Figure 3.
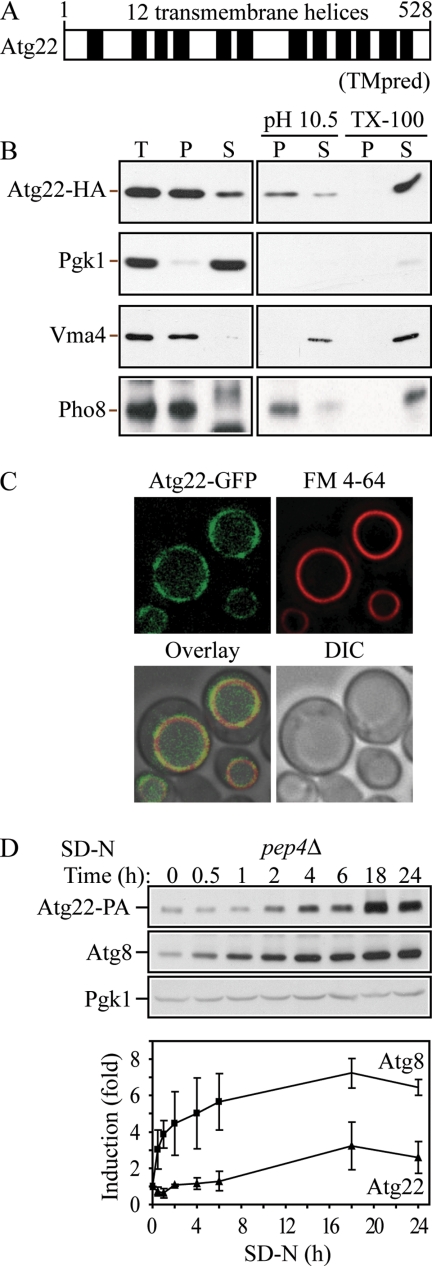
Atg22 is an integral vacuolar membrane protein. (A) Hydrophobicity analysis based on TMpred (Hofmann and Stoffel, 1993) predicts 12 transmembrane helices, which are indicated schematically. (B) Atg22 is an integral membrane protein. Cells expressing Atg22-3xHA (ZFY36) were grown in YPD, converted to spheroplasts, and osmotically lysed and fractionated into total (T), supernatant (S), and pellet (P) fractions, as described in Materials and Methods. The resulting pellet was subjected to the indicated treatment: 0.5 mM Na2CO3, pH 10.5, or 1% Triton X-100. After centrifugation, S and P fractions were collected and analyzed by immunoblots with anti-hemagglutinin (HA) antibody or the indicated antisera. The positions of Atg22-HA, and the markers Pgk1 (cytosolic), Vma4 (peripheral membrane), and Pho8 (integral membrane) are indicated. (C) Atg22 is localized on the vacuolar membrane. Cells expressing Atg22-GFP (ZFY16) were grown in YPD, treated with FM 4-64 to label vacuoles, and analyzed by fluorescence microscopy as described in Materials and Methods. DIC, differential interference contrast. (D) The expression level of Atg22 seemed constant under vegetative growth and was induced under nitrogen starvation conditions. Cells expressing Atg22-protein A (ZFY38) in the background of pep4Δ were grown in YPD and shifted to SD-N. At the indicated times, aliquots were removed and analyzed by immunoblot using anti-protein A (PA) antibody and antisera to Atg8 and Pgk1; Pgk1 was used as a loading control. The blot is shown for a representative experiment and the graph plots the data for three independent experiments. The error bars represent the SD.