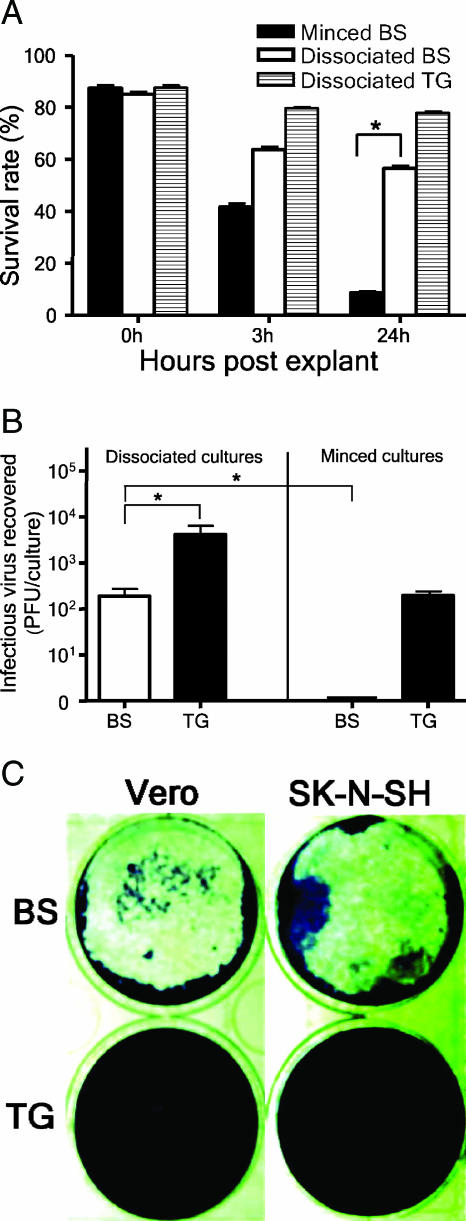
FIG. 3.
The dissociation method sustains the cell viability and viral infectivity of brain stem cultures. (A) Brain stems (BS) and trigeminal ganglia (TG) harvested from uninfected BALB/c mice were minced or dissociated and then cultured before the cell viabilities of minced and dissociated cultures were evaluated by trypan blue exclusion. One hundred nucleated cells were counted, and the unstained (viable) cells were recorded. (B) BS and TG harvested from uninfected BALB/c mice were minced or dissociated and cultured. HSV-1 KOS (2,000 PFU) was added to cultures, and cultures were harvested for titration of infectious virus at 24 h p.i. Data shown in panels A and B are the means ± standard errors of the means from three independent experiments, each done in duplicate. *, P < 0.05 by Student's t test. (C) Dissociated BS, but not TG, preparations damaged less confluent Vero and human neuronal (SK-N-SH) cell monolayers. Dissociated cells from one-third of a BS or one TG were added to monolayers of Vero or SK-N-SH cells and cultured for 48 h before being stained with crystal violet. The data shown represent two experiments.