Figure 7.
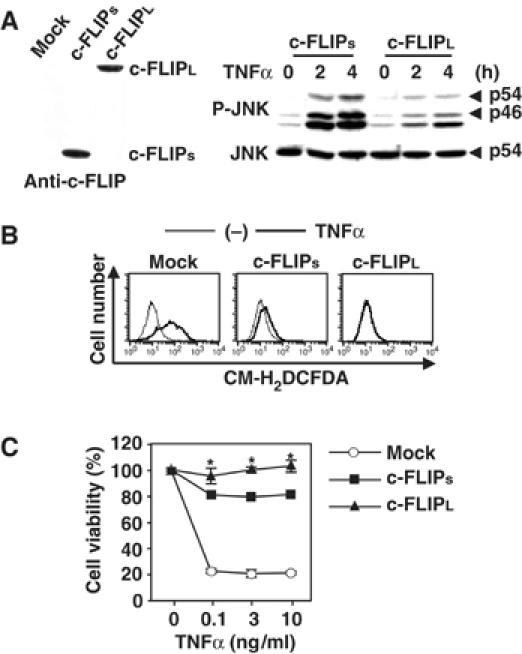
c-FLIPL more efficiently suppresses TNFα-induced ROS accumulation, prolonged JNK activation, and cell death than c-FLIPs. (A) c-FLIPL, but not c-FLIPs, completely inhibits TNFα-induced prolonged JNK activation in c-Flip−/− MEFs. Total cell lysates from mock, c-FLIPs, or c-FLIPL transfectants were immunoblotted with anti-c-FLIP antibody. c-FLIPs and c-FLIPL transfectants were stimulated with TNFα (10 ng/ml) for the indicated times, and then the lysates were analyzed as in Figure 1D. (B) c-FLIPL, but not c-FLIPs, completely inhibits TNFα-induced ROS accumulation in c-Flip−/− MEFs. The transfectants were unstimulated (thin line) or stimulated (bold line) with TNFα (10 ng/ml) for 2 h (for mock transfectant) or 8 h (for c-FLIP transfectants), then accumulated ROS were analyzed as in Figure 1C. (C) c-FLIPL, but not c-FLIPs, completely inhibits TNFα-induced cell death in c-Flip−/− MEFs. Mock or c-FLIP transfectants were stimulated with the indicated amounts of TNFα for 16 h. Cell viability was determined by WST assay as in Figure 1E. *P<0.05 compared to c-FLIPs transfectant.
