Figure 5.
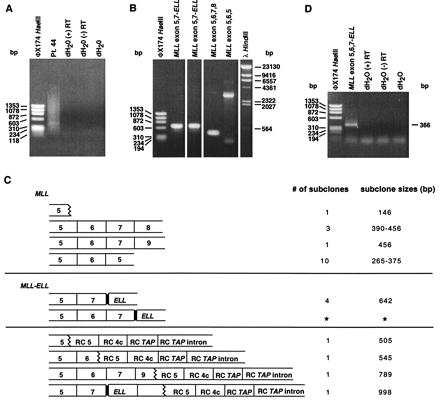
(A) cDNA panhandle PCR analysis of total RNA from t-AML of patient 44. Smear indicates products of heterogeneous sizes (lane Pt. 44). (B) PCR screen of representative recombination PCR-generated subclones of cDNA panhandle PCR products shown in A. MLL-containing subclones shown by sequencing are indicated above respective lanes. (C) Summary of sequences in recombination PCR-generated subclones. Fifteen subclones contained MLL sequence alone (Top). Alternatively spliced and scrambled transcripts were detected. Alternatively spliced chimeric transcript identified by cDNA panhandle PCR in which MLL exon 6 was absent had in-frame fusion of MLL exon 7 to position 148 of ELL cDNA (GenBank accession no. U139480) (Middle). * shows second MLL-ELL chimeric transcript in which MLL exon 6 was present, which was identified by amplification of same first-strand cDNA with gene-specific primers (please see second lane, D). Transcripts with MLL or MLL-ELL and TAP sequences are unconfirmed (Bottom). RC indicates reverse complement. (D) Detection of second MLL-ELL chimeric transcript by PCR with gene-specific primers. Sequence of 366-bp product showed fusion of MLL exon 7 to ELL in transcript in which MLL exons 5–7 all were present (lane 2) (please see * in C).
