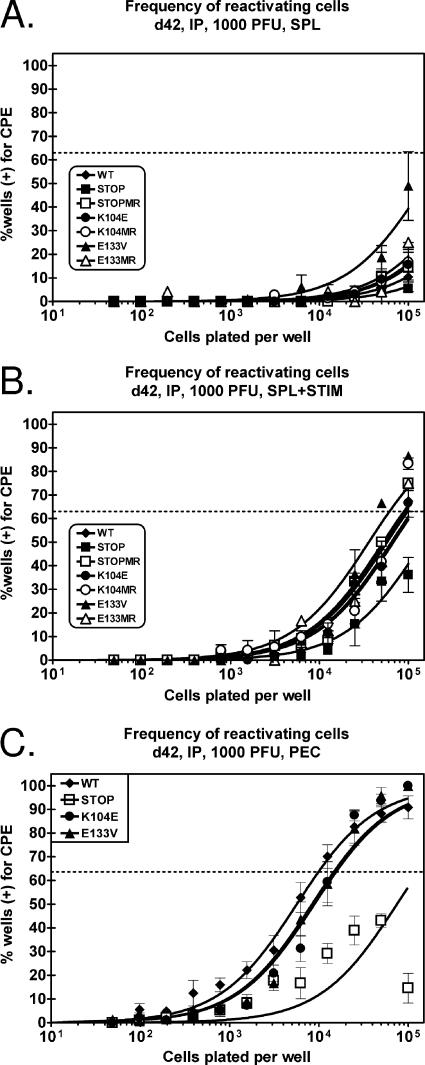
FIG. 8.
Reactivation from latently infected splenocytes and PECs does not require v-cyclin-CDK interactions following intraperitoneal inoculation. C57BL/6 mice were infected with 1,000 PFU of wild-type (WT) γHV68, v-cyc[STOP], v-cyc[STOPMR], v-cyc[K104E], v-cyc[K104MR], v-cyc[E133V], or v-cyc[E133MR] via intraperitoneal (IP) injection. (A and B) Forty-two days postinfection, splenocytes (SPL) were harvested and subjected to twofold limiting dilutions on MEF indicator monolayers for determinations of the ex vivo frequency of cells reactivating from latency in the absence (A) or presence (B) of anti-IgG/IgM and anti-CD40 stimulation. Mechanically disrupted cells were plated in parallel, and preformed infectious virus was undetected in all cases (data not shown). C57BL/6 mice were infected with 1,000 PFU of wild-type γHV68 (closed diamonds), v-cyc[STOP] (closed squares), v-cyc[K104E] (closed circles), and v-cyc[E133V] (closed triangles) via intraperitoneal injection. Data represent three to four independent experiments, with each experiment containing cells pooled from four to five mice. (C) Forty-two days postinfection, PECs were harvested and subjected to twofold limiting dilutions on MEF indicator monolayers for determinations of the ex vivo frequency of cells reactivating from latency. Mechanically disrupted cells were plated in parallel, and preformed infectious virus was undetected in all cases (data not shown). Curve fit lines were derived by nonlinear regression analysis, and symbols represent means and standard errors of the means (error bars) of data from individual experiments as indicated. The dashed line (63%) represents the value used to calculate the frequency of reactivating cells as indicated by a Poisson distribution. Data represent independent experiments (wild-type γHV68, n = 6; v-cyc[STOP], n = 4; v-cyc[K104E], n = 6; v-cyc[E133V], n = 4), with each experiment containing cells pooled from four to five mice. CPE, cytopathic effect.