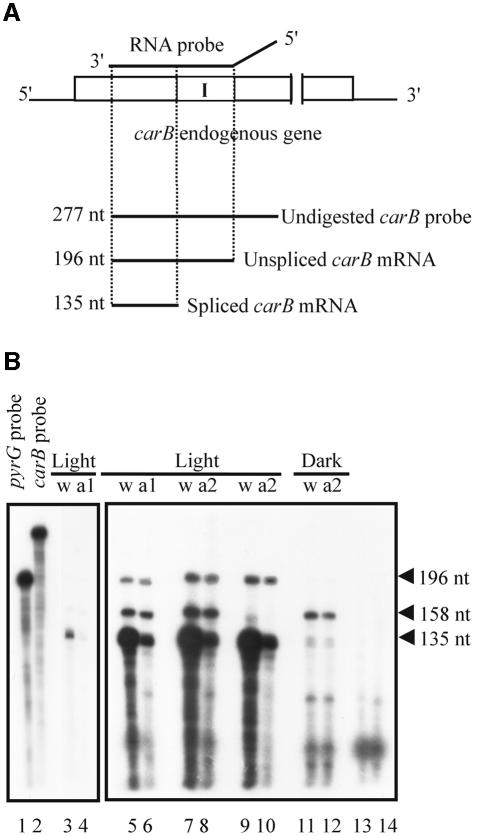
Fig. 4. RNase protection experiments for carB transcripts. (A) Schematic representation of endogenous carB transcripts, showing the expected sizes of fragments protected by unspliced and spliced carB mRNA. The rectangle represents the transcribed region of the endogenous carB gene. Shaded box indicates an intron (I) of the carB gene. The RNA probe (277 nt) was generated from plasmid pMAT643 and is indicated by a solid line above the carB gene. The probe contains sequences derived from the plasmid, which are indicated by the diagonal portion of the solid line. (B) RNase protection analysis was performed on total RNA isolated from light-pulsed or dark-grown mycelia of the wild-type strain (w) or two albino pMAT754 transformants (a1 and a2). A pyrG probe (202 nt) generated from plasmid pMAT645 was used as control to normalize the RNA quantity. This probe protects a 158 nt fragment of the pyrG mRNA. Lanes 1–4 correspond to a filter exposed for 1 h, and lanes 5–14 correspond to a filter exposed for 15 h. Lane 1, undigested pyrG probe; lane 2, undigested carB probe; lanes 3–8, RNase protection experiments using both the carB and the pyrG probes on RNA isolated from light-pulse mycelia; lanes 9 and 10, RNase protection experiments using only the carB probe; lanes 11 and 12, RNase protection experiments using both the carB and the pyrG probes on RNA isolated from dark-grown cultures; lane 13, carB probe digested with RNase; lane 14, pyrG probe digested with RNase.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.