Figure 4.
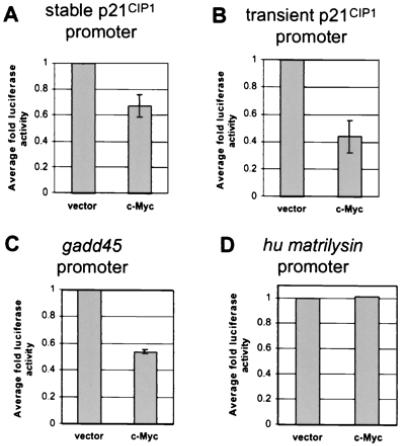
c-Myc-mediated transcriptional repression. (A) Repression of the p21CIP1 promoter in stable reporter lines by c-Myc. Generation of NIH 3T3 cell lines stably expressing p21CIP1-luciferase reporter constructs is described in Materials and Methods. Cells were analyzed for luciferase activity 24 hr after plating and normalized by standard protein assay. Fold luciferase activity was determined as compared to vector alone. Error bars represent standard deviation of the average of duplicate readings from four independent stable clones. (B) Repression of the p21CIP1 promoter by c-Myc. A 2.3-kb fragment of the p21CIP1 promoter linked to a luciferase reporter gene was transiently transfected into NIH 3T3 fibroblasts. Cells were cotransfected with a βgal vector for standardization and 1 μg of either empty CMV vector or c-Myc expression vector. Luciferase activity was determined 48 hr after transfection and normalized to β-gal activity. Fold luciferase activity was determined as compared to vector alone. Error bars represent standard deviation of the average of three independent experiments. (C) Repression of the gadd45 promoter by c-Myc. Reporter assays were performed as described for B, where 1 μg of either empty CMV or c-Myc expression vector was cotransfected into cells with a gadd45 luciferase reporter construct. Error bars represent standard deviation of the average of three independent experiments. (D) c-Myc expression does not affect transcription of the human matrilysin promoter. NIH 3T3 fibroblasts were transiently transfected with a reporter vector containing the human matrilysin promoter. Cells were then cotransfected with 1 μg of either empty CMV vector or c-Myc expression vector. Fold luciferase activity was determined as described for B.
