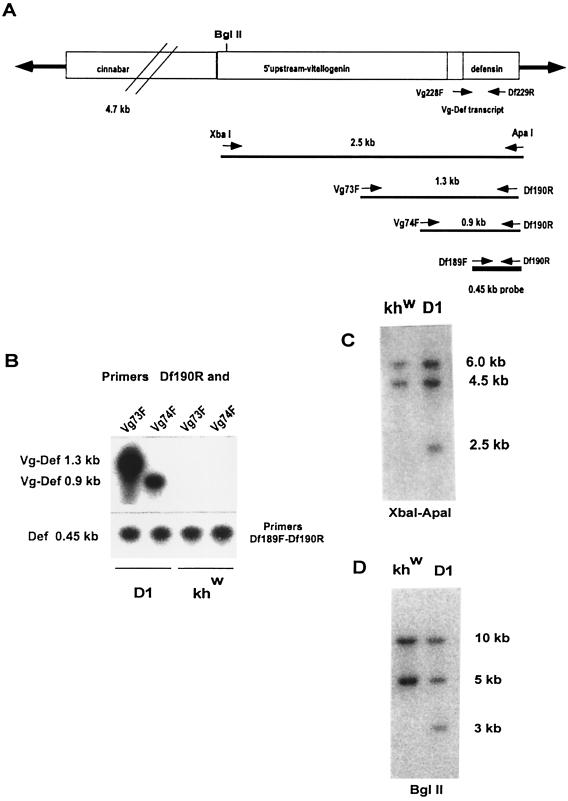
Figure 1.
Stable integration of the Vg-Defensin transgene into the Aedes aegypti genome. (A) Schematic diagram of the transformation vector construct, pH[cn][Vg-DefA], used in this study to transform mosquitoes. The Hermes inverted terminal repeats are represented as solid arrows flanking the 4.7-kb genomic DNA fragment of the D. melanogaster cn+ marker gene and the 2.5-kb Vg-DefA fusion gene as the promoter–reporter part of the construct. The arrows and numbers below the diagram show the relative extents and the expected sizes of the fragments generated by XbaI–ApaI restriction digest and by gene amplification using different pairs of primers specific to the Vg-DefA fusion sequence. The 0.45-kb DefA DNA sequence used as a probe in these experiments is shown as a black box below the map. (B) Gene amplification analysis of genomic DNA isolated from G4 mosquito progeny of the D1 transgenic line and the control khw strain. To confirm the specificity of amplification for the Vg-DefA transgene, the gene amplification products were analyzed by Southern blot hybridization using the DefA DNA as a probe. By using the Vg-DefA primer combinations, Vg73F-Df190R and Vg74F-Df190R, the transgenic mosquito DNA showed specific amplification of fragments of the expected sizes, 1.3-kb and 0.9-kb, respectively. No amplification was observed in the genomic DNA from the control strain (Upper). As a positive control for loading and for the integrity of isolated genomic DNA, DefA-specific primer pairs, Df189F-Df190R, were used, and these produced a band of the expected size, 0.45-kb, in all samples (Lower). (C) Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA prepared from G4 progeny of transformed mosquitoes of the D1 line and the host strain (khw), digested with XbaI–ApaI and hybridized with the DefA DNA probe. A diagnostic hybridization signal of the expected size, 2.5 kb, is associated with the insertion of the Vg-DefA transgene into the mosquito genome and is evident in DNA isolated from transformed mosquitoes, but not in the host strain. The two higher molecular weight signals of 6 kb and 4.5 kb, seen in DNA digests of both the transgenic and the host strains, represented two copies of endogenous DefA genes. (D) Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA isolated from G9 progeny of the D1 transgenic line and the host khw strain, digested with BglII and hybridized with DefA DNA probe. The unique hybridization signal of 3.0-kb associated with Vg-DefA insertion is seen only in the D1 transgenic line.