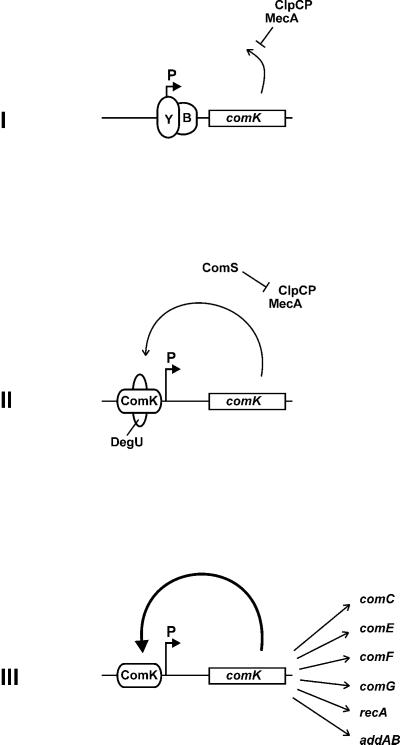
Figure 6.
Schematic representation of the transcriptional and posttranscriptional control of comK in competence development. (I) During logarithmic growth, transcription of comK (open box) is repressed by the transcriptional repressors AbrB (B) and CodY (Y). Residual ComK is degraded by the action of MecA and ClpCP. (II) At the beginning of the stationary growth phase, AbrB and CodY repression is raised, and the MecA/ClpCP complex is destabilized by the cell density-induced synthesis of ComS. DegU stimulates binding of ComK, initiating the autostimulatory expression of comK. (III) When ComK concentrations are sufficiently high (bold arrow), ComK activates the expression of genes constituting the DNA-uptake system (comC, -E, -G, -F), of the DNA-integration system (recA, addAB), and of comK itself, independent of DegU. Binding of AbrB, CodY, DegU, and ComK to the comK promoter (P) is indicated with ellipses.