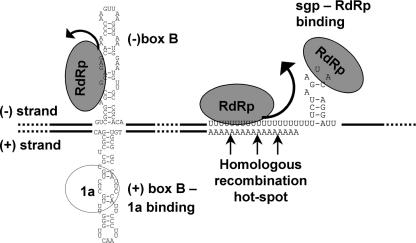
FIG. 6.
Model illustrating the synthesis of sgRNA3a in view of multiple functions of the intergenic region in minus-strand RNA3. The BMV RdRp enzyme complex (represented by gray ovals) migrates alongside the minus-strand RNA template and pauses (represented by curved arrows) at the secondary structure or, most notably, at the oligo(U) tract, leading to the formation of subgenomic sgRNA3a. Yet another molecule of the RdRp enzyme binds to the sgp and initiates the de novo synthesis of sgRNA4. Also, the rehybridization of the sgRNA3a oligo(A) tail to the RNA3 minus template can resume full-length copying, which primes the observed RNA3-RNA3 recombination (5, 69). The positive and minus RNA strands are represented by thick lines and both the oligo(U) tract in the minus-strand template and the oligo(A) 3′-termini are exposed. The stem-and-loop structures adopted by the positive and minus strands upstream of their oligo(U) and oligo(A) tracts (3) are shown. The region that binds to protein 1a via the B box of the stem-loop structure in positive strands (28, 57) is shown.