Abstract
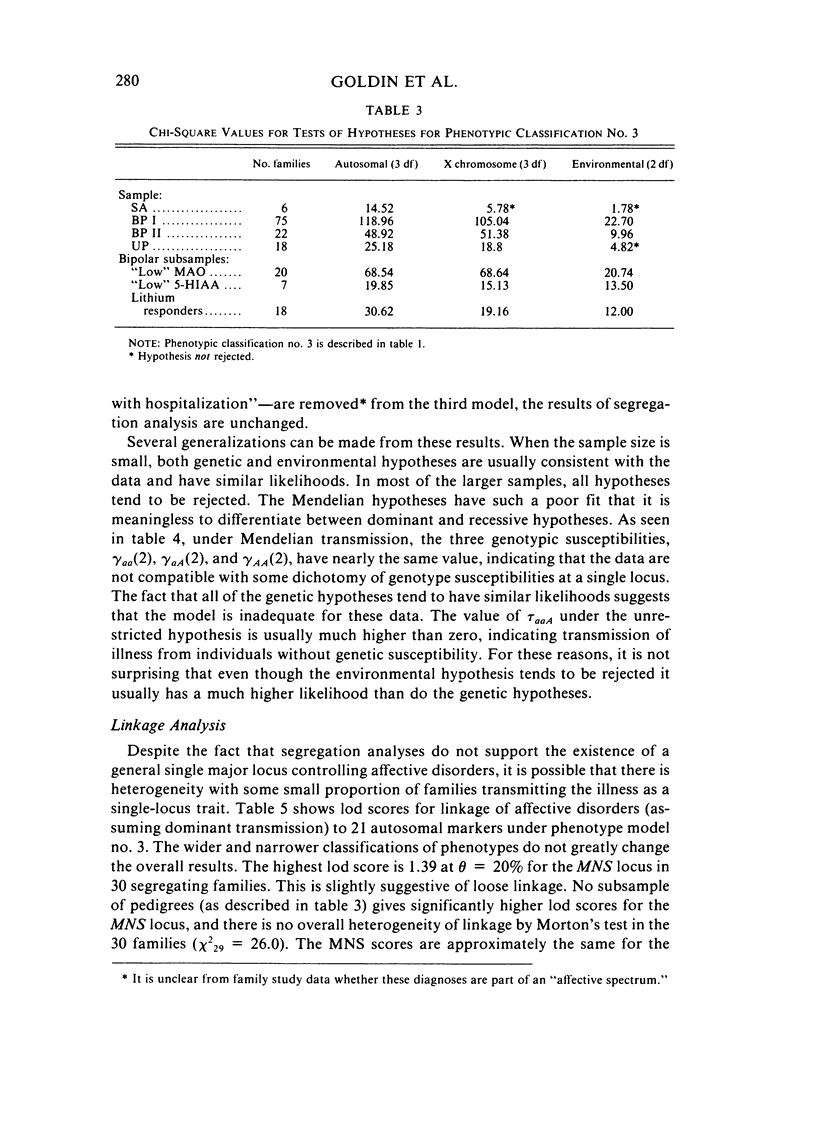
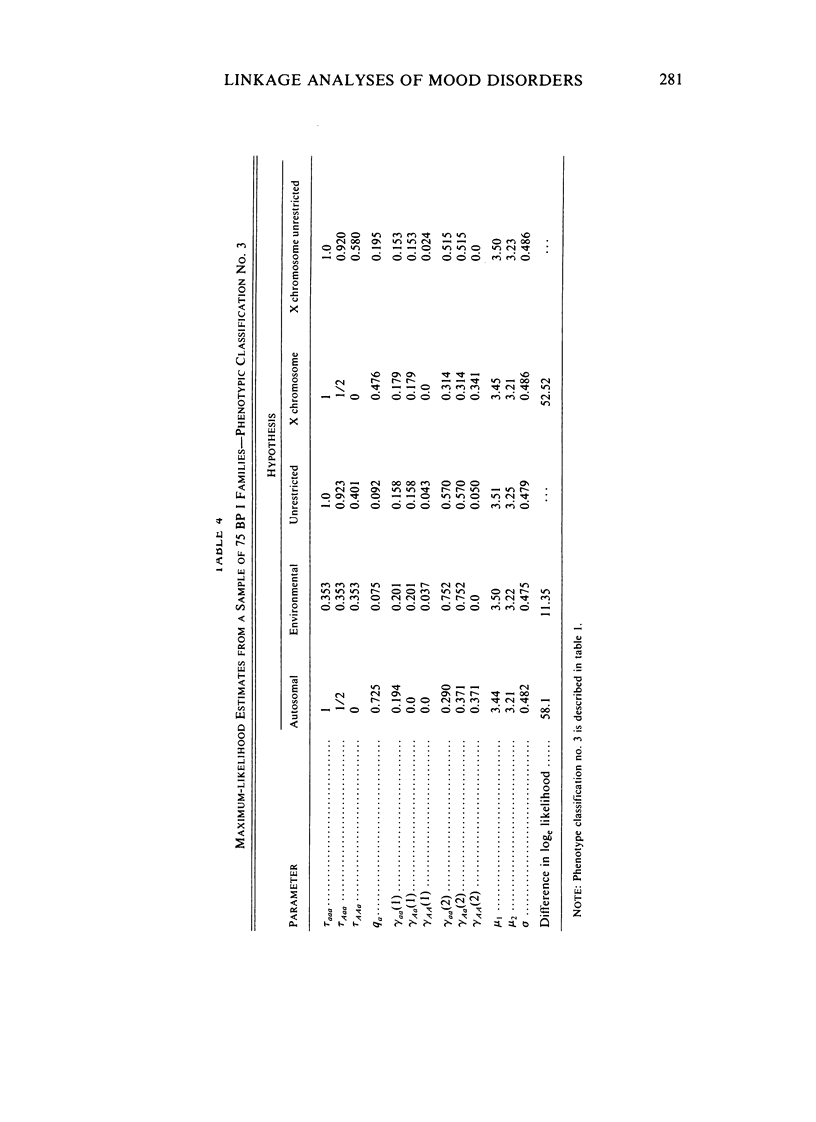
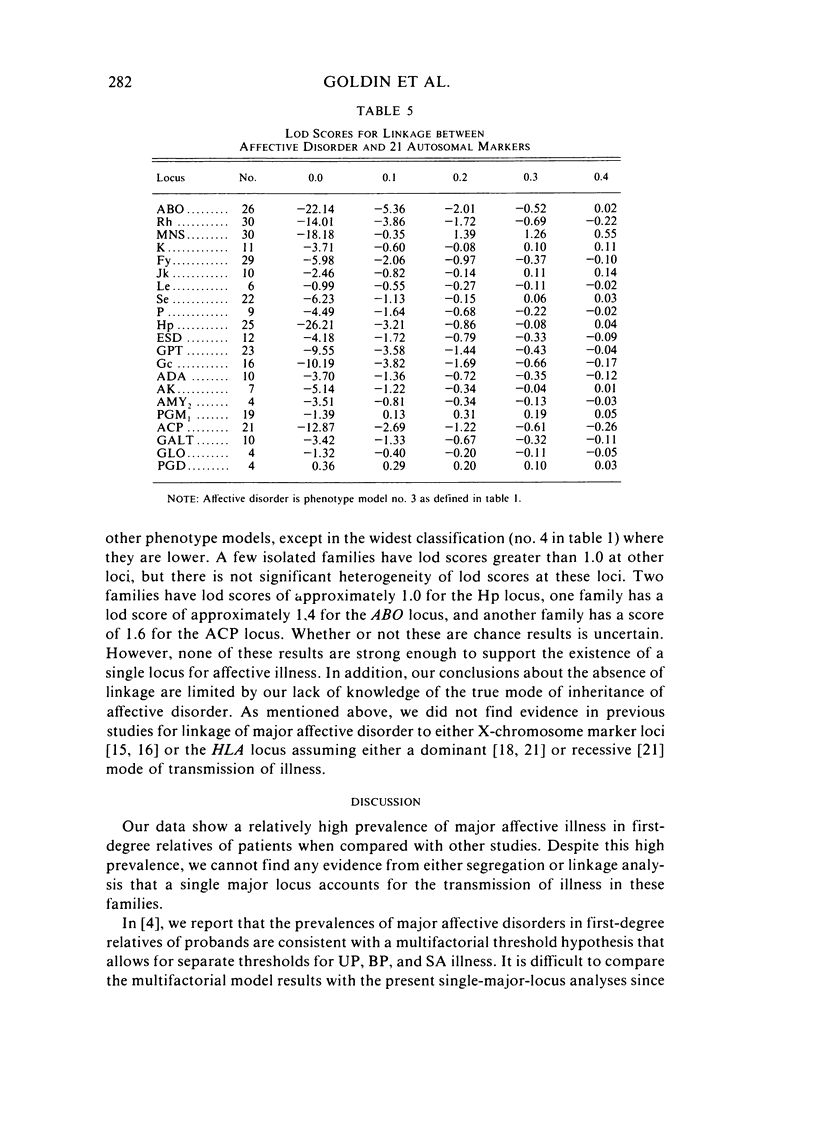
Hypotheses of single major locus transmission (autosomal and X chromosome) of major affective disorder (i.e., bipolar, unipolar, and schizoaffective) are tested using the Elston-Stewart likelihood method of pedigree segregation analysis. The sample consists of families of varying size ascertained through patients treated at the National Institute of Mental Health in Bethesda, Maryland. We test hypotheses on subsamples of families according to: (1) diagnosis of proband (75 bipolar I, 22 bipolar II, 18 unipolar, and six schizoaffective); (2) extreme value of a biological trait in the proband ("low" monoamine oxidase, "low" cerebrospinal fluid serotonin metabolite 5-HIAA); and (3) positive response to lithium in the proband. We cannot find evidence for single major locus transmission of major affective disorder from segregation analysis in any subsample of family even when the diagnostic classification of ill phenotypes is widened to include possible affective "spectrum" diagnoses. In addition, linkage studies of 21 autosomal markers do not provide evidence for single major locus transmission of illness. The maximum lod score, found for 30 families at the MNS locus, was 1.39 at 20% recombination.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiskal H. S., Djenderedjian A. M., Rosenthal R. H., Khani M. K. Cyclothymic disorder: validating criteria for inclusion in the bipolar affective group. Am J Psychiatry. 1977 Nov;134(11):1227–1233. doi: 10.1176/ajp.134.11.1227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashby H. B., Crowe R. R. Unipolar depression: a family study of a large kindred. Compr Psychiatry. 1978 Sep-Oct;19(5):415–417. doi: 10.1016/0010-440x(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. Linkage between an X-chromosome marker (deutan color blindness) and bipolar affective illness. Occurrence in the family of a lithium carbonate-responsive schizo-affective proband. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1977 Jun;34(6):721–725. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1977.01770180107010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher K. D., Elston R. C., Green R., Whybrow P., Helzer J., Reich T., Clayton P., Winokur G. The transmission of manic depressive illness--II. Segregation analysis of three sets of family data. J Psychiatr Res. 1981;16(1):65–78. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(81)90014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher K. D., Elston R. C. The transmission of manic depressive illness--I. Theory, description of the model and summary of results. J Psychiatr Res. 1981;16(1):53–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(81)90013-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannings C., Thompson E. A. Ascertainment in the sequential sampling of pedigrees. Clin Genet. 1977 Oct;12(4):208–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1977.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe R. R., Namboodiri K. K., Ashby H. B., Elston R. C. Segregation and linkage analysis of a large kindred of unipolar depression. Neuropsychobiology. 1981;7(1):20–25. doi: 10.1159/000117829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunner D. L., Fleiss J. L., Addonizio G., Fieve R. R. Assortative mating in primary affective disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 1976 Feb;11(1):43–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elston R. C. Ascertainment and age of onset in pedigree analysis. Hum Hered. 1973;23(2):105–112. doi: 10.1159/000152561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elston R. C., Namboodiri K. K., Spence M. A., Rainer J. D. A genetic study of schizophrenia pedigrees. II. One-locus hypotheses. Neuropsychobiology. 1978;4(4):193–206. doi: 10.1159/000117633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elston R. C., Sobel E. Sampling considerations in the gathering and analysis of pedigree data. Am J Hum Genet. 1979 Jan;31(1):62–69. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elston R. C., Stewart J. A general model for the genetic analysis of pedigree data. Hum Hered. 1971;21(6):523–542. doi: 10.1159/000152448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elston R. C., Yelverton K. C. General models for segregation analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1975 Jan;27(1):31–45. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon E. S., Bunney W. E., Jr, Leckman J. F., Eerdewegh M., DeBauche B. A. The inheritance of affective disorders: a review of data and of hypotheses. Behav Genet. 1976 Jul;6(3):227–261. doi: 10.1007/BF01065722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon E. S., Dunner D. L., Sturt L., Goodwin F. K. Assortative mating in the affective disorders. Biol Psychiatry. 1973 Aug;7(1):63–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon E. S., Hamovit J., Guroff J. J., Dibble E., Leckman J. F., Sceery W., Targum S. D., Nurnberger J. I., Jr, Goldin L. R., Bunney W. E., Jr A family study of schizoaffective, bipolar I, bipolar II, unipolar, and normal control probands. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1982 Oct;39(10):1157–1167. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1982.04290100031006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon E. S., Targum S. D., Leckman J. F. Platelet monoamine oxidase (MAO) activity and genetic vulnerability to bipolar (BP) affective illness. Psychopharmacol Bull. 1979 Jan;15(1):27–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon E. S., Targum S. D., Matthysse S., Bunney W. E., Jr Color blindness not closely linked to bipolar illness. Report of a new pedigree series. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1979 Dec;36(13):1423–1430. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1979.01780130041005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin L. R., Clerget-Darpoux F., Gershon E. S. Relationship of HLA to major affective disorder not supported. Psychiatry Res. 1982 Aug;7(1):29–45. doi: 10.1016/0165-1781(82)90050-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leckman J. F., Gershon E. S., McGinniss M. H., Targum S. D., Dibble E. D. New data do not suggest linkage between the Xg blood group and bipolar illness. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1979 Dec;36(13):1435–1441. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1979.01780130053006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON N. E. The detection and estimation of linkage between the genes for elliptocytosis and the Rh blood type. Am J Hum Genet. 1956 Jun;8(2):80–96. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazure C., Gershon E. S. Blindness and reliability in lifetime psychiatric diagnosis. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1979 May;36(5):521–525. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1979.01780050031002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendlewicz J., Fleiss J. L., Fieve R. R. Evidence for X-linkage in the transmission of manic-depressive illness. JAMA. 1972 Dec 25;222(13):1624–1627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendlewicz J., Fleiss J. L. Linkage studies with X-chromosome markers in bipolar (manic-depressive) and unipolar (depressive) illnesses. Biol Psychiatry. 1974 Dec;9(3):261–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendlewicz J., Linkowski P., Guroff J. J., Van Praag H. M. Color blindness linkage to bipolar manic-depressive illness. New evidence. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1979 Dec;36(13):1442–1447. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1979.01780130060007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendlewicz J., Linkowski P., Wilmotte J. Linkage between glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency and manic-depressive psychosis. Br J Psychiatry. 1980 Oct;137:337–342. doi: 10.1192/bjp.137.4.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendlewicz J., Linkowski P., Wilmotte J. Relationship between schizoaffective illness and affective disorders or schizophrenia. Morbidity risk and genetic transmission. J Affect Disord. 1980 Dec;2(4):289–302. doi: 10.1016/0165-0327(80)90030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt A. D., Rivas M. L., Bixler D., Newell R. Salivary and pancreatic amylase: electrophoretic characterizations and genetic studies. Am J Hum Genet. 1973 Sep;25(5):510–522. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negri F., Melica A. M., Zuliani R., Gasperini M., Macciardi F., Smeraldi E. Genetic implications in assortative mating of affective disorders. Br J Psychiatry. 1981 Mar;138:236–239. doi: 10.1192/bjp.138.3.236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. Estimation of the recombination fraction in human pedigrees: efficient computation of the likelihood for human linkage studies. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Sep;26(5):588–597. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risch N., Baron M. X-linkage and genetic heterogeneity in bipolar-related major affective illness: reanalysis of linkage data. Ann Hum Genet. 1982 May;46(Pt 2):153–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1982.tb00706.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeraldi E., Negri F., Heimbuch R. C., Kidd K. K. Familial patterns and possible modes of inheritance of primary affective disorders. J Affect Disord. 1981 Jun;3(2):173–182. doi: 10.1016/0165-0327(81)90042-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Targum S. D., Gershon E. S., Van Eerdewegh M., Rogentine N. Human leukocyte antigen system not closely linked to or associated with bipolar manic-depressive illness. Biol Psychiatry. 1979 Aug;14(4):615–636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner W. J., King S. Two genetically distinct forms of bipolar affective disorder? Biol Psychiatry. 1981 May;16(5):417–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Eerdewegh M. M., Gershon E. S., Van Eerdewegh P. M. X-chromosome threshold models of bipolar manic-depressive illness. J Psychiatr Res. 1979;15(4):215–238. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(79)90014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitkamp L. R., Pardue L. H., Huntzinger R. S. Genetic marker studies in a family with unipolar depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1980 Oct;37(10):1187–1192. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1980.01780230105016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winokur G. Depression spectrum disease: description and family study. Compr Psychiatry. 1972 Jan;13(1):3–8. doi: 10.1016/0010-440x(72)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Praag H. M., de Haan S. Central serotonin metabolism and frequency of depression. Psychiatry Res. 1979 Dec;1(3):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0165-1781(79)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


