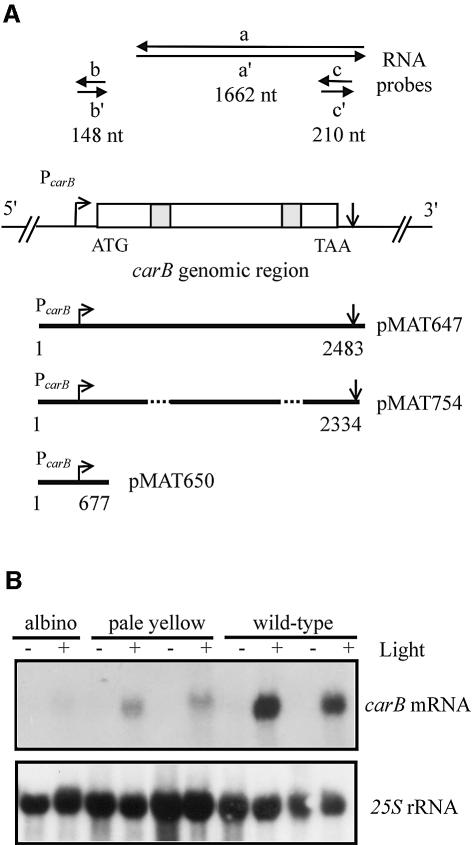
Fig. 1. (A) Schematic representation of the carB genomic region. The transcription start and polyadenylation sites (arrows), the translation start and termination codons, and the exons and introns (open and shaded boxes) are indicated. Above the scheme, carB riboprobes utilized to detect small sense and antisense RNAs. Below, carB constructs used for transformation. The length (in base pairs) of the carB sequence in each construct is indicated. (B) Northern blot analysis of transformants containing carB exogenous sequences. RNAs were extracted from dark-grown or light-pulsed mycelia of five pMAT754 transformants showing different phenotypes. About 5 µg of RNA was loaded in each lane and hybridized with a 1.8 kb cDNA fragment of the carB gene. The membrane was reprobed with a 25S rRNA probe to check loading. Illuminated mycelia were exposed to blue light for 4 min at 4 W/m2, and incubated in the dark for 20 min before RNA isolation. Densitometric analysis was used to estimate the mRNA levels.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.