Abstract
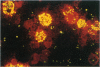
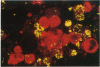
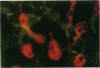
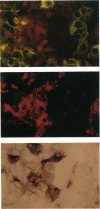
Culture of human amniotic-fluid cells from cases of fetal neural tube defects produces a population of rapidly adhering cells that were initially thought to be macrophages and later interpreted to be of neural origin. In this study double and triple labeling systems for the simultaneous detection of glial and macrophage differentiation marker antigens have been used to demonstrate that rapidly adhering cells cannot be considered a homogeneous population but instead represent two distinct cell types. One of these cell populations is of glial origin and shows specific staining for glial fibrillary acidic protein, while the other population is monocyte-derived macrophages which express marker antigens recognized by Leu M3, KiM7, and Dako antimacrophage monoclonal antibodies.
Full text
PDF

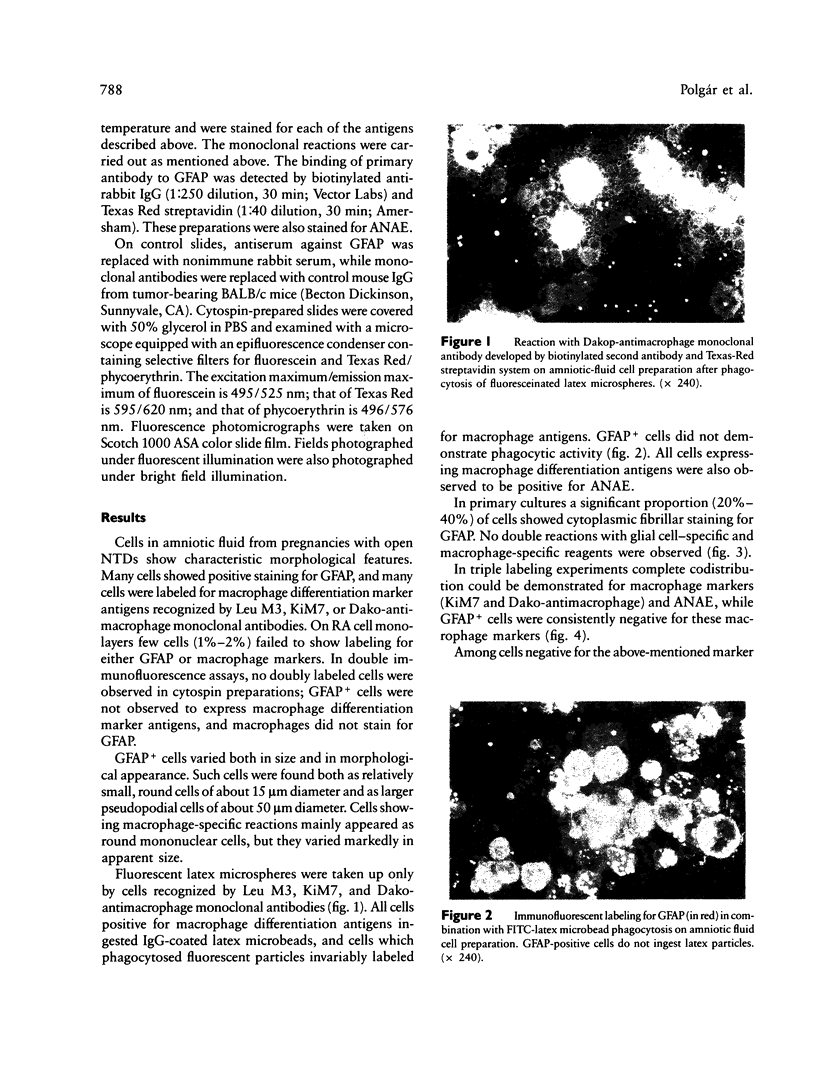
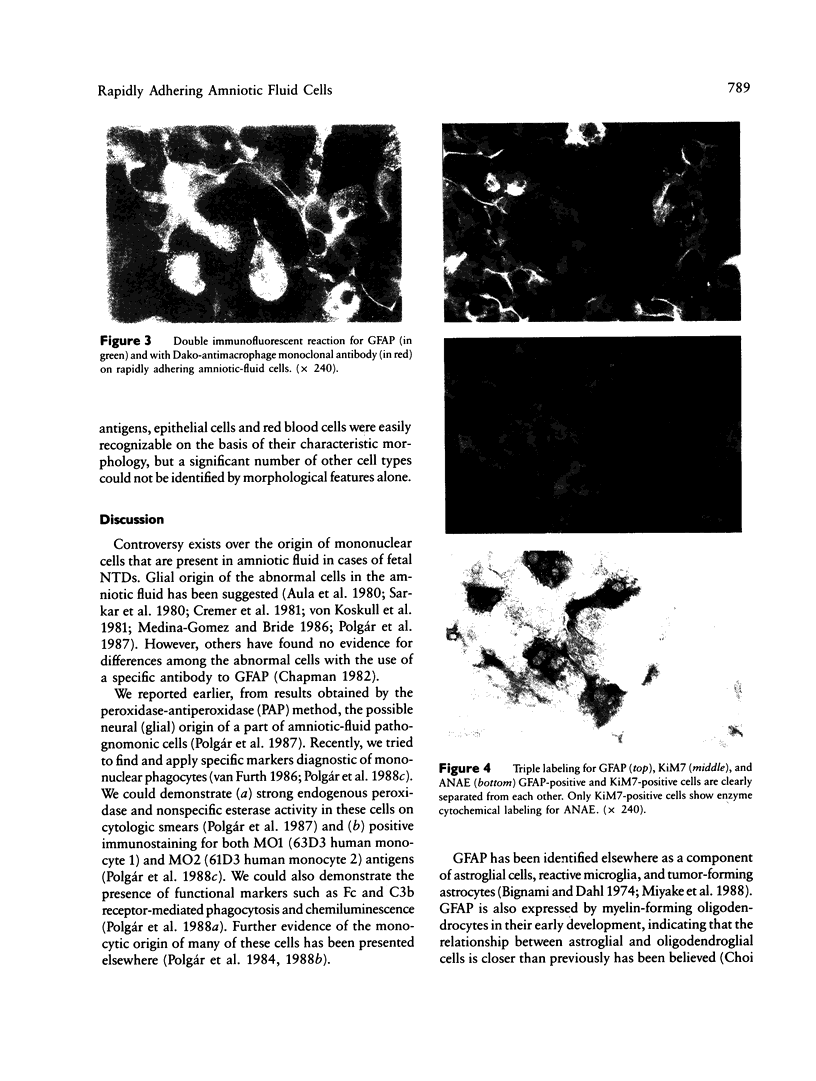



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Ali S. Y., Robinson N. Neuronal and oligodendrocytic response to cortical injury: ultrastructural and cytochemical changes. Histochem J. 1984 Feb;16(2):165–178. doi: 10.1007/BF01003547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aula P., von Koskull H., Teramo K., Karjalainen O., Virtanen I., Lehto V. P., Dahl D. Glial origin of rapidly adhering amniotic fluid cells. Br Med J. 1980 Nov 29;281(6253):1456–1457. doi: 10.1136/bmj.281.6253.1456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bignami A., Dahl D. Astrocyte-specific protein and neuroglial differentiation. An immunofluorescence study with antibodies to the glial fibrillary acidic protein. J Comp Neurol. 1974 Jan 1;153(1):27–38. doi: 10.1002/cne.901530104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brierley J. B., Brown A. W. The origin of lipid phagocytes in the central nervous system: I. The intrinsic microglia. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Nov 10;211(4):397–406. doi: 10.1002/cne.902110406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman P. A. Cytology as a means of detecting neural tube defects. Med Lab Sci. 1982 Jul;39(3):215–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi B. H., Kim R. C. Expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein in immature oligodendroglia. Science. 1984 Jan 27;223(4634):407–409. doi: 10.1126/science.6197755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer M., Schachner M., Cremer T., Schmidt W., Voigtländer T. Demonstration of astrocytes in cultured amniotic fluid cells of three cases with neural-tube defect. Hum Genet. 1981;56(3):365–370. doi: 10.1007/BF00274694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitriu-Bona A., Burmester G. R., Waters S. J., Winchester R. J. Human mononuclear phagocyte differentiation antigens. I. Patterns of antigenic expression on the surface of human monocytes and macrophages defined by monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):145–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esiri M. M., Booss J. Comparison of methods to identify microglial cells and macrophages in the human central nervous system. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Feb;37(2):150–156. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.2.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin W. A., Mason D. Y., Pulford K., Falini B., Bliss E., Gatter K. C., Stein H., Clarke L. C., McGee J. O. Immunohistological analysis of human mononuclear phagocytes and dendritic cells by using monoclonal antibodies. Lab Invest. 1986 Mar;54(3):322–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon S. Biology of the macrophage. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1986;4:267–286. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1986.supplement_4.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreipe H., Radzun H. J., Parwaresch M. R., Haislip A., Hansmann M. L. Ki-M7 monoclonal antibody specific for myelomonocytic cell lineage and macrophages in human. J Histochem Cytochem. 1987 Oct;35(10):1117–1126. doi: 10.1177/35.10.3476670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medina-Gomez P., McBride W. H. Amniotic fluid macrophages from normal and malformed fetuses. Prenat Diagn. 1986 May-Jun;6(3):195–205. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970060306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake T., Hattori T., Fukuda M., Kitamura T., Fujita S. Quantitative studies on proliferative changes of reactive astrocytes in mouse cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1988 Jun 7;451(1-2):133–138. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90757-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller J., Brun del Re G., Buerki H., Keller H. U., Hess M. W., Cottier H. Nonspecific acid esterase activity: a criterion for differentiation of T and B lymphocytes in mouse lymph nodes. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Apr;5(4):270–274. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murabe Y., Sano Y. Morphological studies on neuroglia. VII. Distribution of "brain macrophages" in brains of neonatal and adult rats, as determined by means of immunohistochemistry. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;229(1):85–95. doi: 10.1007/BF00217882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noske W., Lentzen H., Lange K., Keller K. Phagocytotic activity of glial cells in culture. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Dec;142(2):437–445. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90385-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogle J. D., Ogle C. K., Noel J. G., Hurtubise P., Alexander J. W. Studies on the binding of C3b-coated microspheres to human neutrophils. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Jan 21;76(1):47–62. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90480-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papp Z., Bell J. E. Uncultured cells in amniotic fluid from normal and abnormal foetuses. Clin Genet. 1979 Oct;16(4):282–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1979.tb01001.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polgar K., Abel G., Laczko J., Sipka S., Papp Z. Immunocytochemical characterization of amniotic fluid macrophages in cases of fetal neural tube defects. Am J Clin Pathol. 1987 Jan;87(1):37–42. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/87.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polgár K., Abel G., Sipka S., Csongor J., Fachet J., Papp Z. Immunobiological methods in the prenatal diagnosis and evaluation of foetal neural tube defects. Acta Physiol Hung. 1988;71(4):551–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polgár K., Abel G., Sipka S., Laczkó J., Papp Z. Amniotic fluid mononuclear phagocytes: phenotypes and functions. Acta Paediatr Hung. 1988;29(1-2):63–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polgár K., Sipka S., Abel G., Papp Z. Neutral-red uptake by amniotic-fluid macrophages in neural-tube defects: a rapid test. N Engl J Med. 1984 May 31;310(22):1463–1464. doi: 10.1056/nejm198405313102217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Fields K. L., Hakomori S. I., Mirsky R., Pruss R. M., Winter J. Cell-type-specific markers for distinguishing and studying neurons and the major classes of glial cells in culture. Brain Res. 1979 Oct 5;174(2):283–308. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90851-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar S., Chang H. C., Porreco R. P., Jones O. W. Neural origin of cells in amniotic fluid. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Jan 1;136(1):67–72. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(80)90566-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schelper R. L., Adrian E. K., Jr Monocytes become macrophages; they do not become microglia: a light and electron microscopic autoradiographic study using 125-iododeoxyuridine. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1986 Jan;45(1):1–19. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198601000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R., Brock D. J., Scrimgeour J. B. Letter: Amniotic-fluid macrophages and anencephaly. Lancet. 1973 Nov 10;2(7837):1098–1099. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92720-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood G. W., Gollahon K. A., Tilzer S. A., Vats T., Morantz R. A. The failure of microglia in normal brain to exhibit mononuclear phagocyte markers. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1979 Jul;38(4):369–376. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197907000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Koskull H., Virtanen I., Lehto V. P., Vartio T., Dahl D., Aula P. Glial and neuronal cells in amniotic fluid of anencephalic pregnancies. Prenat Diagn. 1981 Oct;1(4):259–267. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970010405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]