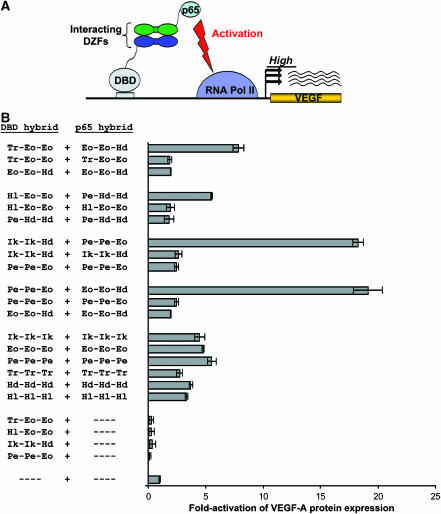
Figure 5.
Synthetic DZFs can mediate assembly of an artificial bi-partite transcription factor and activation of the endogenous VEGF-A gene in human cells. (A) Schematic overview of a mammalian cell-based ‘activator reconstitution' assay for testing DZF interactions. Productive interaction of DZFs (green and dark blue ovals) fused to an NF-κB p65 (p65) transcriptional activation domain and to a synthetic DBD that binds the human VEGF-A gene is expected to mediate reconstitution of a synthetic activator protein capable of stimulating VEGF-A expression. (B) Homo- and heterotypic interaction of synthetic DZFs assessed using the activator reconstitution assay. Controls testing the homotypic interaction of wild-type DZF domains (from which the synthetic DZFs were derived) are shown. ‘- - - -' indicates a plasmid encoding either the DBD or p65 domains with no DZF fused. DZFs tested are represented as in Table I. Fold-stimulation of VEGF-A protein expression was calculated using ELISA measurements of secreted VEGF-A that were performed at least three times. Bars shown represent mean fold-activations of VEGF-A expression and error bars indicate standard errors of the mean.