Abstract
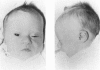
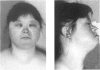
Three Down syndrome patients for whom karyotypic analysis showed a “mirror” (reverse tandem) duplication of chromosome 21 were studied by phenotypic, cytogenetic, and molecular methods. On high-resolution R-banding analysis performed in two cases, the size of the fusion 21q22.3 band was apparently less than twice the size of the normal 21q22.3, suggesting a partial deletion of distal 21q. The evaluation of eight chromosome 21 single-copy sequences of the 21q22 region–namely, SOD1, D21S15, D21S42, CRYA1, PFKL, CD18, COL6A1, and S100B–by a slot blot method showed in all three cases a partial deletion of 21q22.3 and partial monosomy. The translocation breakpoints were different in each patient, and in two cases the rearranged chromosome was found to be asymmetrical. The molecular definition of the monosomy 21 in each patient was, respectively, COL6A1–S100B, CD18–S100B, and PFKL–S100B. DNA polymorphism analysis indicated in all cases a homozygosity of the duplicated material. The duplicated region was maternal in two patients and paternal in one patient. These data suggest that the reverse tandem chromosomes did not result from a telomeric fusion between chromosomes 21 but from a translocation between sister chromatids. The phenotypes of these patients did not differ significantly from that of individuals with full trisomy 21, except in one case with large ears with an unfolded helix. The fact that monosomy of distal 21q22.3 in these patients resulted in a phenotype very similar to Down syndrome suggests that the duplication of the genes located in this part of chromosome 21 is not necessary for the pathogenesis of the Down syndrome features observed in these patients, including most of the facial and hand features, muscular hypotonia, cardiopathy of the Fallot tetralogy type, and part of the mental retardation.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allore R., O'Hanlon D., Price R., Neilson K., Willard H. F., Cox D. R., Marks A., Dunn R. J. Gene encoding the beta subunit of S100 protein is on chromosome 21: implications for Down syndrome. Science. 1988 Mar 11;239(4845):1311–1313. doi: 10.1126/science.2964086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartsch-Sandhoff M., Schade H. Zwei subterminale Heterochromatinregionen bei einer seltenen Form einer 21-21-Translokation. Humangenetik. 1973;18(4):329–336. doi: 10.1007/BF00291130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M., Gardner H. A., Gardner R. J., Goh E. G., Markovic V. D., Simpson N. E., Worton R. G. Dic(21;21) in a Down's syndrome child with an unusual chromosome 9 variant in the mother. J Med Genet. 1980 Apr;17(2):144–148. doi: 10.1136/jmg.17.2.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blouin J. L., Rahmani Z., Chettouh Z., Prieur M., Fermanian J., Poissonnier M., Leonard C., Nicole A., Mattei J. F., Sinet P. M. Slot blot method for the quantification of DNA sequences and mapping of chromosome rearrangements: application to chromosome 21. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Mar;46(3):518–526. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmeister M., Kim S., Price E. R., de Lange T., Tantravahi U., Myers R. M., Cox D. R. A map of the distal region of the long arm of human chromosome 21 constructed by radiation hybrid mapping and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Genomics. 1991 Jan;9(1):19–30. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90216-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantu J. M., Hernandez A., Plascencia L., Vaca G., Moller M., Rivera H. Partial trisomy and monosomy 21 in an infant with an unusual de novo 21/21 translocation. Ann Genet. 1980;23(3):183–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. M., Davidson R. G. Down's syndrome associated with a familial (21q-; 22q+) translocation. Cytogenetics. 1967;6(5):321–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. R., Shimizu N. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of chromosome 21. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1990;55(1-4):235–244. doi: 10.1159/000133017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallapiccola B., De Filippis V., Notarangelo A., Perla G., Zelante L. Ring chromosome 21 in healthy persons: different consequences in females and in males. Hum Genet. 1986 Jul;73(3):218–220. doi: 10.1007/BF00401230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delabar J. M., Chettouh Z., Rahmani Z., Theophile D., Blouin J. L., Bono R., Kraus J., Barton J., Patterson D., Sinet P. M. Gene-dosage mapping of 30 DNA markers on chromosome 21. Genomics. 1992 Jul;13(3):887–889. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90177-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein C. J. The consequences of chromosome imbalance. Am J Med Genet Suppl. 1990;7:31–37. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320370706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garson O. M., Baikie A. G., Pitt D. B., Newman N. M. Down's Syndrome with translocation-en-tandem: a report of two unrelated cases. Aust Paediatr J. 1970 Mar;6(1):53–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1754.1970.tb02860.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo Z., Sharma V., Patterson D., Litt M. TG repeat polymorphism at the D21S167 locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 25;18(16):4967–4967. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.16.4967-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagemeijer A., Smit E. M. Partial trisomy 21. Further evidence that trisomy of band 21q22 is essential for Down's phenotype. Hum Genet. 1977 Aug 31;38(1):15–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00295803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey J., Wiener S., Birner R. 'Mirror image' chromosome No. 21. J Med Genet. 1977 Apr;14(2):152–153. doi: 10.1136/jmg.14.2.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson J. F., North E. R., 3rd, Thomas J. G. Clinical diagnosis of Down's syndrome. Clin Genet. 1976 May;9(5):483–487. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1976.tb01601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. K., O'Connor K., Lee A., Roberts T. M., Springer T. A. Cloning of the beta subunit of the leukocyte adhesion proteins: homology to an extracellular matrix receptor defines a novel supergene family. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):681–690. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90246-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenberg J. R., Bradley C., Disteche C. M. Down syndrome: molecular mapping of the congenital heart disease and duodenal stenosis. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Feb;50(2):294–302. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenberg J. R., Croyle M. L., Cox D. R. Isolation and regional mapping of DNA sequences unique to human chromosome 21. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Dec;41(6):963–978. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenberg J. R., Kalousek D. K., Anneren G., Pulst S. M., Hall J. G., Epstein C. J., Cox D. R. Deletion of chromosome 21 and normal intelligence: molecular definition of the lesion. Hum Genet. 1991 Jun;87(2):112–118. doi: 10.1007/BF00204163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenberg J. R., Kawashima H., Pulst S. M., Ikeuchi T., Ogasawara N., Yamamoto K., Schonberg S. A., West R., Allen L., Magenis E. Molecular definition of a region of chromosome 21 that causes features of the Down syndrome phenotype. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Aug;47(2):236–246. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lejeune J., Berger R., Vidal O. R., Réthoré M. O. Un cas de translocation G G en tandem. Ann Genet. 1965;8(1):60–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levanon D., Danciger E., Dafni N., Groner Y. Construction of a cDNA clone containing the entire coding region of the human liver-type phosphofructokinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Sep 30;147(3):1182–1187. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80194-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieman-Hurwitz J., Dafni N., Lavie V., Groner Y. Human cytoplasmic superoxide dismutase cDNA clone: a probe for studying the molecular biology of Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2808–2811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick M. K., Schinzel A., Petersen M. B., Stetten G., Driscoll D. J., Cantu E. S., Tranebjaerg L., Mikkelsen M., Watkins P. C., Antonarakis S. E. Molecular genetic approach to the characterization of the "Down syndrome region" of chromosome 21. Genomics. 1989 Aug;5(2):325–331. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90065-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt D. S., Hawkins J. W., Jaworski C. J., Piatigorsky J. Isolation and partial characterization of the human alpha A-crystallin gene. Exp Eye Res. 1986 Aug;43(2):285–291. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(86)80098-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinniss M. J., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Stetten G., Petersen M. B., Boman H., Engel E., Greenberg F., Hertz J. M., Johnson A., Laca Z. Mechanisms of ring chromosome formation in 11 cases of human ring chromosome 21. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Jan;50(1):15–28. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McInnis M. G., Lutfalla G., Slaugenhaupt S., Petersen M. B., Uze G., Chakravarti A., Antonarakis S. E. Linkage mapping of highly informative DNA polymorphisms within the human interferon-alpha receptor gene on chromosome 21. Genomics. 1991 Nov;11(3):573–576. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90064-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niebuhr E. Down's syndrome. The possibility of a pathogenetic segment on chromosome no. 21. Humangenetik. 1974 Jan 22;21(1):99–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00278575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellissier M. C., Philip N., Voelckel-Baeteman M. A., Mattei M. G., Mattei J. F. Monosomy 21: a new case confirmed by in situ hybridization. Hum Genet. 1987 Jan;75(1):95–96. doi: 10.1007/BF00273852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen M. B., Slaugenhaupt S. A., Lewis J. G., Warren A. C., Chakravarti A., Antonarakis S. E. A genetic linkage map of 27 markers on human chromosome 21. Genomics. 1991 Mar;9(3):407–419. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90406-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
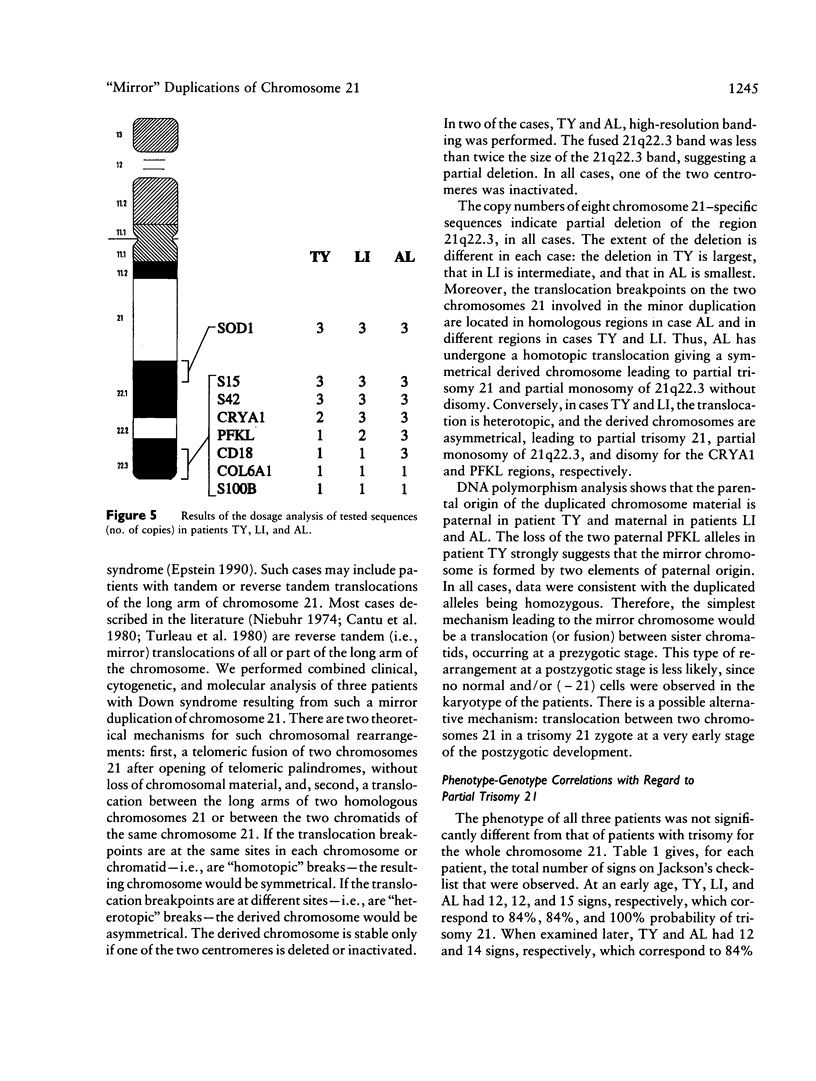
- Petersen M. B., Tranebjaerg L., McCormick M. K., Michelsen N., Mikkelsen M., Antonarakis S. E. Clinical, cytogenetic, and molecular genetic characterization of two unrelated patients with different duplications of 21q. Am J Med Genet Suppl. 1990;7:104–109. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320370721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelan M. C., Morton C. C., Stevenson R. E., Tanzi R. E., Stewart G. D., Watkins P. C., Gusella J. F., Amos J. A. Molecular and cytogenetic characterization of a de novo t(5p;21q) in a patient previously diagnosed as monosomy 21. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Oct;43(4):511–519. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polymeropoulos M. H., Rath D. S., Xiao H., Merril C. R. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the human liver-type 6-phosphofructokinase (PFKL) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2517–2517. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDS B. W., STEWART A., SYLVESTER P. E. RECIPROCAL TRANSLOCATION AND MOSAICISM IN A MONGOL. J Ment Defic Res. 1965 Jun;9:118–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.1965.tb00828.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmani Z., Blouin J. L., Creau-Goldberg N., Watkins P. C., Mattei J. F., Poissonnier M., Prieur M., Chettouh Z., Nicole A., Aurias A. Critical role of the D21S55 region on chromosome 21 in the pathogenesis of Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5958–5962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachdeva S., Wodnicki J., Smith G. F. Fluorescent chromosomes of a tandem translocation in a mongol patient. J Ment Defic Res. 1971 Sep;15(3):181–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.1971.tb01156.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuh B. E., Korf B. R., Salwen M. J. A 21-21 tandem translocation with satellites on both long and short arms. J Med Genet. 1974 Sep;11(3):297–299. doi: 10.1136/jmg.11.3.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. D., Harris P., Galt J., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Cloned DNA probes regionally mapped to human chromosome 21 and their use in determining the origin of nondisjunction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 11;13(11):4125–4132. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.11.4125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Watkins P. C., Stewart G. D., Wexler N. S., Gusella J. F., Haines J. L. A genetic linkage map of human chromosome 21: analysis of recombination as a function of sex and age. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Mar;50(3):551–558. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turleau C., Roubin M., Chavin-Colin F., de Grouchy J. Trisomie 21 par duplication en miroir 46,XX,psu dic(21)ter rea(21q21q). Ann Genet. 1980;23(3):187–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel W. Identification of G-group chromosomes involved in a G-G tandem-translocation by the giemsa-band technique. Humangenetik. 1972;14(3):255–256. doi: 10.1007/BF00278046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARKANY J., SOUKUP S. W. A chromosomal abnormality in a girl with some features of Down's syndrome (mongolism). J Pediatr. 1963 Jun;62:890–894. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(63)80103-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Fang H., Cantor C. R., Smith C. L. A contiguous Not I restriction map of band q22.3 of human chromosome 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3222–3226. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil D., Mattei M. G., Passage E., N'Guyen V. C., Pribula-Conway D., Mann K., Deutzmann R., Timpl R., Chu M. L. Cloning and chromosomal localization of human genes encoding the three chains of type VI collagen. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Mar;42(3):435–445. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZELLWEGER H., MIKAMO K., ABBO G. An unusual translocation in a case of Mongolism. J Pediatr. 1963 Feb;62:225–229. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(63)80396-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]