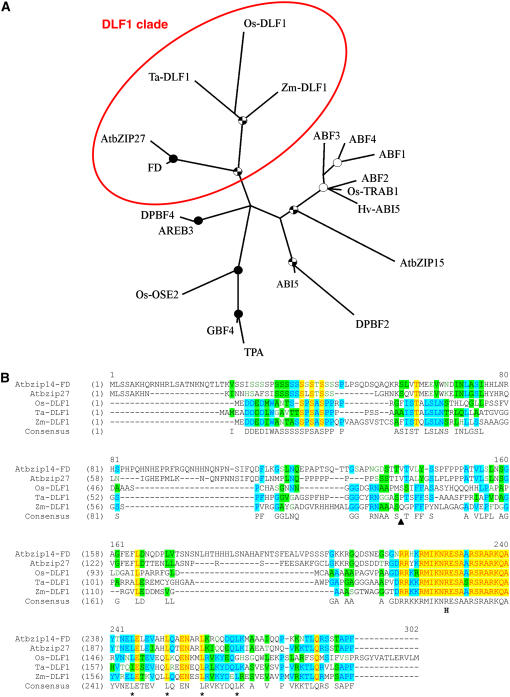
Figure 3.
Phylogeny and sequence comparison of DLF1 and other bZIP proteins. A, Phylogenetic relationship of DLF1 and other bZIP proteins. The unrooted consensus tree built with the PHYLIP program indicates the relationship of maize DLF1 to Arabidopsis, rice, wheat, and barley (Hordeum vulgare) group-A bZIP proteins based on the classification of Jakoby et al. (2002). The DLF1 clade is circled. Details of the proteins used are listed in Supplemental Table S6. One thousand bootstrap replicates were used to assess the confidence of the branching, which is indicated by a black circle for bootstrap values of 90% to 100%, a checked circle for values of 70% to 90%, and a white circle for values of 50% to 70%. B, Alignment of members of the DLF1 clade. Members of the DLF1 clade were aligned with the VectorNTI alignment tool (Invitrogen). Yellow highlights indicate amino acid identity is conserved across all the proteins. Blue highlights indicate 60% amino acid identity and green highlights indicate 40% amino acid identity across the aligned proteins. The black triangle indicates the position of the premature STOP in the dlf1-N2389A nonsense mutation. The “H” indicates the position of the R>H substitution in the dlf1-N2461A missense mutation. The four Leu in the canonical zipper domain are denoted by an asterisk (*). AtbZIP14, the FD gene, Arabidopsis, BN000021; AtbZIP27, Arabidopsis, BN000022; Os-DLF1, rice, AB109206.2; and Ta-DLF1, wheat, EST CK206464.