Fig. 5.
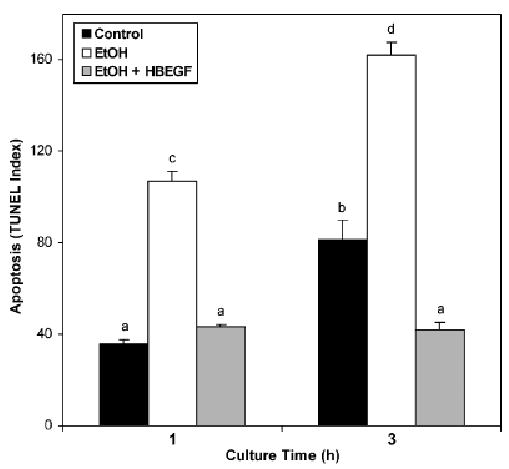
Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like growth factor (HB-EGF) amelioration of embryonic cell death induced by exposure to ethanol in vitro. Intact visceral yolk sacs were isolated from nontreated dams on E7.5 and cultured for 1 or 3 hour in Ham’s F10 medium alone (control), medium containing 400 mg% ethanol (EtOH), or medium containing 400 mg% ethanol and 5 nM HB-EGF (EtOH+HB-EGF). The embryonic portion of the yolk sacs was then isolated, fixed, permeabilized, and assayed for terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP-X nick end labeling (TUNEL) by the fluorescence microscopy procedure detailed in the Materials and Methods section. Mean and SE are shown. N = 4 to 5 embryos per treatment. Bars labeled with nonmatching letters were significantly different.
