Abstract
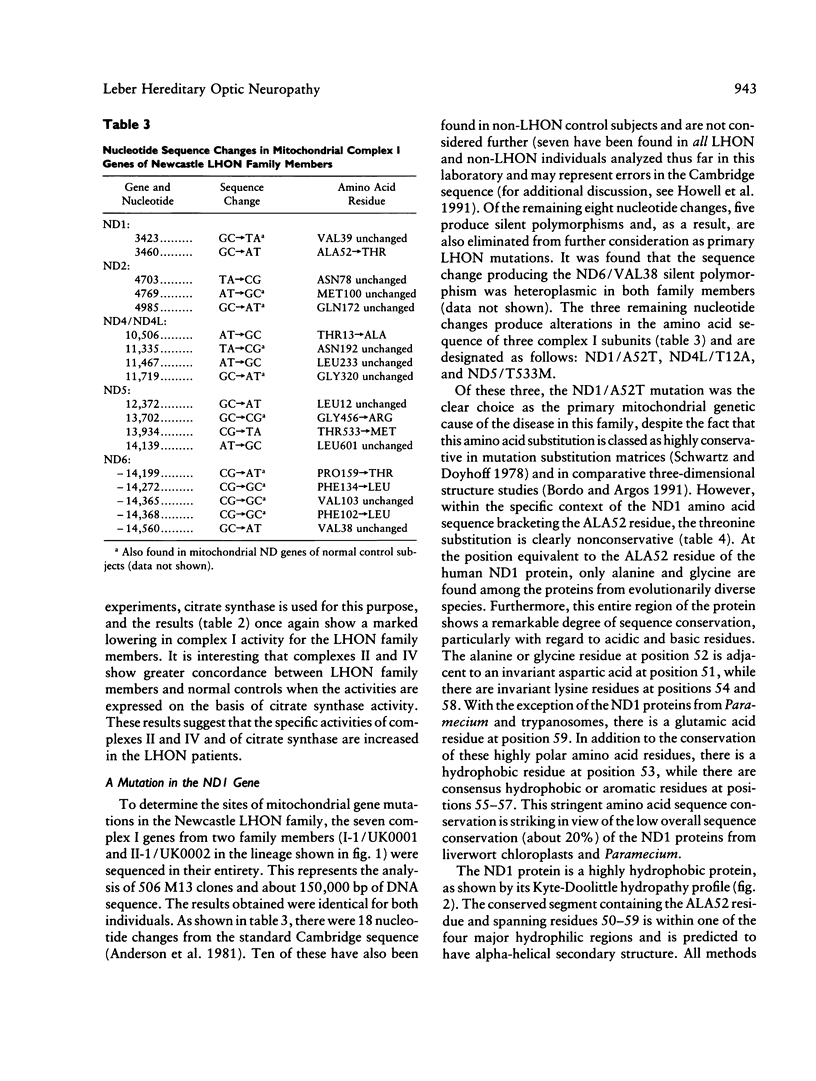
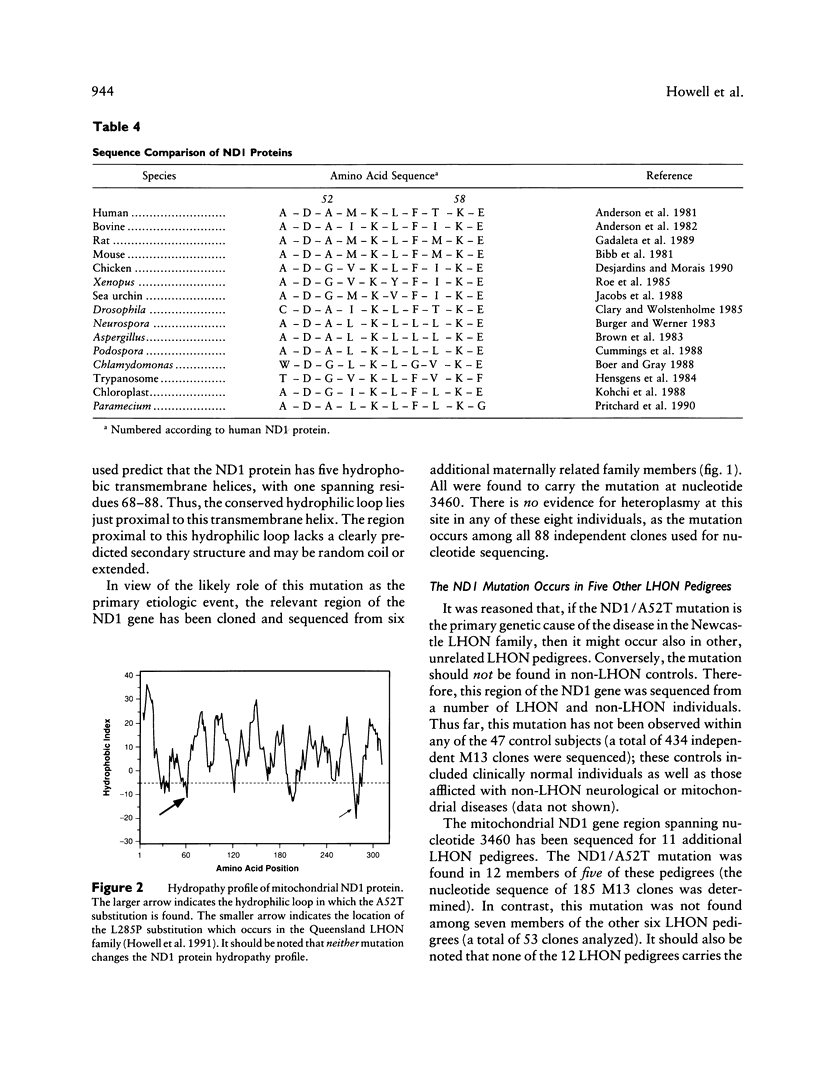
Biochemical and molecular genetic evidence is presented that in six independent pedigrees the development of Leber hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) is due to the same primary mutation in the mitochondrial ND1 gene. A LHON family from the Newcastle area of Great Britain was analyzed in depth to determine the mitochondrial genetic etiology of their disease. Biochemical assays of mitochondrial electron transport in organelles isolated from the platelet/white-blood-cell fraction have established that the members of this family have a substantial and specific lowering of flux through complex I (NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase). To determine the site of the primary mitochondrial gene mutation in this pedigree, all seven mitochondrial complex I genes were sequenced, in their entirety, from two family members. The primary mutation was identified as a homoplasmic transition at nucleotide 3460, which results in the substitution of threonine for alanine at position 52 of the ND1 protein. This residue occurs within a very highly conserved hydrophilic loop, is invariantly alanine or glycine in all ND1 proteins, and is adjacent to an invariant aspartic acid residue. This is only the second instance in which both a biochemical abnormality and a mitochondrial gene mutation have been identified in an LHON pedigree. The sequence analysis of the ND81 gene was extended to a further 11, unrelated LHON pedigrees that had been screened previously and found not to carry the mitochondrial ND4/R340H mutation. The ND1/A52T mutation at nucleotide 3460 was found in five of these 11 pedigrees. In contrast, this sequence change was not found in any of the 47 non-LHON controls. The possible role of secondary complex I mutations in the etiology of LHON is also addressed in these studies.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akke M., Forsén S. Protein stability and electrostatic interactions between solvent exposed charged side chains. Proteins. 1990;8(1):23–29. doi: 10.1002/prot.340080106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S., Bankier A. T., Barrell B. G., de Bruijn M. H., Coulson A. R., Drouin J., Eperon I. C., Nierlich D. P., Roe B. A., Sanger F. Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):457–465. doi: 10.1038/290457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S., de Bruijn M. H., Coulson A. R., Eperon I. C., Sanger F., Young I. G. Complete sequence of bovine mitochondrial DNA. Conserved features of the mammalian mitochondrial genome. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 25;156(4):683–717. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90137-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow D. J., Thornton J. M. Ion-pairs in proteins. J Mol Biol. 1983 Aug 25;168(4):867–885. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80079-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Van Etten R. A., Wright C. T., Walberg M. W., Clayton D. A. Sequence and gene organization of mouse mitochondrial DNA. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):167–180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birch-Machin M. A., Shepherd I. M., Watmough N. J., Sherratt H. S., Bartlett K., Darley-Usmar V. M., Milligan D. W., Welch R. J., Aynsley-Green A., Turnbull D. M. Fatal lactic acidosis in infancy with a defect of complex III of the respiratory chain. Pediatr Res. 1989 May;25(5):553–559. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198905000-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boer P. H., Gray M. W. Genes encoding a subunit of respiratory NADH dehydrogenase (ND1) and a reverse transcriptase-like protein (RTL) are linked to ribosomal RNA gene pieces in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii mitochondrial DNA. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3501–3508. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03226.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordo D., Argos P. Suggestions for "safe" residue substitutions in site-directed mutagenesis. J Mol Biol. 1991 Feb 20;217(4):721–729. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90528-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. A., Davies R. W., Ray J. A., Waring R. B., Scazzocchio C. The mitochondnal genome of Aspergillus nidulans contains reading frames homologous to the human URFs 1 and 4. EMBO J. 1983;2(3):427–435. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01440.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger G., Werner S. The mitochondrial URF1 gene in Neurospora crassa has an intron that contains a novel type of URF. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 20;186(2):231–242. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90100-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clary D. O., Wolstenholme D. R. The mitochondrial DNA molecular of Drosophila yakuba: nucleotide sequence, gene organization, and genetic code. J Mol Evol. 1985;22(3):252–271. doi: 10.1007/BF02099755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings D. J., Domenico J. M., Michel F. DNA sequence and organization of the mitochondrial ND1 gene from Podospora anserina: analysis of alternate splice sites. Curr Genet. 1988 Sep;14(3):253–264. doi: 10.1007/BF00376746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desjardins P., Morais R. Sequence and gene organization of the chicken mitochondrial genome. A novel gene order in higher vertebrates. J Mol Biol. 1990 Apr 20;212(4):599–634. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90225-B. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., Schwarz E., Komaromy M., Wall R. Analysis of membrane and surface protein sequences with the hydrophobic moment plot. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 15;179(1):125–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90309-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich T., Strohdeicher M., Hofhaus G., Preis D., Sahm H., Weiss H. The same domain motif for ubiquinone reduction in mitochondrial or chloroplast NADH dehydrogenase and bacterial glucose dehydrogenase. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jun 4;265(1-2):37–40. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80878-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadaleta G., Pepe G., De Candia G., Quagliariello C., Sbisà E., Saccone C. The complete nucleotide sequence of the Rattus norvegicus mitochondrial genome: cryptic signals revealed by comparative analysis between vertebrates. J Mol Evol. 1989 Jun;28(6):497–516. doi: 10.1007/BF02602930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gascuel O., Golmard J. L. A simple method for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins: implications and accuracy. Comput Appl Biosci. 1988 Aug;4(3):357–365. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/4.3.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensgens L. A., Brakenhoff J., De Vries B. F., Sloof P., Tromp M. C., Van Boom J. H., Benne R. The sequence of the gene for cytochrome c oxidase subunit I, a frameshift containing gene for cytochrome c oxidase subunit II and seven unassigned reading frames in Trypanosoma brucei mitochondrial maxi-circle DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 11;12(19):7327–7344. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.19.7327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt I. J., Miller D. H., Harding A. E. Genetic heterogeneity and mitochondrial DNA heteroplasmy in Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy. J Med Genet. 1989 Dec;26(12):739–743. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.12.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell N., Gilbert K. Mutational analysis of the mouse mitochondrial cytochrome b gene. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 5;203(3):607–618. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90195-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell N., Kubacka I., Xu M., McCullough D. A. Leber hereditary optic neuropathy: involvement of the mitochondrial ND1 gene and evidence for an intragenic suppressor mutation. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 May;48(5):935–942. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell N., McCullough D. An example of Leber hereditary optic neuropathy not involving a mutation in the mitochondrial ND4 gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Oct;47(4):629–634. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huoponen K., Vilkki J., Aula P., Nikoskelainen E. K., Savontaus M. L. A new mtDNA mutation associated with Leber hereditary optic neuroretinopathy. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jun;48(6):1147–1153. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs H. T., Elliott D. J., Math V. B., Farquharson A. Nucleotide sequence and gene organization of sea urchin mitochondrial DNA. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jul 20;202(2):185–217. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90452-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns D. R., Berman J. Alternative, simultaneous complex I mitochondrial DNA mutations in Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Feb 14;174(3):1324–1330. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91567-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein P., Kanehisa M., DeLisi C. The detection and classification of membrane-spanning proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 May 28;815(3):468–476. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90375-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohchi T., Shirai H., Fukuzawa H., Sano T., Komano T., Umesono K., Inokuchi H., Ozeki H., Ohyama K. Structure and organization of Marchantia polymorpha chloroplast genome. IV. Inverted repeat and small single copy regions. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 20;203(2):353–372. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loveland B., Wang C. R., Yonekawa H., Hermel E., Lindahl K. F. Maternally transmitted histocompatibility antigen of mice: a hydrophobic peptide of a mitochondrially encoded protein. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):971–980. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90345-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohana Rao J. K., Argos P. A conformational preference parameter to predict helices in integral membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jan 30;869(2):197–214. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(86)90295-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikoskelainen E. K., Savontaus M. L., Wanne O. P., Katila M. J., Nummelin K. U. Leber's hereditary optic neuroretinopathy, a maternally inherited disease. A genealogic study in four pedigrees. Arch Ophthalmol. 1987 May;105(5):665–671. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1987.01060050083043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker W. D., Jr, Oley C. A., Parks J. K. A defect in mitochondrial electron-transport activity (NADH-coenzyme Q oxidoreductase) in Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy. N Engl J Med. 1989 May 18;320(20):1331–1333. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198905183202007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard A. E., Sable C. L., Venuti S. E., Cummings D. J. Analysis of NADH dehydrogenase proteins, ATPase subunit 9, cytochrome b, and ribosomal protein L14 encoded in the mitochondrial DNA of Paramecium. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 11;18(1):163–171. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roe B. A., Ma D. P., Wilson R. K., Wong J. F. The complete nucleotide sequence of the Xenopus laevis mitochondrial genome. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9759–9774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saqi M. A., Goodfellow J. M. Free energy changes associated with amino acid substitution in proteins. Protein Eng. 1990 Apr;3(5):419–423. doi: 10.1093/protein/3.5.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira A. H., Cooper J. M., Manneschi L., Vital C., Morgan-Hughes J. A., Clark J. B. A mitochondrial encephalomyopathy with specific deficiencies of two respiratory chain polypeptides and a circulating autoantibody to a mitochondrial matrix protein. Brain. 1990 Apr;113(Pt 2):419–432. doi: 10.1093/brain/113.2.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano L., Horovitz A., Avron B., Bycroft M., Fersht A. R. Estimating the contribution of engineered surface electrostatic interactions to protein stability by using double-mutant cycles. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 9;29(40):9343–9352. doi: 10.1021/bi00492a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh G., Lott M. T., Wallace D. C. A mitochondrial DNA mutation as a cause of Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy. N Engl J Med. 1989 May 18;320(20):1300–1305. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198905183202002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANSENUS A. H. LEBER'S DISEASE IN THE NETHERLANDS. Doc Ophthalmol. 1963;17:1–162. doi: 10.1007/BF00573524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilkki J., Ott J., Savontaus M. L., Aula P., Nikoskelainen E. K. Optic atrophy in Leber hereditary optic neuroretinopathy is probably determined by an X-chromosomal gene closely linked to DXS7. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Mar;48(3):486–491. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilkki J., Savontaus M. L., Nikoskelainen E. K. Genetic heterogeneity in Leber hereditary optic neuroretinopathy revealed by mitochondrial DNA polymorphism. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Aug;45(2):206–211. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace D. C. A new manifestation of Leber's disease and a new explanation for the agency responsible for its unusual pattern of inheritance. Brain. 1970;93(1):121–132. doi: 10.1093/brain/93.1.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace D. C., Singh G., Lott M. T., Hodge J. A., Schurr T. G., Lezza A. M., Elsas L. J., 2nd, Nikoskelainen E. K. Mitochondrial DNA mutation associated with Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1427–1430. doi: 10.1126/science.3201231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


