Figure 1.
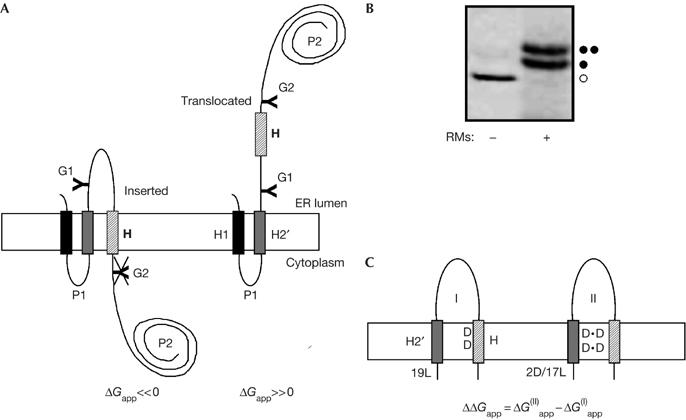
The leader peptidase model protein. (A) Wild-type leader peptidase (Lep) has two transmembrane helices (H1, H2) and a large lumenal domain (P2). It inserts into rough microsomes in an Nlum–Clum orientation. In the studies reported here, the H2 segment was replaced by an H2′ segment of the general composition L19−nNn or L19−nDn (n=0, 1 or 2), and a 19-residue-long H segment (hatched), containing one or two Asn or Asp residues, was inserted into the P2 domain. Asn-X-Thr glycosylation acceptor sites (G1, G2) were introduced on both sides of the H segment, as shown. Constructs in which the H segment was integrated into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane as a transmembrane helix were glycosylated only on the G1 site (left), whereas those in which the H segment was translocated across the ER membrane were glycosylated on both the G1 and G2 sites (right). (B) In vitro translation in the absence (−) and presence (+) of dog pancreas rough microsomes (RMs) of a construct containing the 2N/17L H2′ segment and the 2N/9L/8A (N3N) H segment (see Table 1). Unglycosylated, single glycosylated and double glycosylated forms of the protein are indicated by an open circle, one filled circle and two filled circles, respectively. For this construct, ΔGapp=0.1 kcal/mol. (C) To measure the effect of Asp- or Asn-mediated interactions between the H2′ and H segments, two constructs were compared for each H segment: one with a uniformly hydrophobic 19-Leu H2′ segment (I) and one with an H2′ segment in which one or two of the Leu residues have been replaced by Asp or Asn residues (II). The interaction free energy is expressed as the difference (ΔΔGapp) in the apparent free energy of insertion of the H segment between the two constructs. In the example shown, the H segment contains two Asp residues and the appropriate number of Leu and Ala residues to make ΔG(I)app≈0 kcal/mol. A, Ala, alanine; D, Asp, aspartic acid; L, Leu, leucine; N, Asn, asparagine; T, Thr, threonine.
