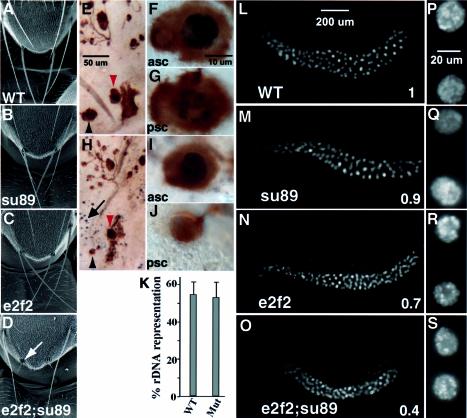
Fig. 4. Macrochaetae and salivary gland phenotypes of the de2f2;dE2F1su89 double mutants. SEM images of the fly notum are shown in (A–D). The wild-type (A), dE2F1su89 mutants (B) and de2f2 (C) showed normal macrochaetaes in the adults. In contrast, de2f2;dE2F1su89 adults showed severe defects in their macrochaetaes (D, white arrow). BrdU and mAb22C10 double labeling of the pupal nota is shown in (E–J). Pupa nota were dissected at 28 h AEL and were stained with mAb22C10 to mark the cell bodies of the sensory cluster (in brown) and BrdU antibody to visualize S phase cells (in black). A wild-type notum is shown in (E–G). (E) Low magnification view. The anterior scutellar bristle (asc, red arrowhead) and the posterior scutellar bristle (psc, black arrowhead) are shown in (F) and (G), respectively. The same developmental stage de2f2;de2f1su89 notum is show in (H–J). (H) Low magnification view. (I and J) High magnification views of the asc and psc, respectively. (K) The relative copy numbers of the rDNA sequences in wild-type and de2f2;dE2F1su89 mutant salivary glands are shown. The ratios of the hybridization signals of the rDNA sequences to a euchromatic sequencs from the salivary gland DNA were determined. Mitotically active diploid disc DNA, which is considered to have 100% representation of all the heterochromatic sequences, was used for normalization. The averages of at least three experiments are shown. WT, wild-type; Mut, de2f2;dE2F1su89 mutants. (L–S) Images of salivary glands stained with DAPI are shown. Low (L–O) and high (P–S) magnification images of salivary glands from wild-type (L and P), dE2F1su89 mutants (M and Q), de2f2 mutants (N and R) and de2f2;dE2F1su89 mutants (O and S). Numbers in (L–O) indicate the average DNA content of the salivary gland nuclei normalized by that from the wild-type. Note that while the salivary gland nuclei from the dE2F1su89 mutant had a similar DNA content to those from the wild-type (P = 0.24), the DNA content of the de2f2 mutant salivary gland nuclei was less than that of the wild-type (P < 0.00001) but more than that of the de2f2;dE2F1su89 (P < 0.00001).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.