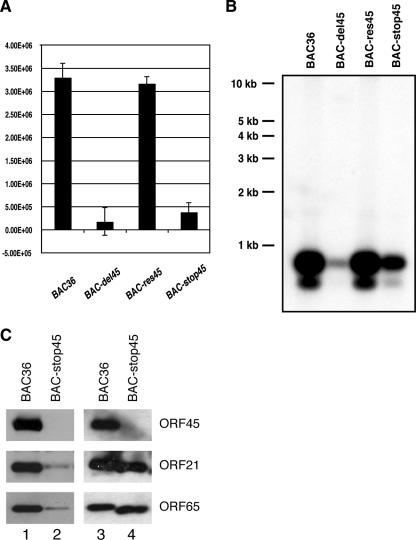
FIG. 6.
Extracellular progeny viruses produced by BAC36 and BAC-stop45. The pooled hygromycin-resistant cells were induced with TPA and butyrate for 4 days, and viruses in the supernatants were concentrated 100-fold. Virus stocks (200 μl) were treated with Turbo DNase I for 1 h at 37°C, and viral DNAs were extracted. (A) Viral DNAs were analyzed by a real-time PCR assay using primers to LANA. A serial dilution of a known amount of BAC36 DNA was used to construct a standard curve. Copy numbers were normalized and are expressed as copy number per milliliter of supernatant. (B) Viral DNAs were digested with NotI, resolved on a 0.8% agarose gel, and subjected to Southern analysis with a probe of the KSHV terminal repeat sequence. (C) Virion proteins in the preparations were analyzed by Western blotting. Samples of 15 μl of 100-fold-concentrated viruses of BAC36 (lane 1) and BAC-stop45 (lane 2) were subjected to Western blot analysis with antibodies against KSHV virion proteins as indicated. Equal numbers of virions (1 × 107) of BAC36 (lane 3) and BAC-stop45 (lane 4), based on the viral genomic copy number determined by real-time PCR, were diluted to equal volumes with 1× PBS, and viral particles were precipitated with PEG. The pellets were dissolved in SDS loading buffer and analyzed by Western blotting.