Figure 2.
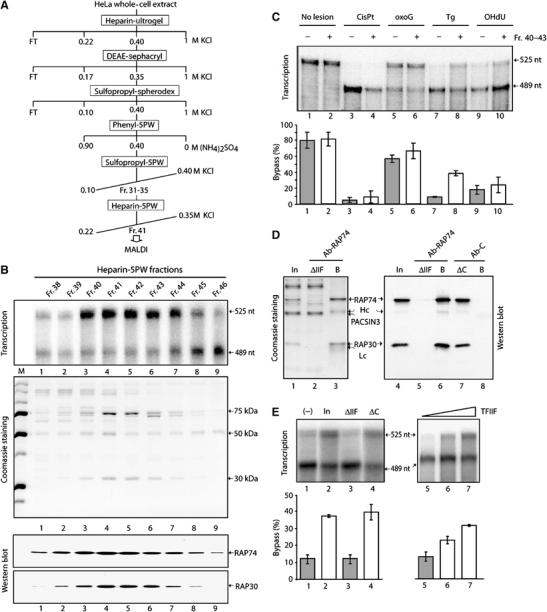
The bypass factor TFIIF. (A) Purification scheme from HeLa WCE. (B) Transcription, Coomassie staining, and TFIIF-Western blot using the fractions from the final heparin 5PW column. (C) Fr. 40–43 bypass activity towards several DNA lesions as indicated at the top of the panel. The quantification (mean±s.d.) was performed from at least three independent experiments. (D) TFIIF immunodepletion from the Pool of Fr.40–43 of the Heparin-5PW column (In), using either Ab-RAP74, an antibody raised against the larger subunit of TFIIF, or Ab-C, a control-antibody. The heavy (Hc) and light (Lc) chains are indicated. The proteins retained on the beads (B) as well as the ones in the flow through fraction (ΔIIF) were analyzed by SDS–PAGE (Coomassie staining, lanes 1–3) and Western blot (lanes 4–8) using the RAP74 and RAP30 antibodies. (E) These fractions (lanes 1–4) as well as the recombinant TFIIF (lanes 5–7) were further tested for their bypass activity in transcription. Quantitative data derived from at least three independent experiments are shown (mean±s.d., lower panels).
