Figure 1.
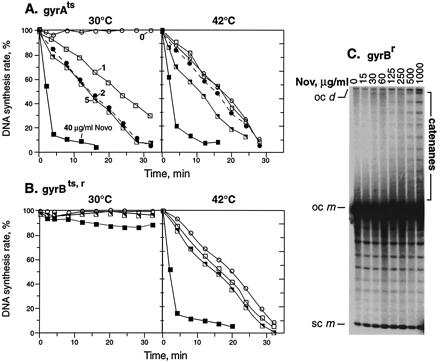
Effects on DNA replication of novobiocin addition and mutational inactivation of gyrase. Novobiocin (Nov) was added to acrAgyrA43ts cells (A) or acrA gyrBts,r novobiocin-resistant cells (B) at time 0. Cells were pulsed for 1 min with [3H]thymidine at each time point and acid precipitable counts determined. (A and B) Novobiocin concentrations were (○) 0 μg/ml; (□) 1 μg/ml; (●) 2 μg/ml; (└) 5 μg/ml; and (▪) 40 μg/ml. The rate of DNA synthesis shown is the percentage of the rate in an isogenic wild-type strain grown in parallel but without drug. (C) A acrA+gyrBr strain was treated with the indicated concentrations of novobiocin for 15 min at 30°C, and plasmid DNA from the strain was nicked and analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. Positions of catenanes, supercoiled monomers (sc m), open circular monomer (oc m), and open circular dimer (oc d) are indicated.
