Figure 1.
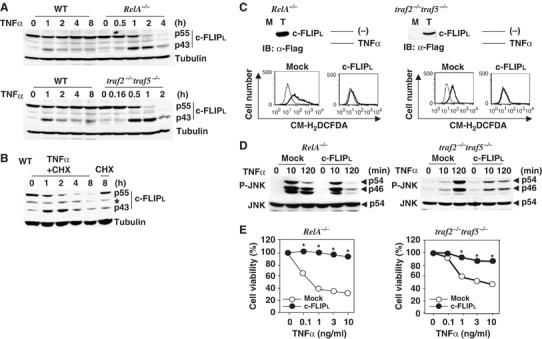
TNFα induces rapid degradation of c-FLIPL and ectopic expression of c-FLIPL inhibits TNFα-induced accumulation of ROS, prolonged JNK activation, and cell death in RelA−/− and traf2−/−traf5−/− MEFs. (A) WT, RelA−/−, and traf2−/−traf5−/− MEFs were stimulated with TNFα (10 ng/ml) for the indicated times, then the lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-c-FLIP (upper panel) and anti-tubulin (lower panel) antibodies. p55 and p43 indicate full and degraded form of c-FLIPL, respectively. (B) WT MEFs were stimulated with TNFα (10 ng/ml) in the presence of CHX (10 μg/ml) for the indicated times. Immunoblotting were performed as in (A). The asterisks indicate nonspecific bands. (C) Transfection of c-FLIPL inhibits TNFα-induced ROS accumulation in RelA−/− and traf2−/−traf5−/− MEFs. Total cell lysates from mock (M) or respective transfectants (T) were immunoblotted with anti-Flag antibody. The transfectants were unstimulated (thin line) or stimulated (bold line) with TNFα (10 ng/ml) for 4 h, and then the cells were labeled with CM-H2DCFDA (1 μM) and analyzed by flow cytometry. (D) c-FLIPL inhibits prolonged, but not early JNK activation in RelA−/− and traf2−/−traf5−/− MEFs. Mock- or c-FLIPL-transfected RelA−/− and traf2−/−traf5−/− MEFs were stimulated with TNFα (10 ng/ml) for the indicated times, and then the lysates were immunoblotted with anti-phospho-JNK (upper panel) and anti-total JNK (lower panel) antibodies. (E) c-FLIPL inhibits TNFα-induced cell death in RelA−/− and traf2−/−traf5−/− MEFs. Mock- or c-FLIPL-transfected RelA−/− and traf2−/−traf5−/− MEFs were stimulated with the indicated amounts of TNFα for 16 h. Cell viability was determined by WST assay. Results are presented as the mean of triplicate samples and represent three independent experiments with similar results. Standard errors are within 5%. *P<0.05 compared to mock transfectant.
