Figure 3.
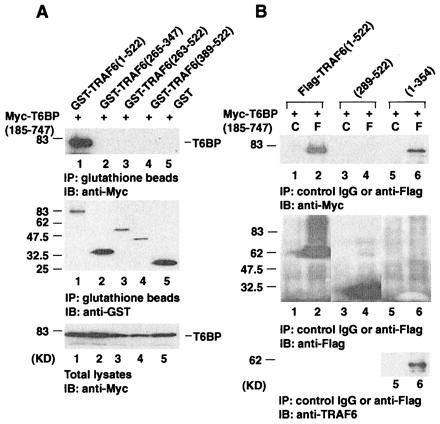
The N-terminal ring finger and zinc finger regions of TRAF6 are required for its interaction with T6BP. (A) 293 cells were transiently transfected with the Myc-epitope tagged T6BP (amino acids 185–747) and the GST-tagged TRAF6 deletion mutants. Cell extracts were prepared and immunoprecipitated (IP) with glutathione beads. Coprecipitating Myc-T6BP was detected by immunoblotting (IB) analysis with the anti-Myc polyclonal antibody (Top). The amounts of GST-TRAF6 deletion mutants immunoprecipitated and the expression levels of Myc-T6BP in total cell extracts were determined by immunoblotting with anti-GST antibody (Middle) and anti-Myc antibody (Bottom). (B) Myc-epitope tagged T6BP (amino acids 185–747) and the Flag-tagged TRAF6 deletion mutants were transiently expressed in 293 cells. Cell extracts were prepared and immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag monoclonal antibody (F) or control mouse IgG (C). Coprecipitating Myc-T6BP was detected by immunoblotting analysis with the anti-Myc polyclonal antibody (Top). The amounts of TRAF6 deletion mutants immunoprecipitated were determined by immunoblotting with anti-Flag polyclonal antibody (Middle). The expression of Flag-TRAF6 (amino acids 1–354) is weak but can be detected with anti-TRAF6 monoclonal antibody (Bottom). KD, kilodalton.
