Abstract
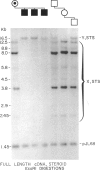
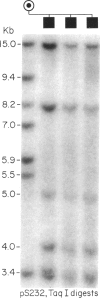
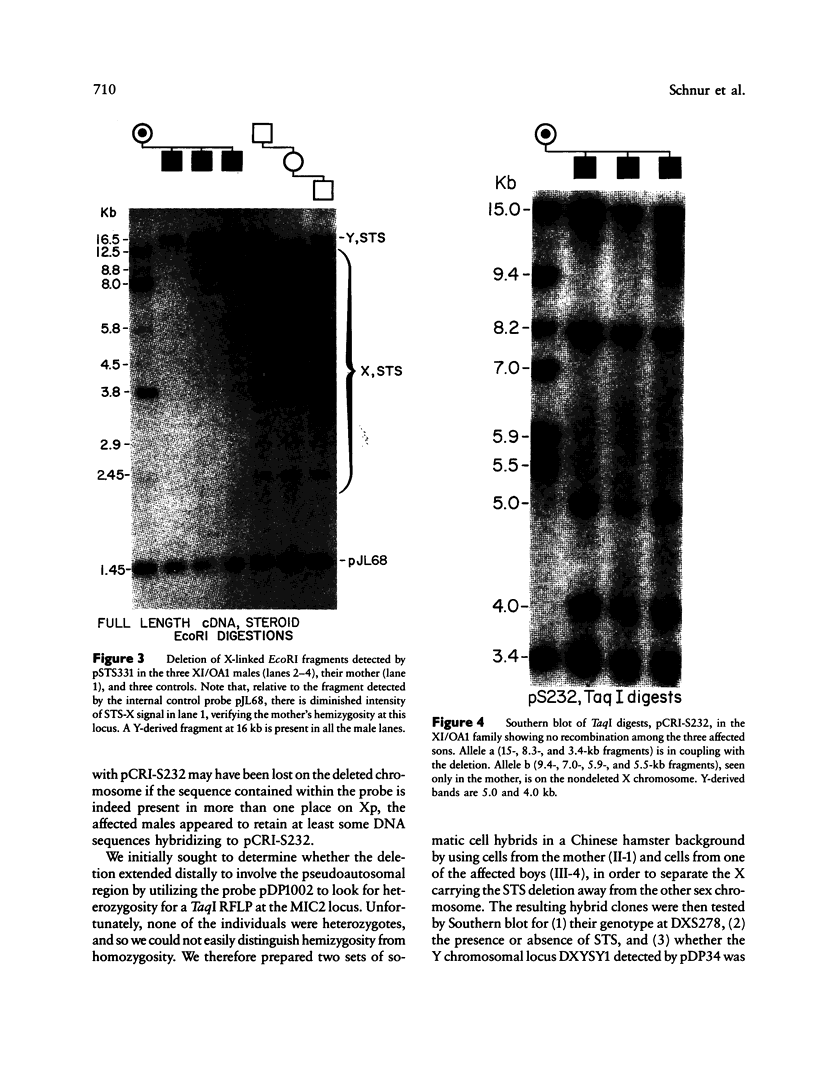
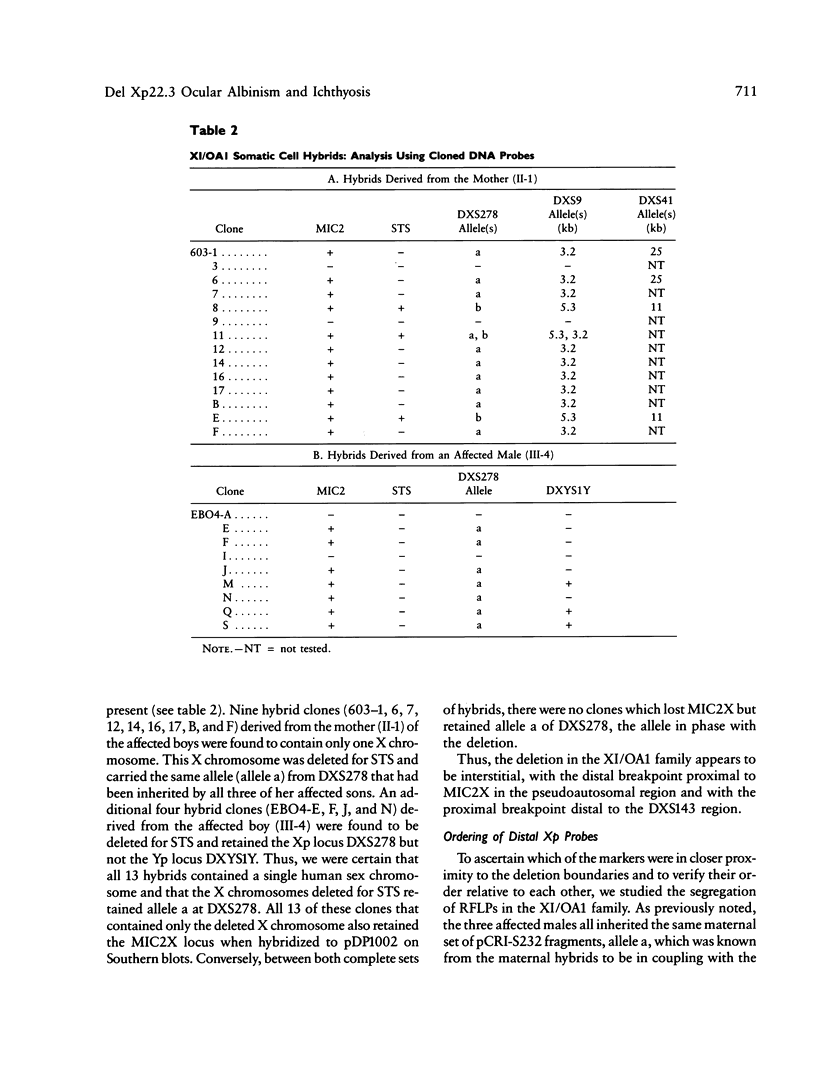
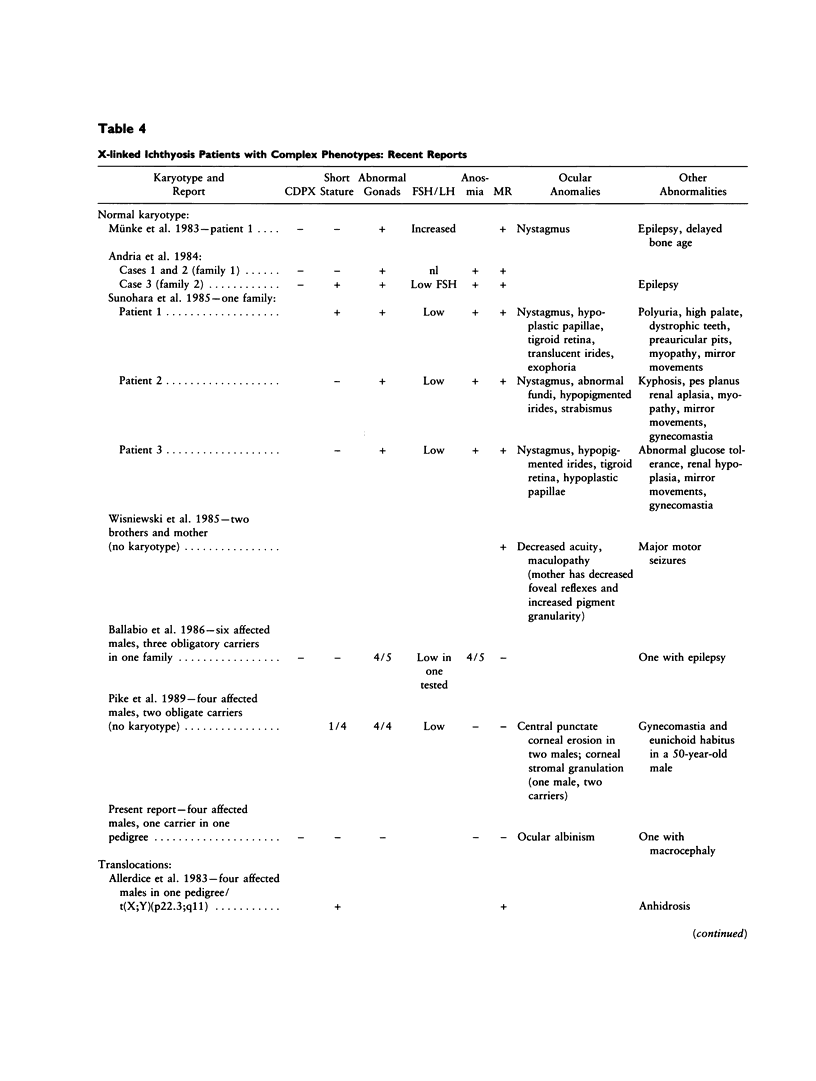
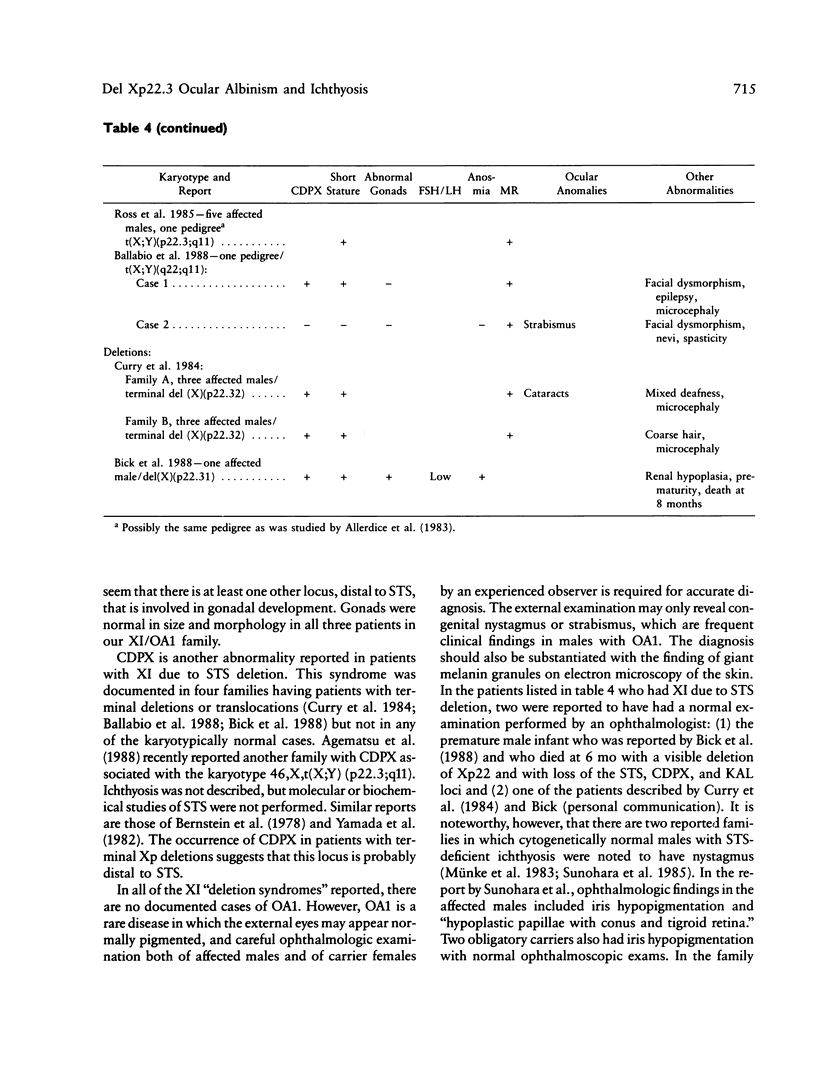
Ocular albinism of the Nettleship-Falls type (OA1) and X-linked ichthyosis (XI) due to steroid sulfatase (STS) deficiency are cosegregating in three cytogenetically normal half-brothers. The mother has patchy fundal hypopigmentation consistent with random X inactivation in an OA1 carrier. Additional phenotypic abnormalities that have been observed in other STS "deletion syndromes" are not present in this family. STS is entirely deleted on Southern blot in the affected males, but the loci MIC2X, DXS31, DXS143, DXS85, DXS43, DXS9, and DXS41 are not deleted. At least part of DXS278 is retained. Flow cytometric analysis of cultured lymphoblasts from one of the XI/OA1 males and his mother detected a deletion of about 3.5 million bp or about 2% of the X chromosome. Southern blot and RFLP analysis in the XI/OA1 family support the order tel-[STS-OA1-DXS278]-DXS9-DXS41-cen. An unrelated patient with the karyotype 46,X,t(X;Y) (p22;q11) retains the DXS143 locus on the derivative X chromosome but loses DXS278, suggesting that DXS278 is the more distal locus and is close to an XI/OA1 deletion boundary. If a contiguous gene deletion is responsible for the observed XI/OA1 phenotype, it localizes OA1 to the Xp22.3 region.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe K., Matsuda I., Matsuura N., Murayama T., Uzuki K., Okuno A. X-linked ichthyosis, bilateral cryptorchidism, hypogenitalism and mental retardation in two siblings. Clin Genet. 1976 Mar;9(3):341–345. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1976.tb01583.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agematsu K., Koike K., Morosawa H., Nakahori Y., Nakagome Y., Akabane T. Chondrodysplasia punctata with X;Y translocation. Hum Genet. 1988 Sep;80(1):105–107. doi: 10.1007/BF00451470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldridge J., Kunkel L., Bruns G., Tantravahi U., Lalande M., Brewster T., Moreau E., Wilson M., Bromley W., Roderick T. A strategy to reveal high-frequency RFLPs along the human X chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 May;36(3):546–564. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andria G., Ballabio A., Parenti G., Di Maio S., Piccirillo A. Steroid sulphatase deficiency is present in patients with the syndrome 'ichthyosis and male hypogonadism' and with 'Rud syndrome'. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1984;7 (Suppl 2):159–160. doi: 10.1007/978-94-009-5612-4_54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andria G., Ballabio A., Parenti G. X-linked ichthyosis due to steroid sulfatase deficiency associated with hypogonadism and anosmia. Ann Neurol. 1987 Jul;22(1):98–99. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballabio A., Carrozzo R., Parenti G., Gil A., Zollo M., Persico M. G., Gillard E., Affara N., Yates J., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Molecular heterogeneity of steroid sulfatase deficiency: a multicenter study on 57 unrelated patients, at DNA and protein levels. Genomics. 1989 Jan;4(1):36–40. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90311-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballabio A., Parenti G., Carrozzo R., Coppa G., Felici L., Migliori V., Silengo M., Franceschini P., Andria G. X/Y translocation in a family with X-linked ichthyosis, chondrodysplasia punctata, and mental retardation: DNA analysis reveals deletion of the steroid sulphatase gene and translocation of its Y pseudogene. Clin Genet. 1988 Jul;34(1):31–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1988.tb02612.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballabio A., Parenti G., Carrozzo R., Sebastio G., Andria G., Buckle V., Fraser N., Craig I., Rocchi M., Romeo G. Isolation and characterization of a steroid sulfatase cDNA clone: genomic deletions in patients with X-chromosome-linked ichthyosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4519–4523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballabio A., Parenti G., Tippett P., Mondello C., Di Maio S., Tenore A., Andria G. X-linked ichthyosis, due to steroid sulphatase deficiency, associated with Kallmann syndrome (hypogonadotropic hypogonadism and anosmia): linkage relationships with Xg and cloned DNA sequences from the distal short arm of the X chromosome. Hum Genet. 1986 Mar;72(3):237–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00291885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballabio A., Sebastio G., Carrozzo R., Parenti G., Piccirillo A., Persico M. G., Andria G. Deletions of the steroid sulphatase gene in "classical" X-linked ichthyosis and in X-linked ichthyosis associated with Kallmann syndrome. Hum Genet. 1987 Dec;77(4):338–341. doi: 10.1007/BF00291422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein R., Wagner J., Isdale J., Nurse G. T., Lane A. B., Jenkins T. X-Y translocation in a retarded phenotypic male. Clinical, cytogenetic, biochemical, and serogenetic studies. J Med Genet. 1978 Dec;15(6):466–474. doi: 10.1136/jmg.15.6.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggs B. A., Nussbaum R. L. Two anonymous X-specific human sequences detecting restriction fragment length polymorphisms in region Xq26----qter. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1984 Nov;10(6):607–613. doi: 10.1007/BF01535226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonifas J. M., Morley B. J., Oakey R. E., Kan Y. W., Epstein E. H., Jr Cloning of a cDNA for steroid sulfatase: frequent occurrence of gene deletions in patients with recessive X chromosome-linked ichthyosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9248–9251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. J., Mahtani M. M., Willard H. F. Genetic mapping of four DNA markers (DXS16, DXS43, DXS85, and DXS143) from the p22 region of the human X chromosome. Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;80(3):296–298. doi: 10.1007/BF01790101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conary J. T., Lorkowski G., Schmidt B., Pohlmann R., Nagel G., Meyer H. E., Krentler C., Cully J., Hasilik A., von Figura K. Genetic heterogeneity of steroid sulfatase deficiency revealed with cDNA for human steroid sulfatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 29;144(2):1010–1017. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80064-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke A., Gillard E. F., Yates J. R., Mitchell M. J., Aitken D. A., Weir D. M., Affara N. A., Ferguson-Smith M. A. X chromosome deletions detectable by flow cytometry in some patients with steroid sulphatase deficiency (X-linked ichthyosis). Hum Genet. 1988 May;79(1):49–52. doi: 10.1007/BF00291709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry C. J., Magenis R. E., Brown M., Lanman J. T., Jr, Tsai J., O'Lague P., Goodfellow P., Mohandas T., Bergner E. A., Shapiro L. J. Inherited chondrodysplasia punctata due to a deletion of the terminal short arm of an X chromosome. N Engl J Med. 1984 Oct 18;311(16):1010–1015. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198410183111603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. E., Mandel J. L., Weissenbach J., Fellous M. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of the X and Y chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1987;46(1-4):277–315. doi: 10.1159/000132481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel B. S. Molecular cytogenetics: toward dissection of the contiguous gene syndromes. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;43(5):575–578. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FALLS H. F. Sex-linked ocular albinism displaying typical fundus changes in the female heterozygote. Am J Ophthalmol. 1951 May;34(5 2):41–50. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(51)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fialkow P. J., Giblett E. R., Motulsky A. G. Measurable linkage between ocular albinism and Xg. Am J Hum Genet. 1967 Jan;19(1):63–69. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Ochs H. D., de Martinville B., Giacalone J., Lindgren V., Distèche C., Pagon R. A., Hofker M. H., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. Minor Xp21 chromosome deletion in a male associated with expression of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, chronic granulomatous disease, retinitis pigmentosa, and McLeod syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Mar;37(2):250–267. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner A., Jay B. S. Macromelanosomes in X-linked ocular albinism. Histopathology. 1980 May;4(3):243–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1980.tb02919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillard E. F., Affara N. A., Yates J. R., Goudie D. R., Lambert J., Aitken D. A., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Deletion of a DNA sequence in eight of nine families with X-linked ichthyosis (steroid sulphatase deficiency). Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):3977–3985. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.3977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoefnagel D., Allen F. H., Jr, Walker M. Ocular albinism and Xg. Lancet. 1969 Jun 28;1(7609):1314–1314. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)92247-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofker M. H., Wapenaar M. C., Goor N., Bakker E., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. Isolation of probes detecting restriction fragment length polymorphisms from X chromosome-specific libraries: potential use for diagnosis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Hum Genet. 1985;70(2):148–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00273073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger C., Jay B. X-linked ocular albinism: a family containing a manifesting heterozygote, and an affected male married to a female with autosomal recessive ocular albinism. Hum Genet. 1981;56(3):299–304. doi: 10.1007/BF00274683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowlton R. G., Nelson C. A., Brown V. A., Page D. C., Donis-Keller H. An extremely polymorphic locus on the short arm of the human X chromosome with homology to the long arm of the Y chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):423–437. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYON M. F. Sex chromatin and gene action in the mammalian X-chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1962 Jun;14:135–148. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewen R. M. Ocular albinism. Arch Ophthalmol. 1988 Jan;106(1):120–121. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1988.01060130126042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litt M., White R. L. A highly polymorphic locus in human DNA revealed by cosmid-derived probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6206–6210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lykkesfeldt G., Høyer H., Ibsen H. H., Brandrup F. Steroid sulphatase deficiency disease. Clin Genet. 1985 Sep;28(3):231–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1985.tb00391.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metaxotou C., Ikkos D., Panagiotopoulou P., Alevizaki M., Mavrou A., Tsenghi C., Matsaniotis N. A familial X/Y translocation in a boy with ichthyosis, hypogonadism and mental retardation. Clin Genet. 1983 Nov;24(5):380–383. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1983.tb00089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlesworth W., Bertelson C., Kunkel L. M. An RFLP detecting single copy X-chromosome fragment, dic56, from Xp22-Xpter [HGM8 assignment no. DXS 143]. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 12;13(15):5723–5723. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.15.5723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. M., Davies K. E., Harper P. S., Meredith L., Mueller C. R., Williamson R. Linkage relationship of a cloned DNA sequence on the short arm of the X chromosome to Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nature. 1982 Nov 4;300(5887):69–71. doi: 10.1038/300069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münke M., Kruse K., Goos M., Ropers H. H., Tolksdorf M. Genetic heterogeneity of the ichthyosis, hypogonadism, mental retardation, and epilepsy syndrome. Clinical and biochemical investigations on two patients with Rud syndrome and review of the literature. Eur J Pediatr. 1983 Oct;141(1):8–13. doi: 10.1007/BF00445661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissley P. S., Thomas G. H. The Rud syndrome: ichthyosis, hypogonadism, mental retardation. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1971 Jun;7(8):246–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum R. L., Lesko J. G., Lewis R. A., Ledbetter S. A., Ledbetter D. H. Isolation of anonymous DNA sequences from within a submicroscopic X chromosomal deletion in a patient with choroideremia, deafness, and mental retardation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6521–6525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell F. E., Green W. R., McKusick V. A., Forsius H., Eriksson A. W. Forsius-Eriksson syndrome: its relation to the Nettleship-Falls X-linked ocular albinism. Clin Genet. 1980 Jun;17(6):403–408. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1980.tb00170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell F. E., Jr, Green W. R., Fleischman J. A., Hambrick G. W. X-linked ocular albinism in Blacks. Ocular albinism cum pigmento. Arch Ophthalmol. 1978 Jul;96(7):1189–1192. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1978.03910060023005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell F. E., Jr, Hambrick G. W., Jr, Green W. R., Iliff W. J., Stone D. L. X-linked ocular albinism. An oculocutaneous macromelanosomal disorder. Arch Ophthalmol. 1976 Nov;94(11):1883–1892. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1976.03910040593001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell F. E., Jr, King R. A., Green W. R., Witkop C. J., Jr Autosomal recessively inherited ocular albinism. A new form of ocular albinism affecting females as severely as males. Arch Ophthalmol. 1978 Sep;96(9):1621–1625. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1978.03910060255013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page D. C., Brown L. G., de la Chapelle A. Exchange of terminal portions of X- and Y-chromosomal short arms in human XX males. 1987 Jul 30-Aug 5Nature. 328(6129):437–440. doi: 10.1038/328437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page D., de Martinville B., Barker D., Wyman A., White R., Francke U., Botstein D. Single-copy sequence hybridizes to polymorphic and homologous loci on human X and Y chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5352–5356. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce W. G., Johnson G. J., Sanger R. Ocular albinism and Xg. Lancet. 1971 May 22;1(7708):1072–1072. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91636-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce W. G., Sanger R., Race R. R. Ocular albinism and Xg. Lancet. 1968 Jun 15;1(7555):1282–1283. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92295-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike M. G., Hammerton M., Edge J., Atherton D. J., Grant D. B. A family with X-linked ichthyosis and hypogonadism. Eur J Pediatr. 1989 Feb;148(5):442–444. doi: 10.1007/BF00595908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puck J. M., Nussbaum R. L., Smead D. L., Conley M. E. X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency: localization within the region Xq13.1-q21.1 by linkage and deletion analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 May;44(5):724–730. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J. B., Allderdice P. W., Shapiro L. J., Aveling J., Eales B. A., Simms D., Jr Familial X-linked ichthyosis, steroid sulfatase deficiency, mental retardation, and nullisomy for Xp223-pter. Arch Dermatol. 1985 Dec;121(12):1524–1528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmickel R. D. Contiguous gene syndromes: a component of recognizable syndromes. J Pediatr. 1986 Aug;109(2):231–241. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80377-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro L. J. Steroid sulfatase deficiency and the genetics of the short arm of the human X chromosome. Adv Hum Genet. 1985;14:331-81, 388-9. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9400-0_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunohara N., Sakuragawa N., Satoyoshi E., Tanae A., Shapiro L. J. A new syndrome of anosmia, ichthyosis, hypogonadism, and various neurological manifestations with deficiency of steroid sulfatase and arylsulfatase C. Ann Neurol. 1986 Feb;19(2):174–181. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szymanski K. A., Boughman J. A., Nance W. E., Olansky D. C., Weinberg R. S. Genetic studies of ocular albinism in a large Virginia kindred. Ann Ophthalmol. 1984 Feb;16(2):183-5, 188-91, 194-6 passim. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiepolo L., Zuffardi O., Fraccaro M., di Natale D., Gargantini L., Müller C. R., Ropers H. H. Assignment by deletion mapping of the steroid sulfatase X-linked ichthyosis locus to Xp223. Hum Genet. 1980;54(2):205–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00278973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traupe H., Müller-Migl C. R., Kolde G., Happle R., Kövary P. M., Hameister H., Ropers H. H. Ichthyosis vulgaris with hypogenitalism and hypogonadism: evidence for different genotypes by lipoprotein electrophoresis and steroid sulfatase testing. Clin Genet. 1984 Jan;25(1):42–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1984.tb00461.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieacker P., Davies K. E., Mevorah B., Ropers H. H. Linkage studies in a family with X-linked recessive ichthyosis employing a cloned DNA sequence from the distal short arm of the X chromosome. Hum Genet. 1983;63(2):113–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00291528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winship I., Gericke G., Beighton P. X-linked inheritance of ocular albinism with late-onset sensorineural deafness. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Dec;19(4):797–803. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320190421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth B., Herrmann F. H., Neugebauer M., Gillard E. F., Wulff K., Stein C., von Figura K., Ferguson-Smith M. A., Gal A. Linkage analysis in X-linked ichthyosis (steroid sulfatase deficiency). Hum Genet. 1988 Oct;80(2):191–192. doi: 10.1007/BF00702868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrogemann K., Koenig M., Alembik Y., Mandel J. L. An XmnI RFLP at the subtelomeric Xp locus DXS31 [HGM7, LA, 1985]. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 27;14(10):4377–4377. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.10.4377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K., Nanko S., Hattori S., Isurugi K. Cytogenetic studies in a Y-to-X translocation observed in three members of one family, with evidence of infertility in male carriers. Hum Genet. 1982;60(1):85–90. doi: 10.1007/BF00281273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. R., Goudie D. R., Gillard E. F., Aitken D. A., Affara N. A., Clayton J. F., Tippett P. A., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Multipoint linkage analysis of steroid sulfatase (X-linked ichthyosis) and distal Xp markers. Genomics. 1987 Sep;1(1):52–59. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90104-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen P. H., Allen E., Marsh B., Mohandas T., Wang N., Taggart R. T., Shapiro L. J. Cloning and expression of steroid sulfatase cDNA and the frequent occurrence of deletions in STS deficiency: implications for X-Y interchange. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):443–454. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90447-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshiike T., Manabe M., Hayakawa M., Ogawa H. Macromelanosomes in X-linked ocular albinism (XLOA). Acta Derm Venereol. 1985;65(1):66–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dorp D. B. Albinism, or the NOACH syndrome (the book of Enoch c.v. 1-20). Clin Genet. 1987 Apr;31(4):228–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1987.tb02801.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Engh G. J., Trask B. J., Gray J. W., Langlois R. G., Yu L. C. Preparation and bivariate analysis of suspensions of human chromosomes. Cytometry. 1985 Mar;6(2):92–100. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990060203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Engh G., Trask B., Lansdorp P., Gray J. Improved resolution of flow cytometric measurements of Hoechst- and chromomycin-A3-stained human chromosomes after addition of citrate and sulfite. Cytometry. 1988 May;9(3):266–270. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990090313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]