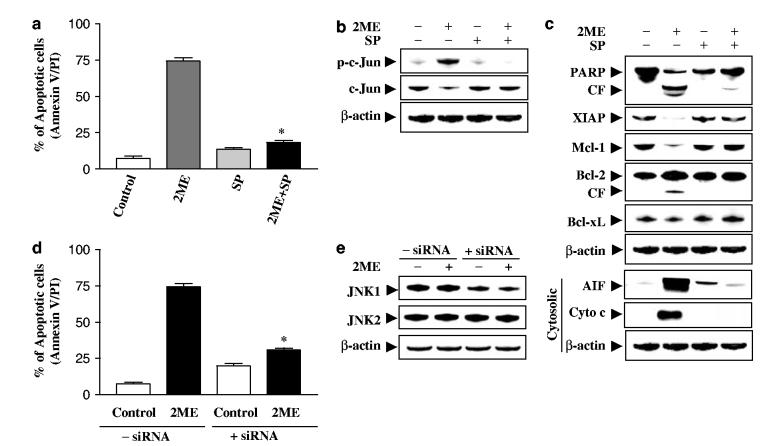
Figure 6.
Pharmacological inhibition of JNK and transfection of JNK1 siRNA significantly protect cells from 2ME-induced apoptosis. U937cells were pretreated with 10 μM of JNK inhibitor, SP600125 (SP), for 1 h, followed by the addition of 4 μM of 2ME for 24 h. (a) Cells were stained with annexin V/PI, and apoptosis was determined using flow cytometry as described in Materials and methods. The values obtained from annexin V/PI assays represent the mean±s.d. for three separate experiments. *Values for cells treated with 2ME and SP were significantly less than those obtained for cells treated with 2ME alone by Student’s t-test; P<0.01. After treatment, total cellular and cytosolic extracts were prepared and subjected to Western blot analysis using antibodies against phospho-c-Jun, c-Jun (b), and apoptosis-related proteins including PARP, XIAP, Mcl-1, Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, cytochrome c, and AIF (cytosolic S-100 fraction) (c). U937cells were transfected with JNK1 siRNA oligonucleotides or controls and incubated for 24 h at 371C, after which cells were treated with 4 μM of 2ME for 24 h. (d) Apoptosis was determined using the annexin V-FITC assay as described in Materials and methods. *Values for cells treated with 2ME after transfection with JNK1 siRNA oligonucleotides were significantly decreased compared to those for control cells treated with 2ME by Student’s t-test; P<0.01. (e) Total cellular extracts were prepared and subjected to Western blot analysis using antibodies against JNK1 and JNK2. For Western blot assay, each lane was loaded with 30 μg of protein; blots were subsequently stripped and reprobed with antibody against β-actin to ensure equivalent loading. Two additional studies yielded equivalent results