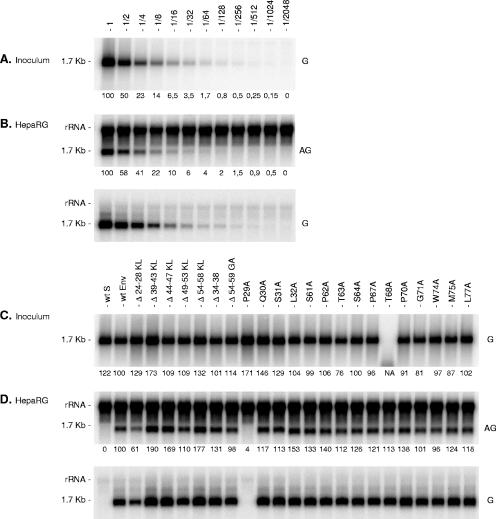
FIG. 5.
Effects of envelope protein CYL-I mutations on the infectivity of HDV virions. (A) Supernatant (1 ml) containing approximately 2 × 108 ge of wt HDV virions was serially diluted prior to analysis by Northern blot hybridization with a genomic-strand-specific, 32P-labeled RNA probe (G). One milliliter of undiluted or 2- to 2,048-fold diluted wt HDV-containing medium was added to HepaRG cells in the presence of 4% PEG 8000. (B) Cells were harvested 8 days after inoculation and analyzed for the presence of HDV RNA by Northern blot hybridization with an antigenomic (AG) or a genomic (G) strand-specific, 32P-labeled RNA probe. Dilution factor is indicated. (C) Supernatants (1 ml) from HuH-7 cell cultures were normalized for their genomic HDV RNA concentration. One ml of normalized inoculum was added to HepaRG cells in the presence of 4% PEG 8000. Inocula were recovered after overnight exposure to cells, and their genomic HDV RNA content was controlled by Northern blot hybridization using a genomic strand-specific, 32P-labeled RNA probe. Signals are from 0.5 ml of postexposure inocula. Cells were harvested 8 days after exposure and analyzed for the presence of HDV RNA as described above. rRNA which hybridized nonspecifically to antigenomic-specific HDV RNA probes served as a loading control. The size in kilobases of HDV RNA is indicated. wt S, HDV particles coated with the wt S-HBsAg only. wt Env, HDV particles coated with wt S-, M-, and L-HBsAg. Numbers below each panel are percentages of the wt value. NA, not applicable.