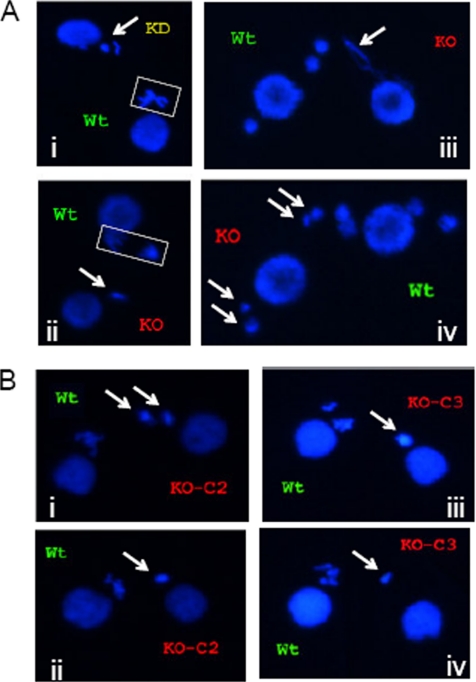
Figure 1.
Cytogenetic evidence for micronuclear genome instability, developmental delay, and/or meiotic arrest in TIF1-deficient strains. The wild-type strain (CU428) was mated with TIF1 mutants (TXh48 [KD, knockdown]; TXk202 [KO, knockout/null]), and mating pairs were examined at various times during development by DAPI fluorescent staining. Wild-type and mutant strains were prelabeled with MitoTracker Red and Green dyes, respectively, to identify each partner. (A) Meiotic aberrations in TIF1-deficient strains. Meiotic stages: i, wild type: metaphase, mutant: prophase (?); ii, wild type: anaphase, mutant: prophase (?); iii, wild type: postmeiotic pronuclei, mutant: meiotic crescent or aberrant anaphase (?); and iv, wild type and mutant: postmeiotic pronuclei. Arrows point to mutant nuclei. (B) Comparative cytogenetic analysis of siblings cells in subcloned parental lines KO-C2 and KO-C3 derived from the tif1-1::neo knockout strain TXh202. The newly generated clonal lines were briefly expanded and then mated with the wild-type strain CU428 to examine meiosis. Arrows point to condensed, micronuclear-derived DAPI-staining chromosomes in siblings within the same mating culture. Micrographs i and ii, representative tif1-1::neo/TIF1 knockout clone C2 siblings; micrographs iii and iv, representative tif1-1::neo knockout clone C3 siblings.