Abstract
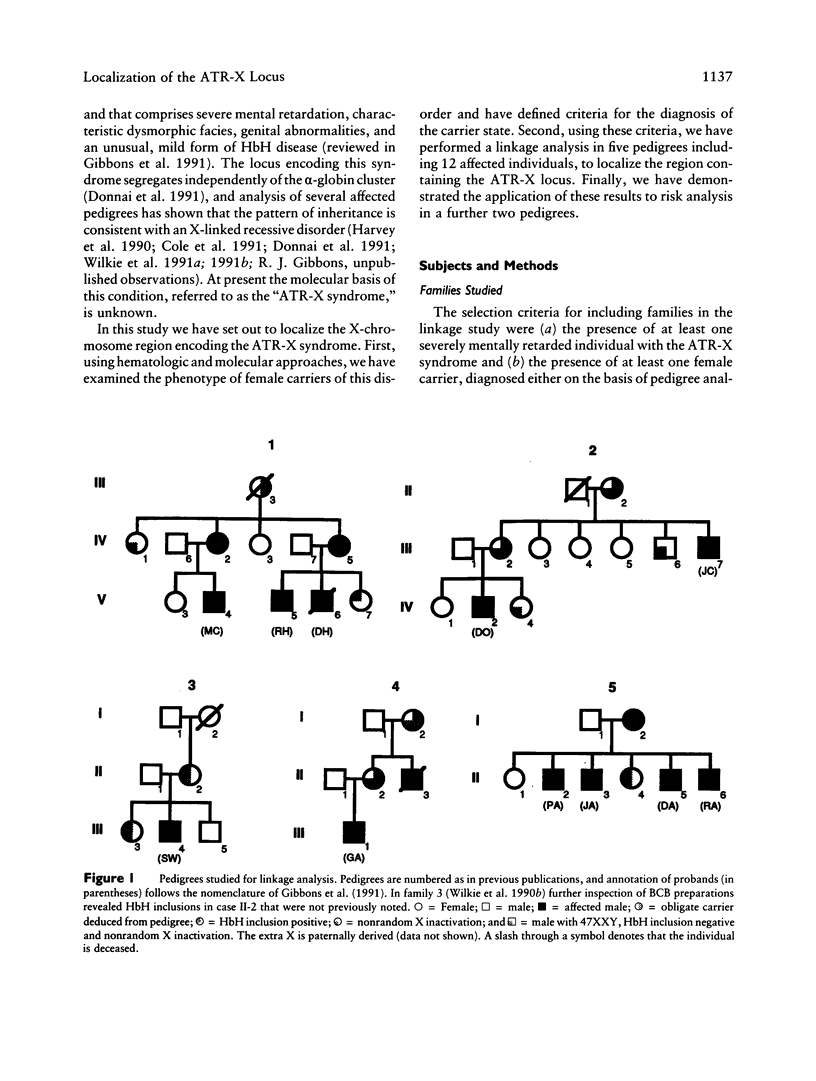
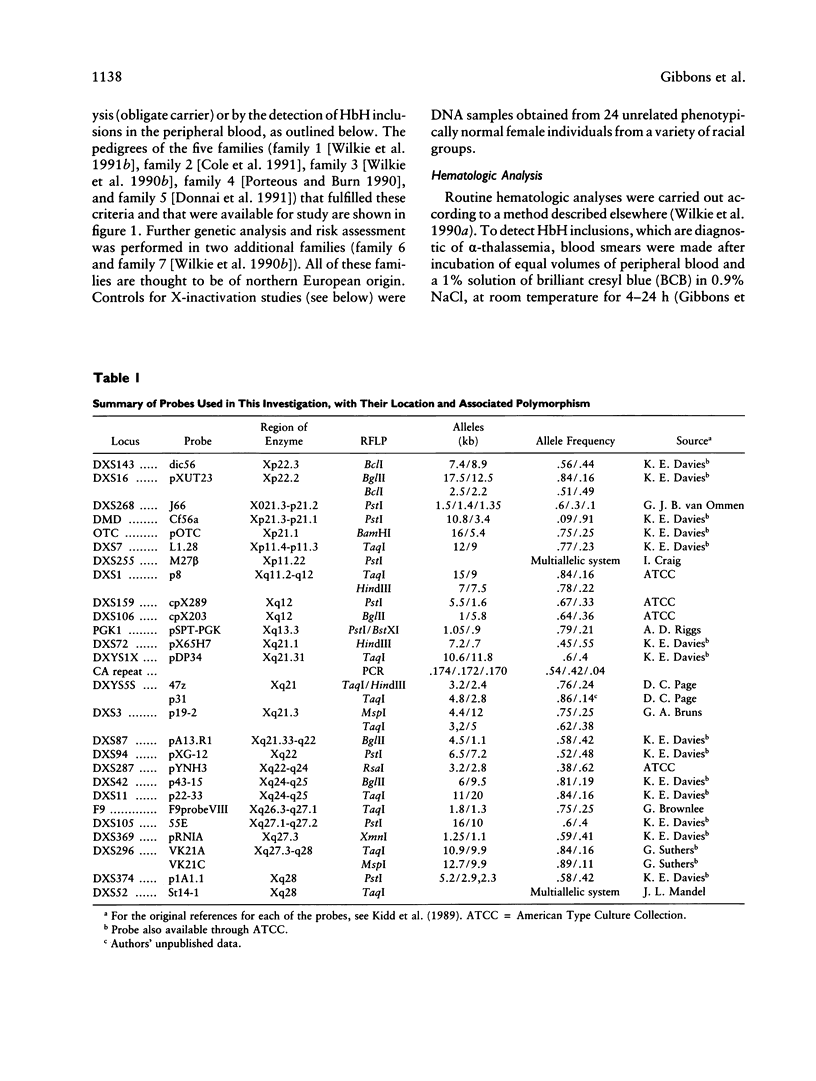
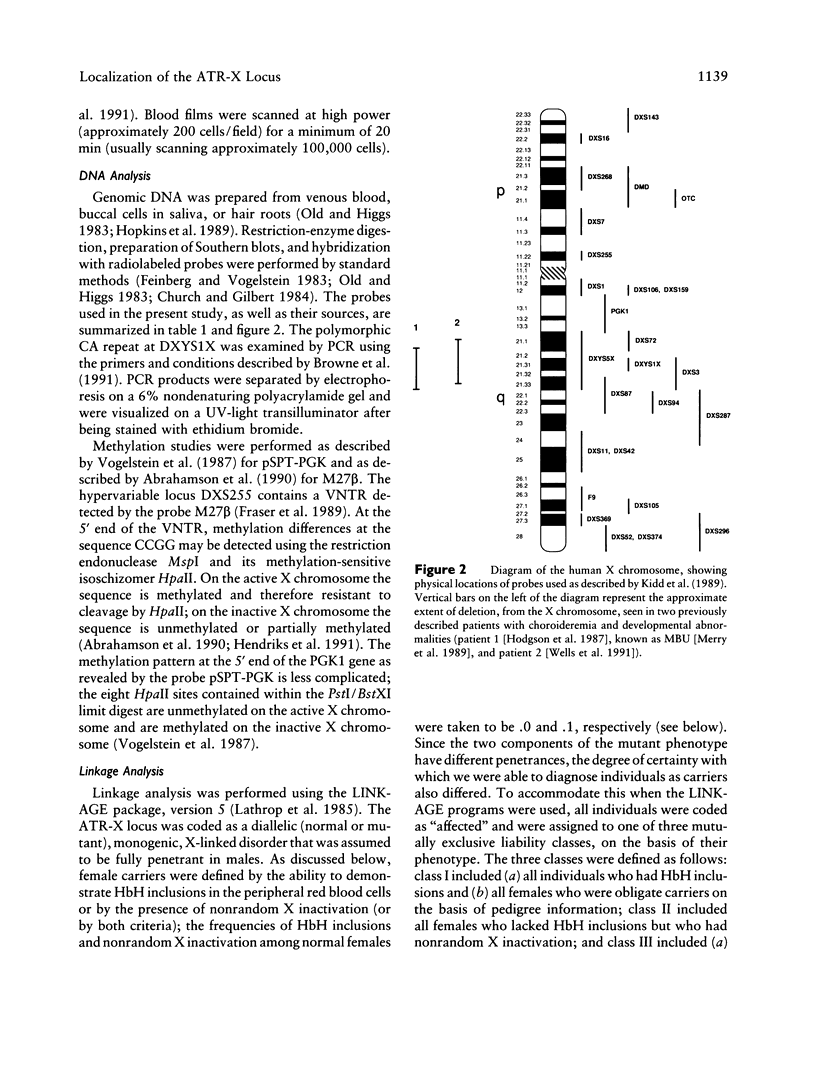
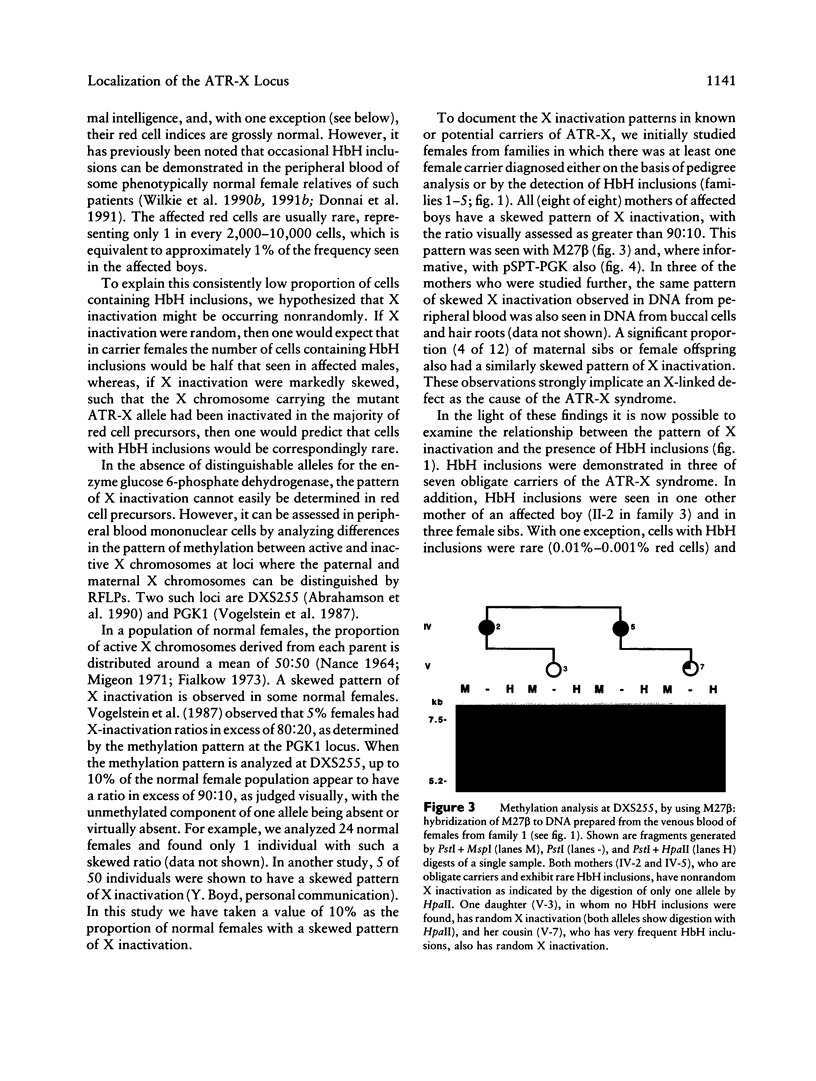
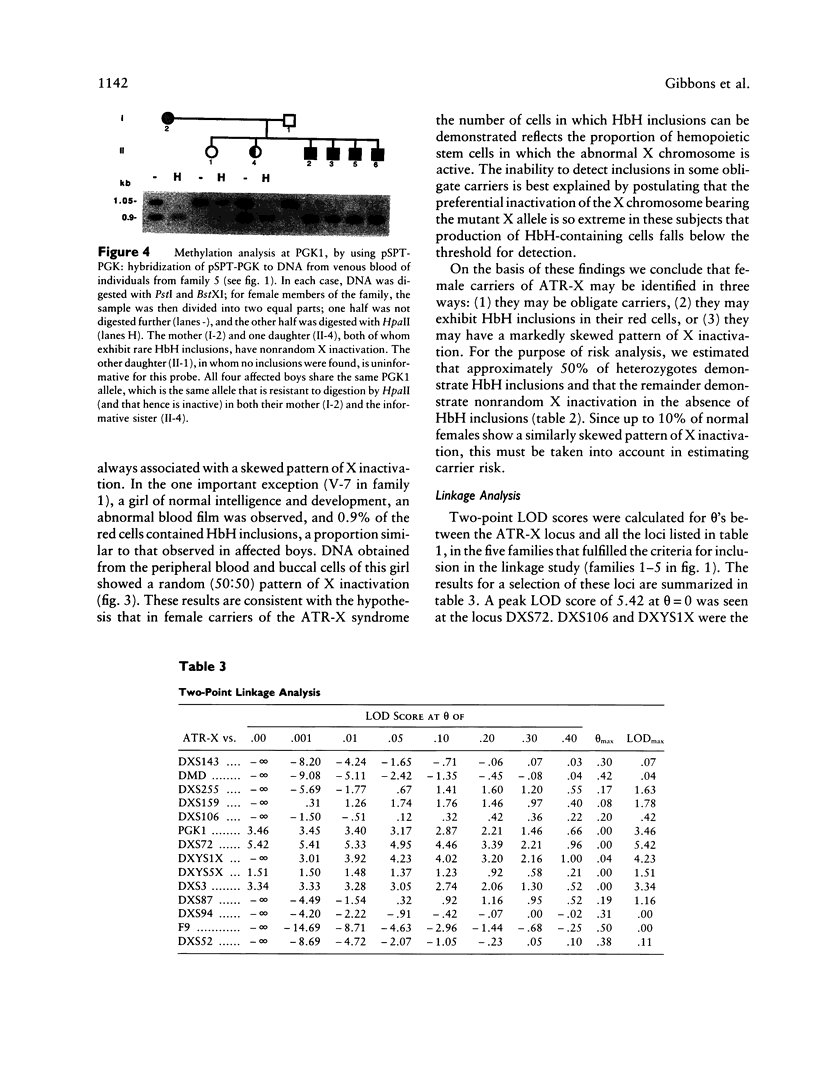
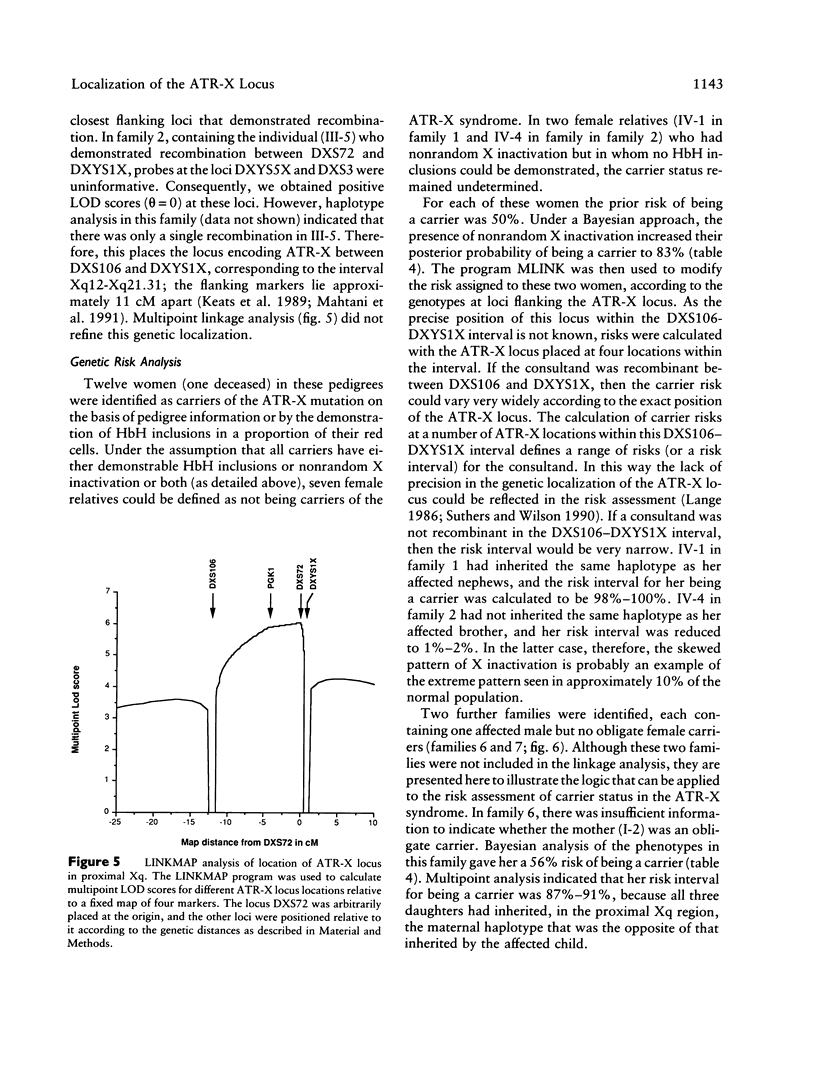
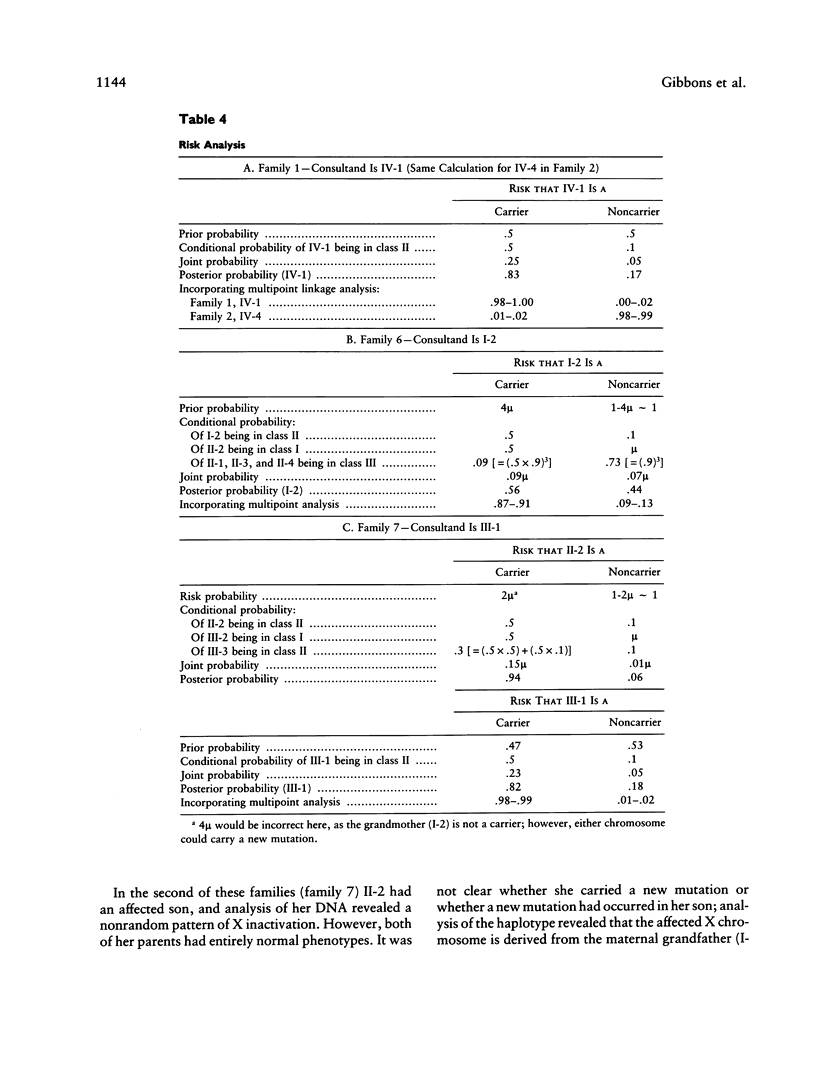
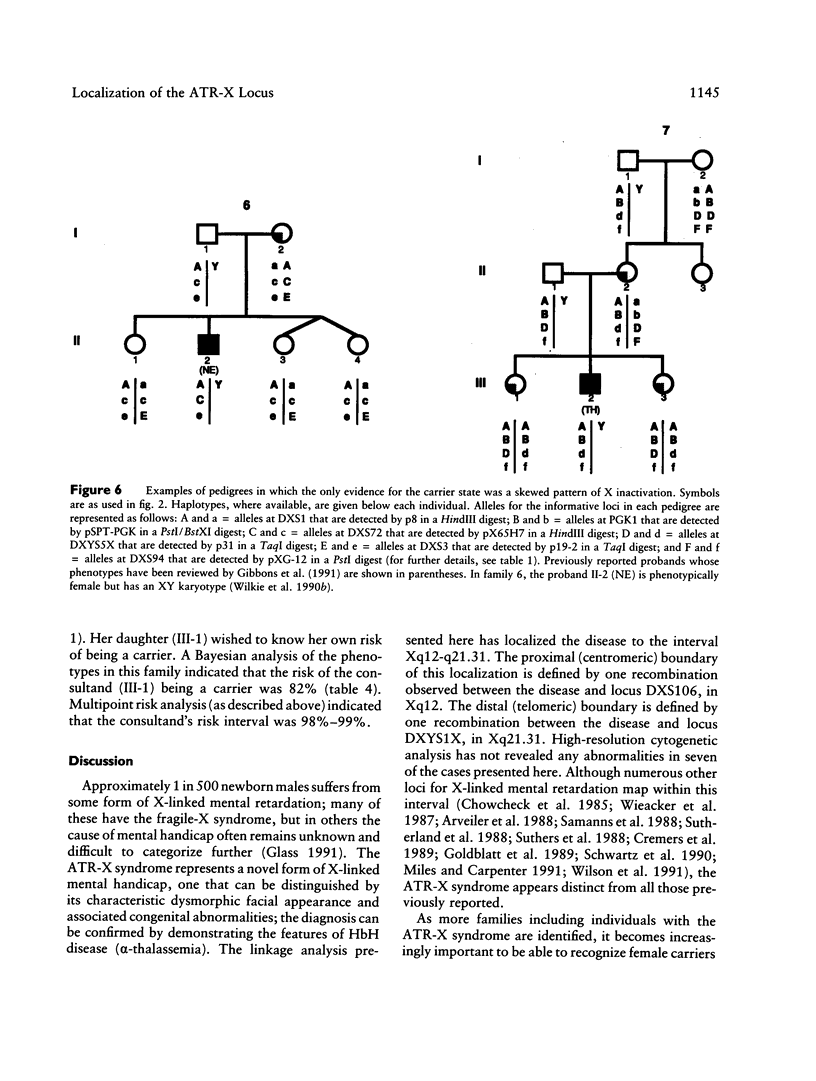
We have examined seven pedigrees that include individuals with a recently described X-linked form of severe mental retardation associated with alpha-thalassemia (ATR-X syndrome). Using hematologic and molecular approaches, we have shown that intellectually normal female carriers of this syndrome may be identified by the presence of rare cells containing HbH inclusions in their peripheral blood and by an extremely skewed pattern of X inactivation seen in cells from a variety of tissues. Linkage analysis has localized the ATR-X locus to an interval of approximately 11 cM between the loci DXS106 and DXYS1X (Xq12-q21.31), with a peak LOD score of 5.4 (recombination fraction of 0) at DXS72. These findings provide the basis for genetic counseling, assessment of carrier risk, and prenatal diagnosis of the ATR-X syndrome. Furthermore, they represent an important step in developing strategies to understand how the mutant ATR-X allele causes mental handicap, dysmorphism, and down-regulation of the alpha-globin genes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahamson G., Fraser N. J., Boyd J., Craig I., Wainscoat J. S. A highly informative X-chromosome probe, M27 beta, can be used for the determination of tumour clonality. Br J Haematol. 1990 Mar;74(3):371–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb02601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arveiler B., Alembik Y., Hanauer A., Jacobs P., Tranebjaerg L., Mikkelsen M., Puissant H., Piet L. L., Mandel J. L. Linkage analysis suggests at least two loci for X-linked non-specific mental retardation. Am J Med Genet. 1988 May-Jun;30(1-2):473–483. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320300150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. J., Lafreniere R. G., Powers V. E., Sebastio G., Ballabio A., Pettigrew A. L., Ledbetter D. H., Levy E., Craig I. W., Willard H. F. Localization of the X inactivation centre on the human X chromosome in Xq13. Nature. 1991 Jan 3;349(6304):82–84. doi: 10.1038/349082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browne D. L., Zonana J., Litt M. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the DXYS1X locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 11;19(7):1721–1721. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole T. R., May A., Hughes H. E. Alpha thalassaemia/mental retardation syndrome (non-deletional type): report of a family supporting X linked inheritance. J Med Genet. 1991 Nov;28(11):734–737. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.11.734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowchock F. S., Duckett S. W., Streletz L. J., Graziani L. J., Jackson L. G. X-linked motor-sensory neuropathy type-II with deafness and mental retardation: a new disorder. Am J Med Genet. 1985 Feb;20(2):307–315. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320200214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremers F. P., van de Pol D. J., Diergaarde P. J., Wieringa B., Nussbaum R. L., Schwartz M., Ropers H. H. Physical fine mapping of the choroideremia locus using Xq21 deletions associated with complex syndromes. Genomics. 1989 Jan;4(1):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90312-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnai D., Clayton-Smith J., Gibbons R. J., Higgs D. R. The non-deletion alpha thalassaemia/mental retardation syndrome: further support for X linkage. J Med Genet. 1991 Nov;28(11):742–745. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.11.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fialkow P. J. Primordial cell pool size and lineage relationships of five human cell types. Ann Hum Genet. 1973 Jul;37(1):39–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1973.tb01813.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser N. J., Boyd Y., Craig I. Isolation and characterization of a human variable copy number tandem repeat at Xcen-p11.22. Genomics. 1989 Jul;5(1):144–148. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90099-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Wilkie A. O., Weatherall D. J., Higgs D. R. A newly defined X linked mental retardation syndrome associated with alpha thalassaemia. J Med Genet. 1991 Nov;28(11):729–733. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.11.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass I. A. X linked mental retardation. J Med Genet. 1991 Jun;28(6):361–371. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.6.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblatt J., Ballo R., Sachs B., Moosa A. X-linked spastic paraplegia: evidence for homogeneity with a variable phenotype. Clin Genet. 1989 Feb;35(2):116–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1989.tb02915.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey M. P., Kearney A., Smith A., Trent R. J. Occurrence of the alpha thalassaemia-mental retardation syndrome (non-deletional type) in an Australian male. J Med Genet. 1990 Sep;27(9):577–581. doi: 10.1136/jmg.27.9.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendriks R. W., De Weers M., Mensink R. G., Kraakman M. E., Mollee-Versteegde I. F., Veerman A. J., Sandkuyl L. A., Schuurman R. K. Diagnosis of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome by analysis of the X chromosome inactivation patterns in maternal leucocyte populations using the hypervariable DXS255 locus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 May;84(2):219–222. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs D. R., Vickers M. A., Wilkie A. O., Pretorius I. M., Jarman A. P., Weatherall D. J. A review of the molecular genetics of the human alpha-globin gene cluster. Blood. 1989 Apr;73(5):1081–1104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs D. R., Wood W. G., Jarman A. P., Sharpe J., Lida J., Pretorius I. M., Ayyub H. A major positive regulatory region located far upstream of the human alpha-globin gene locus. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1588–1601. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson S. V., Robertson M. E., Fear C. N., Goodship J., Malcolm S., Jay B., Bobrow M., Pembrey M. E. Prenatal diagnosis of X-linked choroideremia with mental retardation, associated with a cytologically detectable X-chromosome deletion. Hum Genet. 1987 Mar;75(3):286–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00281076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarman A. P., Wood W. G., Sharpe J. A., Gourdon G., Ayyub H., Higgs D. R. Characterization of the major regulatory element upstream of the human alpha-globin gene cluster. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4679–4689. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keats B., Ott J., Conneally M. Report of the committee on linkage and gene order. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):459–502. doi: 10.1159/000132805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd K. K., Bowcock A. M., Schmidtke J., Track R. K., Ricciuti F., Hutchings G., Bale A., Pearson P., Willard H. F., Gelernter J. Report of the DNA committee and catalogs of cloned and mapped genes and DNA polymorphisms. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):622–947. doi: 10.1159/000132810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange K. Approximate confidence intervals for risk prediction in genetic counseling. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 May;38(5):681–687. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Multilocus linkage analysis in humans: detection of linkage and estimation of recombination. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 May;37(3):482–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahtani M. M., Lafrenière R. G., Kruse T. A., Willard H. F. An 18-locus linkage map of the pericentromeric region of the human X chromosome: genetic framework for mapping X-linked disorders. Genomics. 1991 Aug;10(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90172-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattei M. G., Mattei J. F., Ayme S., Giraud F. X-autosome translocations: cytogenetic characteristics and their consequences. Hum Genet. 1982;61(4):295–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00276593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merry D. E., Lesko J. G., Sosnoski D. M., Lewis R. A., Lubinsky M., Trask B., van den Engh G., Collins F. S., Nussbaum R. L. Choroideremia and deafness with stapes fixation: a contiguous gene deletion syndrome in Xq21. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Oct;45(4):530–540. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migeon B. R. Studies of skin fibroblasts from 10 families with HGPRT deficiency, with reference in X-chromosomal inactivation. Am J Hum Genet. 1971 Mar;23(2):199–210. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles J. H., Carpenter N. J. Unique X-linked mental retardation syndrome with fingertip arches and contractures linked to Xq21.31. Am J Med Genet. 1991 Feb-Mar;38(2-3):215–223. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320380209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NANCE W. E. GENETIC TESTS WITH A SEX-LINKED MARKER: GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1964;29:415–425. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1964.029.01.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyhan W. L., Bakay B., Connor J. D., Marks J. F., Keele D. K. Hemizygous expression of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in erythrocytes of heterozygotes for the Lesch-Nyhan syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jan;65(1):214–218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.1.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwaber J., Rosen F. S. X chromosome linked immunodeficiency. Immunodefic Rev. 1990;2(3):233–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz C. E., Ulmer J., Brown A., Pancoast I., Goodman H. O., Stevenson R. E. Allan-Herndon syndrome. II. Linkage to DNA markers in Xq21. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Sep;47(3):454–458. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R., Gedeon A. K., Haan E. A., Woodroffe P., Mulley J. C. Linkage studies with the gene for an X-linked syndrome of mental retardation, microcephaly and spastic diplegia (MRX2) Am J Med Genet. 1988 May-Jun;30(1-2):493–508. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320300152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suthers G. K., Turner G., Mulley J. C. A non-syndromal form of X-linked mental retardation (XLMR) is linked to DXS14. Am J Med Genet. 1988 May-Jun;30(1-2):485–491. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320300151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suthers G. K., Wilson S. R. Genetic counseling in rare syndromes: a resampling method for determining an approximate confidence interval for gene location with linkage data from a single pedigree. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Jul;47(1):53–61. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thode A., Partington M. W., Yip M. Y., Chapman C., Richardson V. F., Turner G. A new syndrome with mental retardation, short stature and an Xq duplication. Am J Med Genet. 1988 May-Jun;30(1-2):239–250. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320300125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Fearon E. R., Hamilton S. R., Preisinger A. C., Willard H. F., Michelson A. M., Riggs A. D., Orkin S. H. Clonal analysis using recombinant DNA probes from the X-chromosome. Cancer Res. 1987 Sep 15;47(18):4806–4813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weatherall D. J., Higgs D. R., Bunch C., Old J. M., Hunt D. M., Pressley L., Clegg J. B., Bethlenfalvay N. C., Sjolin S., Koler R. D. Hemoglobin H disease and mental retardation: a new syndrome or a remarkable coincidence? N Engl J Med. 1981 Sep 10;305(11):607–612. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198109103051103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells S., Mould S., Robins D., Robinson D., Jacobs P. Molecular and cytogenetic analysis of a familial microdeletion of Xq. J Med Genet. 1991 Mar;28(3):163–166. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.3.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieacker P., Wolff G., Wienker T. F. Close linkage of the Wieacker-Wolff syndrome to the DNA segment DXYS1 in proximal Xq. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Sep;28(1):245–253. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie A. O., Buckle V. J., Harris P. C., Lamb J., Barton N. J., Reeders S. T., Lindenbaum R. H., Nicholls R. D., Barrow M., Bethlenfalvay N. C. Clinical features and molecular analysis of the alpha thalassemia/mental retardation syndromes. I. Cases due to deletions involving chromosome band 16p13.3. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Jun;46(6):1112–1126. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie A. O., Gibbons R. J., Higgs D. R., Pembrey M. E. X linked alpha thalassaemia/mental retardation: spectrum of clinical features in three related males. J Med Genet. 1991 Nov;28(11):738–741. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.11.738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie A. O., Pembrey M. E., Gibbons R. J., Higgs D. R., Porteous M. E., Burn J., Winter R. M. The non-deletion type of alpha thalassaemia/mental retardation: a recognisable dysmorphic syndrome with X linked inheritance. J Med Genet. 1991 Oct;28(10):724–724. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.10.724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie A. O., Zeitlin H. C., Lindenbaum R. H., Buckle V. J., Fischel-Ghodsian N., Chui D. H., Gardner-Medwin D., MacGillivray M. H., Weatherall D. J., Higgs D. R. Clinical features and molecular analysis of the alpha thalassemia/mental retardation syndromes. II. Cases without detectable abnormality of the alpha globin complex. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Jun;46(6):1127–1140. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M., Mulley J., Gedeon A., Robinson H., Turner G. New X-linked syndrome of mental retardation, gynecomastia, and obesity is linked to DXS255. Am J Med Genet. 1991 Sep 15;40(4):406–413. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320400405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelstein J. A., Fearon E. Carrier detection of the X-linked primary immunodeficiency diseases using X-chromosome inactivation analysis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1990 Jun;85(6):1090–1097. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(90)90055-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]