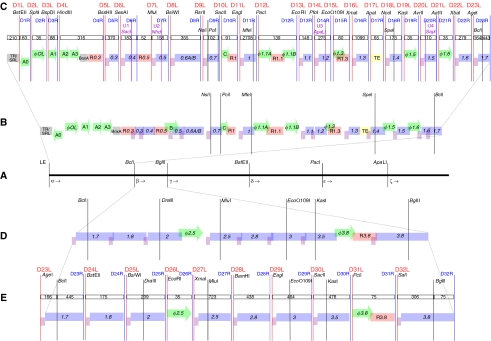
Figure 2.
Genome design. (A) We split the wild-type T7 genome into six sections, alpha through zêta, using five restriction sites unique across the natural sequence. (B) Wild-type section alpha genetic elements: protein coding regions (blue), RBSs (purple), promoters (green), RNaseIII recognition sites (pink), a transcription terminator (yellow), and others (gray). Elements are labeled by convention (Dunn and Studier, 1983). Images are not to scale, but overlapping boundaries indicate elements with shared sequence. The five useful natural restriction sites across section alpha are shown (black lines). (C) T7.1 section alpha parts. Parts are given integer numbers, 1–73, starting at the left end of the genome. Unique restriction site pairs bracket each part (red/blue lines, labeled D[part #]L/R). Added unique restriction sites (purple lines, U[part #]) and part length (# base pairs, open boxes) are shown. We do not know if sequence changes in and around parts 6 and 7 destroy the minor E. coli promoter, B. (D) Wild-type section beta genetic elements. (E) T7.1 section beta parts. Supplementary Figure S2 depicts the six sections, alpha through zêta, which make up the T7.1 genome.