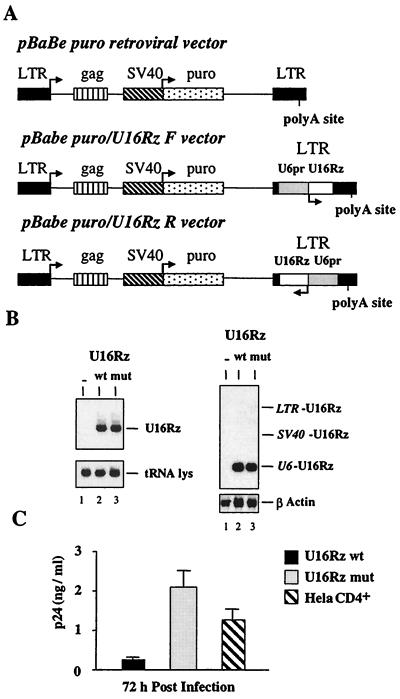
Figure 3.
Delivery and in vivo activity of the U16Rz in the HeLa CD4+ cell line. (A) Schematic representation of pBabe puro retroviral constructs. The expression cassette U6+1/U16Rz wt and U16Rz mutant were cloned in both orientations in the 3′LTR (U3 region) of the pBabe puro parental vector (48), giving rise to the constructs pBabe puro/U16Rz wt or U16Rz mutant, F (forward) and pBabe puro/U16Rz wt or U16Rz mutant, R (reverse). (B) HeLa CD4+ cells were transfected with the pBabe puro retroviral vector constructs, and pooled populations were selected for puromycin resistance. Five micrograms of total RNAs was extracted from the different transfected HeLa CD4+ pooled populations and electrophoresed in a 6% polyacrylamide/7 M urea gel (Left) or in a 1% agarose/formaldehyde gel (Right), blotted onto nylon filters, and hybridized with specific probes as described in Materials and Methods. Lane 1 contains total RNA extracted from parental HeLa CD4+ cells. Lanes 2 and 3 contain total RNA extracted from the HeLa CD4+ pooled populations transfected with either the pBabe puro/U16Rz wt or pBabe puro/U16Rz mutant, respectively, both in the F orientation. (C) The pooled populations of HeLa CD4+ expressing U16Rz wt, U16Rz mutant, or the untransfected parental HeLa CD4+ cells were infected with HIV-1-IIIB at an moi of 0.001. The HIV-1 p24 antigen accumulation was determined at 72 h after infection. The data presented represent average values of four independent experiments, including the standard deviation.