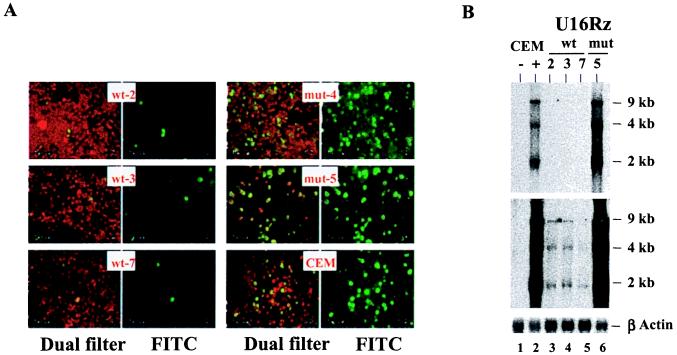
Figure 5.
CEM stable clones expressing the U16Rz wt are resistant to an elevated moi of HIV-1. (A) HIV indirect immunofluorescence assays were performed as described in Fig. 4C. CEM clones 2, 3, and 7 expressing the U16Rz wt, clones 4 and 5 expressing the U16Rz mutant, and parental CEM cells were infected with HIV-1NL4–3 at an moi of 0.002. Immunofluorescence monitoring of infection was performed at day 11 after infection. The infected cells are FITC-stained (Right). The dual filter (FITC/rhodamine, Left) shows uninfected cells (red) and infected cells (green). (B) Northern blot analysis was performed on 5-μg RNA samples electrophoresed in a 1% agarose/formaldehyde gel. Total RNAs were extracted from the above HIV-1-infected CEM stable clones. Hybridization was carried out with a Rev cDNA sequence. The signals obtained from the endogenous β-actin (Bottom) were used as loading controls. After overnight exposure the HIV-1 RNA was detected (Top) only in the parental CEM cells (lane 2) and in the CEM clone 5 expressing the U16Rz mutant (lane 6). RNA prepared from uninfected CEM cells (lane 1) was used as a negative control. HIV-1 RNAs from the U16Rz wt-expressing clones 2, 3, and 7 (lanes 3, 4, and 5, respectively) was detectable only after 3 days of prolonged exposure of the hybridized filter, as shown in Middle.