Abstract
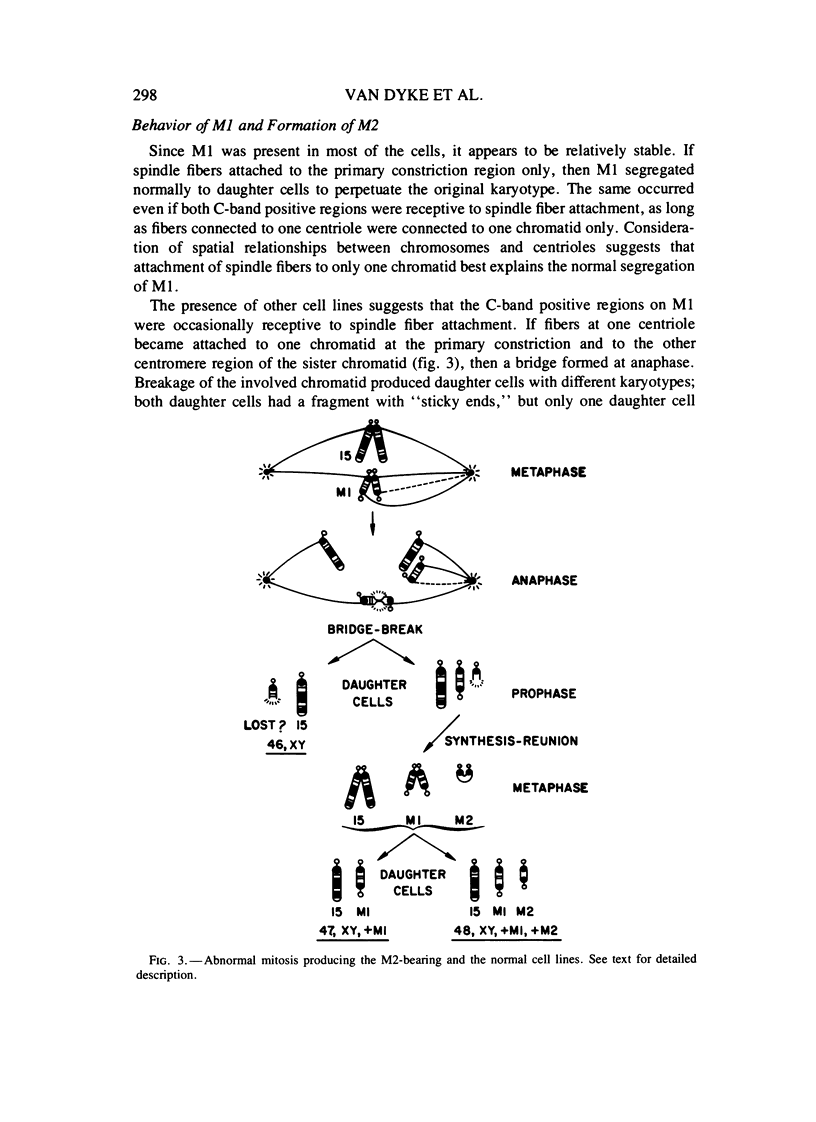
Karyotyping revealed three cell lines in a boy with mental retardation and few other abnormalities. Thirty cells exhibited a normal karyotype, and 54 had an extra acrocentric chromosome of E group size with satellites on the long and short arms. The remaining 20 cells each had, in addition to the first marker (M1), a second tiny bisatellited chromosome (M2). C-banding demonstrated that both markers were dicentric. G-, C-, and Q-banding and satellite association data were consistent with the markers having originated from chromosome 15 material. We propose that M1 was formed from a meiotic breakage and a chromatid fusion in the proximal long arms of an acrocentric pair. This would have produced a symmetrical isodicentric chromosomes, plus one or two acentric fragments. M2 then could have resulted from a dicentric bridge-break-synthesis-reunion phenomenon. This model of abnormal meiotic exchange can be generalized to encompass the formation of other dicentric isochromosome cases of isochromosome X.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baĺicek P., Zizka J., Lichý J. An isochromosome of the short arms of the no. 18 chromosome in a mentally retarded girl. Clin Genet. 1976 Feb;9(2):192–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1976.tb01567.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centerwall W. R., Morris J. P. Partial D 15 trisomy. A case and general review. Hum Hered. 1975;25(6):442–452. doi: 10.1159/000152759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crandall B. F., Muller H. M., Bass H. N. Partial trisomy of chromosome number 15 identified by trypsin-Giemsa banding. Am J Ment Defic. 1973 Mar;77(5):571–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De la Chapelle A., Stenstrand K. Dicentric human X chromosomes. Hereditas. 1974;76(2):259–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1974.tb01344.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distèche C., Hagemeijer A., Frederic J., Progneaux D. An abnormal large human chromosome identified as an end-to-end fusion of two X's by combined results of the new banding techniques and microdensitometry. Clin Genet. 1972;3(5):388–395. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1972.tb01472.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich U., Nielsen J. Bisatellited extra small metacentric chromosome in newborns. Clin Genet. 1974;6(1):23–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1974.tb00626.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez A. C., Salamanca F., Lisker R., Segovia A. Supernumerary bisatellited chromosome in a family ascertained through a patient with Sturge-Weber syndrome. Ann Genet. 1975 Mar;18(1):45–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakati S., Sinha A. K. Induction of distinctive chromosomal bands in selected human subjects with D, G, and Y chromosome anomalies. Hum Hered. 1973 Apr;23(4):313–330. doi: 10.1159/000152592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewandowski R. C., Jr, Yunis J. J. New chromosomal syndromes. Am J Dis Child. 1975 Apr;129(4):515–529. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1975.02120410075021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubs H. A., McKenzie W. H., Patil S. R., Merrick S. New staining methods for chromosomes. Methods Cell Biol. 1973;6:345–380. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magenis R. E., Overton K. M., Reiss J. A., Macfarlane J. P., Hecht F. Partial trisomy 15. Lancet. 1972 Dec 23;2(7791):1365–1366. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92806-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J., Hreidarsson A. B., Berggreen S., Ried E., Tsuboi T., Saldaña-Garcia P. A mentally retarded male with karyotype 47,XY, plus mar equal ?i (18p). Ann Genet. 1974 Jun;17(2):129–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J., Hreidarsson A. B. Father and daughter with presumptive isochromosome satellites-short arms D or G. Humangenetik. 1973 Sep 20;19(3):271–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00278401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENROSE L. S., ELLIS J. R., DELHANTY J. D. Chromosomal translocations in mongolism and in normal relatives. Lancet. 1960 Aug 20;2(7147):409–410. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(60)92846-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer C. G., Conneally P. M., Christian J. C. Translocations of D chromosomes in two families: t(13q14q) and t(13q14q)+(13p14p). J Med Genet. 1969 Jun;6(2):166–173. doi: 10.1136/jmg.6.2.166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. E., Alfi O. S. Partial trisomy of chromosome 15. Lancet. 1972 May 13;1(7759):1073–1073. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91259-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priest J. H., Blackston R. D., Au K. S., Ray S. L. Differences in human X isochromosomes. J Med Genet. 1975 Dec;12(4):378–389. doi: 10.1136/jmg.12.4.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohde R. A. A masculinizing syndrome associated with a doubly-satellited extra chromosome. J Med Genet. 1965 Dec;2(4):243–245. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2.4.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. D., Steinberger E., Steinberger S., Perloff W. H. A familial centric chromosome fragment. Cytogenetics. 1965;4(4):219–226. doi: 10.1159/000129858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soudek D., McCreary B. D., Laraya P., Dill F. J. Two kinships with accessory bisatellited chromosomes. Ann Genet. 1973 Jun;16(2):101–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tangheroni W., Cao A., Furbetta M. Multiple anomalies associated with an extra small metacentric chromosome: modified Giemsa stain results. Humangenetik. 1973;18(4):291–295. doi: 10.1007/BF00291125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K. M., Wolfinger H. L., Brown M. G., Chadwick D. L. Origin of a small metacentric chromosome: familial and cytogenic evidence. Clin Genet. 1975 Nov;8(5):364–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1975.tb01515.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Therman E., Sarto G. E., Patau K. Apparently isodicentric but functionally monocentric X chromosome in man. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Jan;26(1):83–92. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson E. J., Gordon R. R. A case of partial trisomy 15. J Med Genet. 1974 Dec;11(4):400–402. doi: 10.1136/jmg.11.4.400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb G. C., Garson M., Robson M. K., Pitt D. B. A partial D-trisomy-normal mosaic female. J Med Genet. 1971 Dec;8(4):522–527. doi: 10.1136/jmg.8.4.522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa S., Yokoyama H. Symptoms of Turner's syndrome and interstitial heterochromatin in i(Xq). Clin Genet. 1975 Apr;7(4):299–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1975.tb00332.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



