Figure 1.
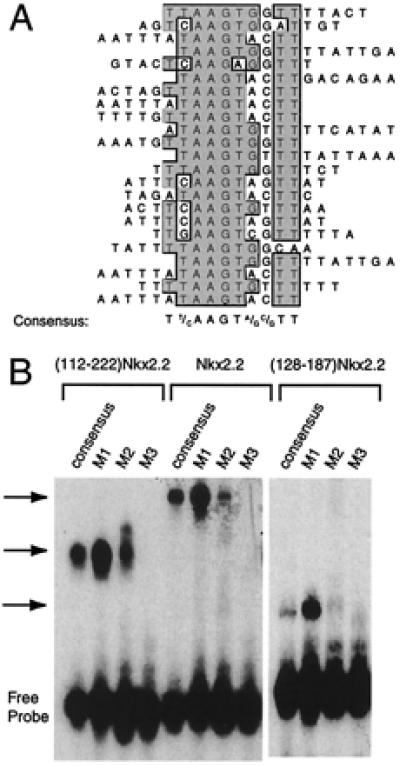
Nkx2.2 binding site selection. (A) Binding site selection was performed with the human Nkx2.2 homeodomain and NK2-SD (amino acids 112–221) and a set of oligonucleotides containing a 15-bp random stretch flanked by PCR primer sites. Sequenced products from the eighth round of selection are shown aligned by the clustal w alignment algorithm in macvector 6.5 software (Oxford Molecular). The consensus sequence that emerges from the best-fit line-up is shown. (B) An EMSA using in vitro translated ()Nkx2.2, full-length Nkx2.2, and the Nkx2.2 homeodomain alone (amino acids 128–187). Different 32P-labeled oligonucleotides (sequences shown in Table 1) were incubated with 1 μl of each in vitro translated protein for 15 min at room temperature and then subjected to electrophoresis on a 5% polyacrylamide gel. The free probe and retarded complex are indicated.
