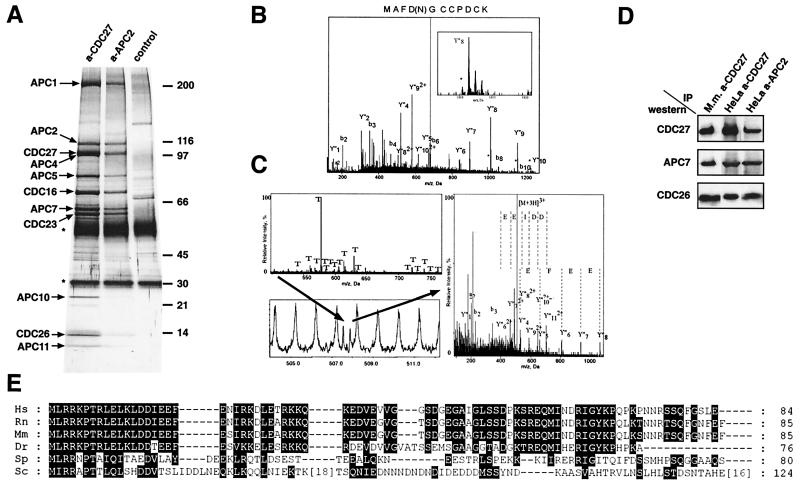
Figure 1.
Characterization of CDC26 and APC11 as subunits of the vertebrate APC. (A) Identification of APC subunits by silver staining. Immunoprecipitates obtained from logarithmically growing HeLa cells with CDC27 or APC2 antibodies were analyzed by SDS/PAGE and silver staining. The positions of APC subunits are indicated. The IgG light and heavy chains are marked by stars. (B and C) Identification of APC11 and CDC26 by nanoelectrospray tandem mass spectrometry. (B) Mass spectrometric sequencing of APC11. Tandem mass spectrum of a tryptic peptide (m/z 680.9) obtained after in-gel digestion of p10. The presence of peaks shifted by 1 Da (marked by asterisks) allowed to localize the site of deamidation. (C) Mass spectrometric sequencing of CDC26. Mass spectrum of in-gel digested human p14 (Upper left). The peaks marked with T correspond to trypsin autolysis products. The peak marked by an arrow (Lower left) was sequenced by nanoelectrospray mass spectrometry. The right panel shows the tandem mass spectrum of the selected peak. (D) APC was immunoprecipitated from logarithmically growing HeLa cells (HeLa) and from mouse myeloma Ag8.653 cells (Mm) with CDC27 or APC2 antibodies. Precipitates were subsequently analyzed by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotting by using CDC27, APC7, and CDC26 antibodies. (E) Alignment of the amino acid sequences of CDC26 orthologs from various species. CDC26 orthologs were identified by psi-blast by using the human CDC26 sequence as a query. Amino acid residues that are identical or similar (according to the Blosum 62 substitution matrix) are highlighted by black boxes. Amino acid residues are given in the one-letter code. For Sc Cdc26 insertions of 18 and 16 amino acids are indicated. Ce, Caenorhabditis elegans; Dr, Danio rerio; Hs, Homo sapiens; Mm, Mus musculus; Rn, Rattus norwegicus; Sc, Saccharomyces cerevisiae; Sp, Schizosaccharomyces pombe.