Abstract
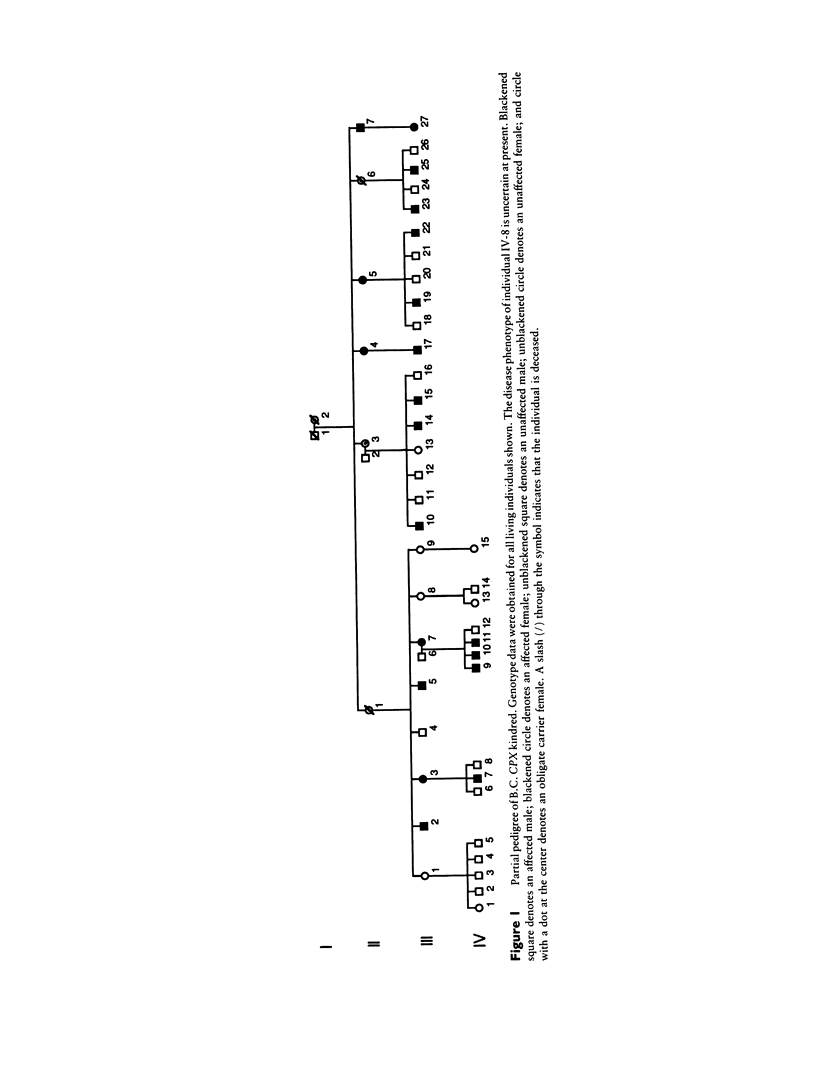
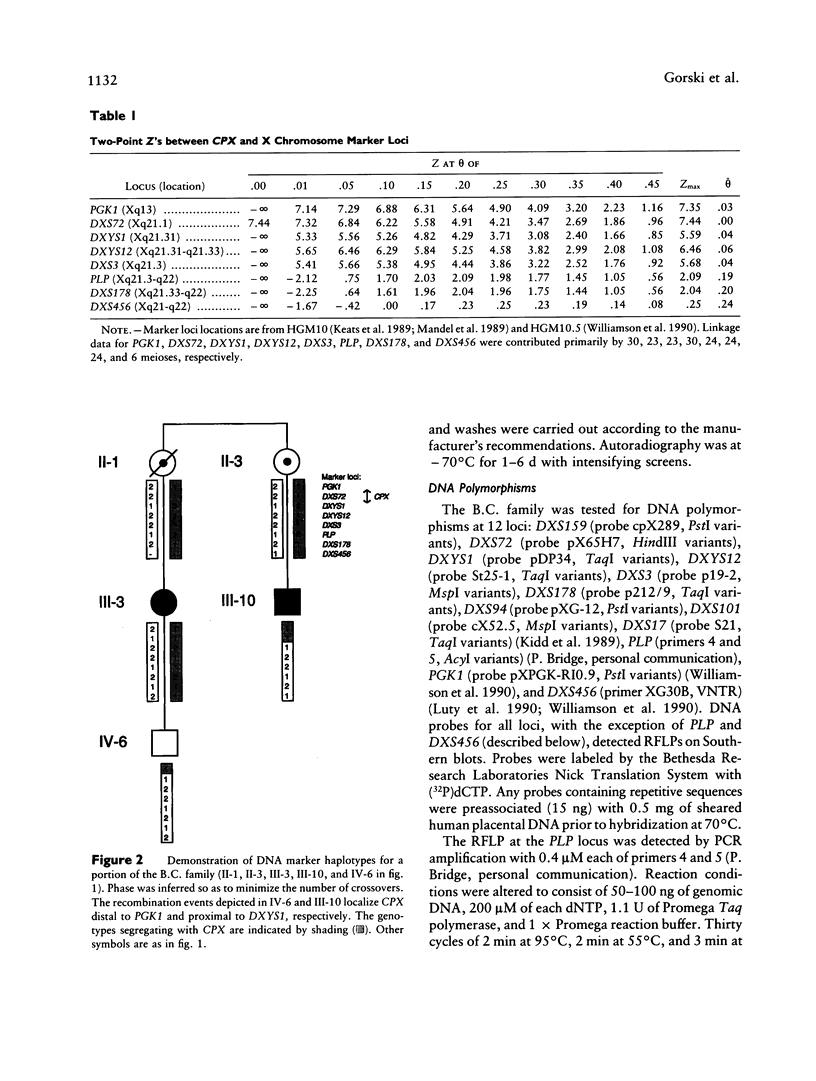
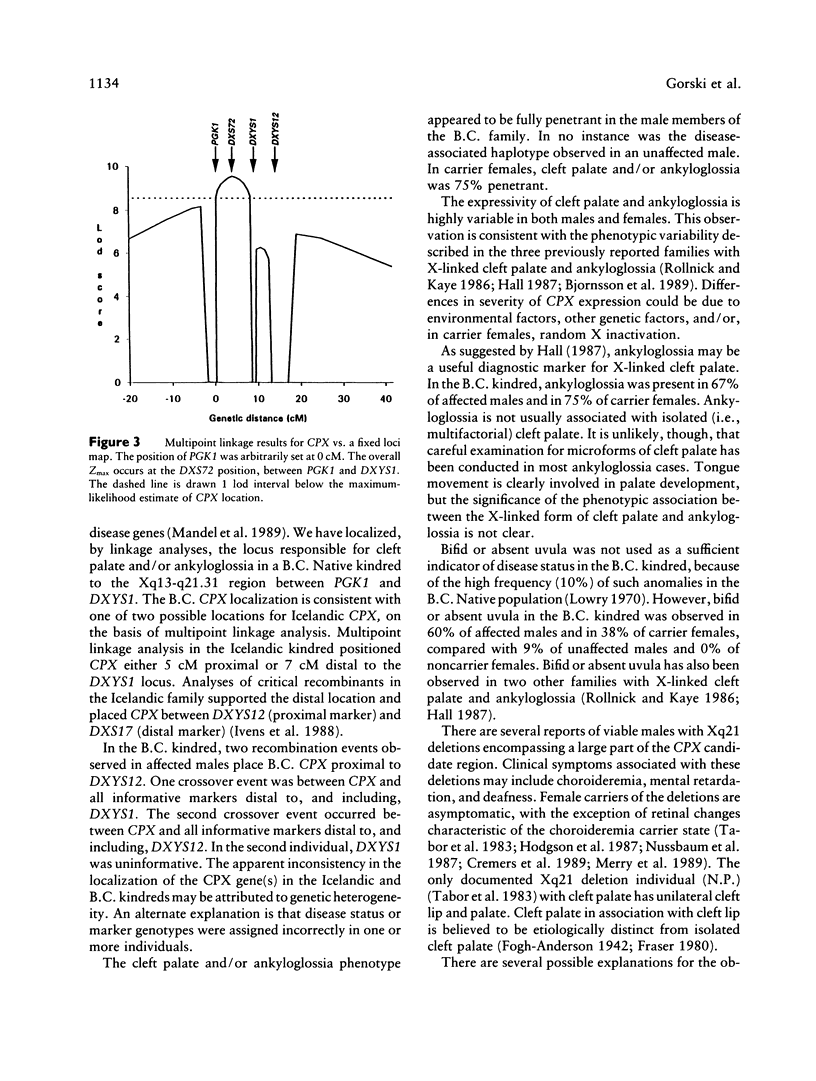
Human craniofacial malformations are a class of common congenital anomalies in which the etiology is heterogeneous and often poorly understood. To better delineate the molecular basis of craniofacial development, we have undertaken a series of experiments directed toward the isolation of a gene involved in human secondary palate formation. DNA marker linkage studies have been performed in a large British Columbia (B.C.) Native family in which cleft palate segregates as an X-linked trait. We have examined 62 family members, including 15 affected males and 8 obligate carrier females. A previous clinical description of the clefting defect in this kindred included submucous cleft palate and bifid or absent uvula. Our recent reevaluation of the family has indicated that ankyloglossia (tongue-tie) is also a feature of X-linked cleft palate in some of the affected males and carrier females. Ankyloglossia has previously been associated with X-linked cleft palate in an Icelandic kindred in which a gene responsible for cleft palate (CPX) was assigned to the Xq21.3-q22 region between DXYS12 and DXS17. For the B.C. kindred reported here, we have mapped the gene responsible for cleft palate and/or ankyloglossia to a more proximal position on the X chromosome. No recombination was observed between B.C. CPX and the DNA marker DXS72 (peak lod score [Zmax] = 7.44 at recombination fraction [theta] = .0) localized to Xq21.1. Recombination was observed between CPX and PGK1 (Zmax = 7.35 at theta = .03) and between CPX and DXYS1 (Zmax = 5.59 at theta = .04). These recombination events localize B.C. CPX between PGK1 and DXYS1 in the Xq13-q21.31 region.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bixler D. X-linked cleft palate. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Oct;28(2):503–505. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björnsson A., Arnason A., Tippet P. X-linked cleft palate and ankyloglossia in an Icelandic family. Cleft Palate J. 1989 Jan;26(1):3–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremers F. P., van de Pol D. J., Diergaarde P. J., Wieringa B., Nussbaum R. L., Schwartz M., Ropers H. H. Physical fine mapping of the choroideremia locus using Xq21 deletions associated with complex syndromes. Genomics. 1989 Jan;4(1):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90312-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diewert V. M., Pratt R. M. Cortisone-induced cleft palate in A/J mice: failure of palatal shelf contact. Teratology. 1981 Oct;24(2):149–162. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420240206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. W. Palate development. Development. 1988;103 (Suppl):41–60. doi: 10.1242/dev.103.Supplement.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall B. D. A further X-linked isolated nonsyndromic cleft palate family with a nonexpressing obligate affected male. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Jan;26(1):239–240. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320260140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson S. V., Robertson M. E., Fear C. N., Goodship J., Malcolm S., Jay B., Bobrow M., Pembrey M. E. Prenatal diagnosis of X-linked choroideremia with mental retardation, associated with a cytologically detectable X-chromosome deletion. Hum Genet. 1987 Mar;75(3):286–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00281076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivens A., Moore G. E., Chambers J., Arnason A., Jensson O., Bjornsson A., Williamson R. X-linked cleft palate: the gene is localized between polymorphic DNA markers DXYS12 and DXS17. Hum Genet. 1988 Apr;78(4):356–358. doi: 10.1007/BF00291735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins M., Stady C. Dominant inheritance of cleft of the soft palate. Hum Genet. 1980;53(3):341–342. doi: 10.1007/BF00287053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keats B. J., Sherman S. L., Ott J. Report of the committee on linkage and gene order. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1990;55(1-4):387–394. doi: 10.1159/000133023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keats B., Ott J., Conneally M. Report of the committee on linkage and gene order. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):459–502. doi: 10.1159/000132805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd K. K., Bowcock A. M., Schmidtke J., Track R. K., Ricciuti F., Hutchings G., Bale A., Pearson P., Willard H. F., Gelernter J. Report of the DNA committee and catalogs of cloned and mapped genes and DNA polymorphisms. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):622–947. doi: 10.1159/000132810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leck I. The geographical distribution of neural tube defects and oral clefts. Br Med Bull. 1984 Oct;40(4):390–395. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry R. B., Courtemanche A. D., MacDonald C. Submucous cleft palate and the general practitioner. Can Med Assoc J. 1973 Nov 17;109(10):995–passim. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry R. B. Sex-linked cleft palate in a British Columbia Indian family. Pediatrics. 1970 Jul;46(1):123–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry R. B., Thunem N. Y., Uh S. H. Birth prevalence of cleft lip and palate in British Columbia between 1952 and 1986: stability of rates. CMAJ. 1989 May 15;140(10):1167–1170. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luty J. A., Guo Z., Willard H. F., Ledbetter D. H., Ledbetter S., Litt M. Five polymorphic microsatellite VNTRs on the human X chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Apr;46(4):776–783. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel J. L., Willard H. F., Nussbaum R. L., Romeo G., Puck J. M., Davies K. E. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of the X chromosome. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):384–437. doi: 10.1159/000132801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McWilliams B. J. Submucous clefts of the palate: how likely are they to be symptomatic? Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 1991 Jul;28(3):247–251. doi: 10.1597/1545-1569_1991_028_0247_scotph_2.3.co_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merry D. E., Lesko J. G., Sosnoski D. M., Lewis R. A., Lubinsky M., Trask B., van den Engh G., Collins F. S., Nussbaum R. L. Choroideremia and deafness with stapes fixation: a contiguous gene deletion syndrome in Xq21. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Oct;45(4):530–540. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. E., Ivens A., Chambers J., Farrall M., Williamson R., Page D. C., Bjornsson A., Arnason A., Jensson O. Linkage of an X-chromosome cleft palate gene. Nature. 1987 Mar 5;326(6108):91–92. doi: 10.1038/326091a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. E., Ivens A., Newton R., Balacs M. A., Henderson D. J., Jensson O. X chromosome genes involved in the regulation of facial clefting and spina bifida. Cleft Palate J. 1990 Apr;27(2):131–135. doi: 10.1597/1545-1569(1990)027<0131:xcgiit>2.3.co;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum R. L., Lesko J. G., Lewis R. A., Ledbetter S. A., Ledbetter D. H. Isolation of anonymous DNA sequences from within a submicroscopic X chromosomal deletion in a patient with choroideremia, deafness, and mental retardation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6521–6525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollnick B. R., Kaye C. I. Mendelian inheritance of isolated nonsyndromic cleft palate. Am J Med Genet. 1986 Jul;24(3):465–473. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320240309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushton A. R. Sex-linked inheritance of cleft palate. Hum Genet. 1979 Apr 27;48(2):179–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00286901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor A., Andersen O., Lundsteen C., Niebuhr E., Sardemann H. Interstitial deletion in the "critical region" of the long arm of the X chromosome in a mentally retarded boy and his normal mother. Hum Genet. 1983;64(2):196–199. doi: 10.1007/BF00327127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weatherley-White R. C., Sakura C. Y., Jr, Brenner L. D., Stewart J. M., Ott J. E. Submucous cleft palate. Its incidence, natural history, and indications for treatment. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1972 Mar;49(3):297–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson R., Bowcock A., Kidd K., Pearson P., Schmidtke J., Chan H. S., Chipperfield M., Cooper D. N., Hewitt J., Lewitter F. Report of the DNA committee and catalogues of cloned and mapped genes and DNA polymorphisms. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1990;55(1-4):457–778. doi: 10.1159/000133027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


