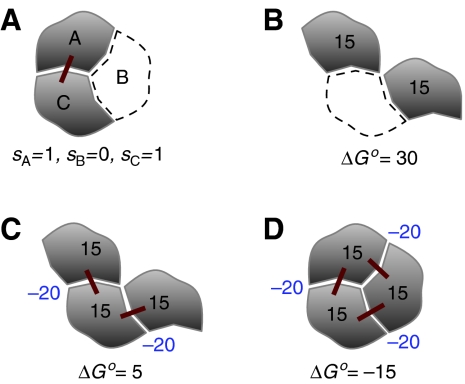
Figure 1.
Representation and thermodynamics of macromolecular assembly. (A) An example of a macromolecular complex in one of eight possible states is used as illustration of the binary description. The complex consists of three molecular positions A, B, and C, described by binary variables sA, sB, and sC, respectively. In this case, A and C are occupied (gray shapes) and B is unoccupied (white shape with dashed contour). Red lines represent pairwise interactions between the components. This description can easily be connected to the thermodynamic properties of different configurations. Here, the free energy ΔGo for the configurations and their contributions are expressed in units of kcal/mol. The positional and interaction free energies are assumed to be 15 and −20, respectively. Note that the description refers to a three-molecule complex at a specific location. If, instead, one molecule is used as a reference, its positional free energy should not be counted. The free energy of the disconnected configuration (B) is much higher than the free energy of the connected configuration (C). These energetic considerations indicate that the disconnected configuration is extremely less abundant than the connected one. The stability of a compact structure (D) is considerably higher than that of a chain-like structure (C) because of the additional free energy of interaction.