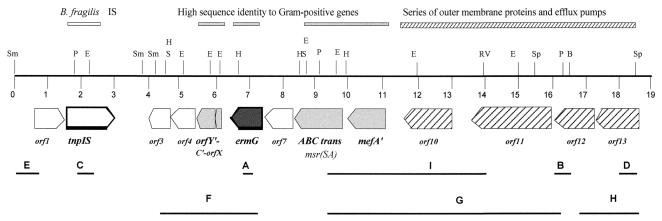
FIG. 2.
Schematic diagram of the 19-kb region isolated from CTnGERM1. Restriction enzymes shown include SmaI (Sm), PstI (P), EcoRI (E), SacI (S), BamHI (B), SphI (Sp), HindIII (H), and EcoRV (RV). Size in kb is indicated by numbers from 0 to 19. Fragments A, B, C, D, and E were used either as inserts cloned into pLYL001 for plasmid rescue or as probes for hybridization to the chromosome DNA. Fragment F was used as the probe for detecting the ermG-containing bands in Fig. 1B. Fragments G and H were used as probes for detecting the distribution of the upstream ermG multidrug resistance region in Bacteroides strains. Fragment I, a 4.9-kb PstI-EcoRV fragment including the mefA, was cloned into pGW47 to determine whether this fragment contained a gene that was responsible for low-level erythromycin resistance in Bacteroides hosts. Description of the functions and sequence identities are indicated by the bars above the map. Genes in light gray are homologs to known gram-positive genes, the striped arrows indicate the genes that are homologs to efflux and membrane proteins involved in antibiotic resistance mechanisms, and the putative Bacteroides IS transposase is indicated.