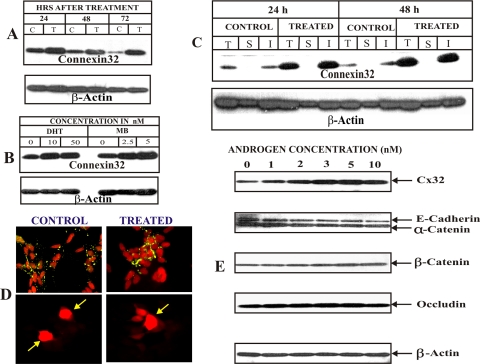
Figure 2.
Androgens increase Cx32 expression level and gap junction formation. Cx32-expressing LNCaP cells were treated with the androgens as indicated. (A) Kinetics of enhancement of Cx32 level upon testosterone (10 nM) treatment. Note that significant enhancement is observed up to 72 h. (B) Synthetic androgen, mibolerone (MB), is more potent than dihydro-testosterone (DHT) in increasing Cx32 expression level. Cells were treated with various concentrations of DHT and MB for 48 h. Note that MB is at least 4–5 times more potent than DHT on an equimolar basis. (C and D) MB enhances Cx32 expression level and gap junction assembly. Formation of gap junctions was analyzed by detergent insolubility of Cx32 by Western blot analysis (C) and by immunocytochemical analysis (D, top panels) 48 h after treatment with MB (5 nM). Note an increase in size of gap junctions after treatment (compare control and treated, top panels). Note also that increase in Cx32 expression level is accompanied by an increase in detergent-insoluble fraction. (D, bottom) junctional transfer of fluorescent tracer, Alexa 594 (MW 760), was examined as described in Material and Methods. Note extensive junctional transfer to several first-order neighbors upon MB treatment. (E) Androgens have no effect on adherens and tight junction proteins. Cx32-expressing LNCaP cells were treated with various MB concentrations (1–10 nM) for 24 h. Expression of Cx32, adherens junction–associated proteins E-cadherin and α- and β-catenins, and tight junction–associated protein, occludin, was analyzed by Western blot analysis of total cell lysate (5 μg). Detection of E-cadherin and α-catenin was done simultaneously with monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies, respectively. Note that MB increased the expression of only Cx32, but not of adherens and tight junction–associated proteins, at all the concentrations tested.