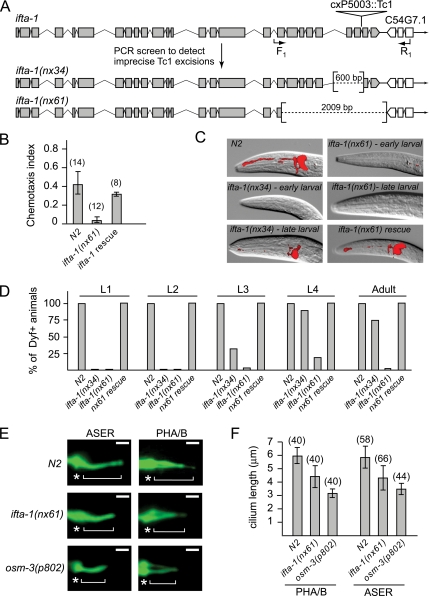
Figure 4.
ifta-1 is a ciliogenic gene required for the normal structure and function of sensory cilia. (A) Generation of two mutant alleles of ifta-1 by transposon excision. Shown is the genomic position of cxP5003::Tc1 within ifta-1, and the resultant 600- and 2009-base pair deletions obtained after excision. (B) ifta-1(nx61) mutants are defective in chemotaxis toward iso-amyl alcohol compared with wild-type (N2) animals. Rescue of the chemotaxis defect was observed in ifta-1(nx61) worms expressing a wild-type ifta-1::gfp transgene. (C) ifta-1(nx34) and ifta-1(nx61) animals are defective in their ability to uptake the fluorescent dye DiI. Shown are DIC-fluorescence merged images of the head region of wild-type and ifta-1 mutant worms after a dye-fill assay. Note that the dye-fill defective phenotype (Dyf) of ifta-1 mutants is fully rescued in ifta-1 mutants expressing a wild-type ifta-1::gfp transgene. (D) The Dyf phenotype of ifta-1(nx61) mutants is fully penetrant at all larval and adult stages, whereas ifta-1(nx34) animals have a stage-specific Dyf phenotype. Note that each data point represents the analysis of 50 worms. (E and F) The cilia length of ifta-1(nx61) mutants is shorter than wild-type worms but longer than osm-3(p802) mutants. Presented are fluorescence images (E) and a graph (F) showing the cilia lengths obtained for PHA/B phasmid and ASER amphid neurons, by using srb-6p::gfp and gcy-5p::gfp reporters, respectively. For E: Bar, 2 μm; star, transition zone; bracket, cilia. The n values for F are presented in brackets.