Figure 3.
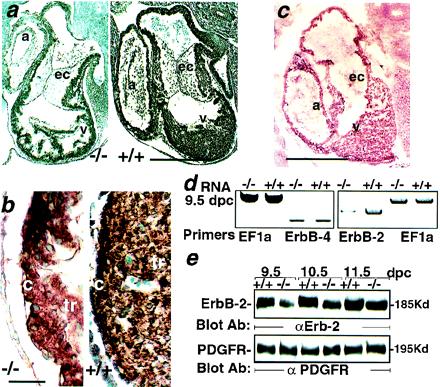
Reduced ErbB-2 expression in 5-HT2B mutant embryos. (a) The immunohistochemical staining of paraffin sections with anti-ErbB-2 antibody through the heart region of 10.5 dpc wild-type (Right) and mutant embryos (Left). (b) Enlargement of a. The ErbB-2 expression is globally reduced, including over the trabeculae (tr) and the compact zone (c) of the mutant ventricle (v). (c) Immunohistochemical labeling with an anti-5-HT2B-specific antibody performed on cryostat sections of 10.5-dpc embryos illustrates the wild-type expression of 5-HT2B receptor in the trabecular and the compact zone of the heart but not in the endocardial cushions (ec). (d) Semiquantitative reverse transcription–PCR shows a strong reduction of ErbB-2 mRNA in 9.5-dpc mutant embryos whereas ErbB-4 and the ribosomal elongation factor EF1a expression in the same RNA preparation remains unchanged. (e) A Western blot analysis with an anti-ErbB-2 antibody demonstrates a reduction of ErbB-2 expression in total protein extract from 5-HT2B mutant embryos (from 9.5 to 11.5 dpc) (Upper). The platelet-derived growth factor receptor immunoreactivity in the same mutant embryo extracts remains unmodified (Lower). a, Atrium; α, anti-. (Bars for a and c = 250 μm, and b = 25 μm.)
