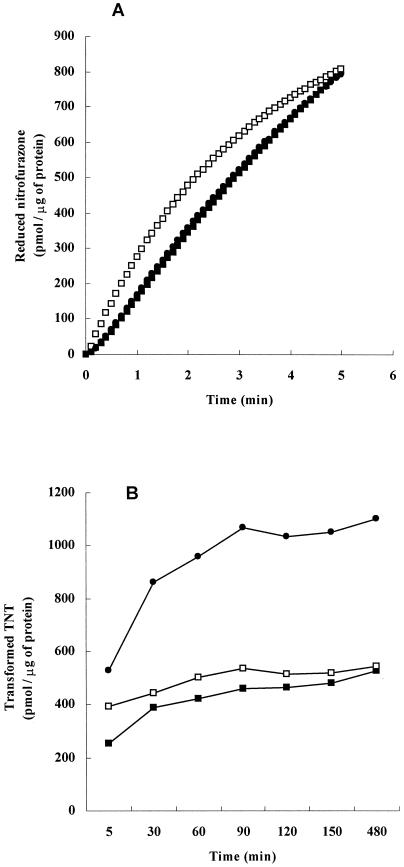
FIG. 2.
(A) Nitrofurazone-reducing activity. The reduction of nitrofurazone was determined by measuring the decrease in the absorbance of nitrofurazone at 400 nm (molar extinction coefficient, 12,960 M−1 cm−1). A basic enzyme reaction mixture (1.5 ml) containing 10 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 7.0), 0.1 mM NADH, 10 μM nitrofurazone, and 10 μg of either GST-EcNfsA (▪), GST-EcNfsB (□), or GST-VhNfsA (•) was incubated at 30°C. The reaction was started by the addition of NADH. One unit was defined as the amount of the enzyme that reduced 1 pmol of nitrofurazone/μg of protein. (B) TNT-reducing activity. The transformation of TNT was determined by measuring the decrease in the absorbance of TNT at 447 nm. The standard assay mixture (1 ml) containing 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.0), 0.1 mM TNT, 1 mM NADH, and either 172 μg of GST-EcNfsA (▪), 166 μg of GST-EcNfsB (□), or 82 μg of GST-VhNfsA (•) was incubated at 30°C. Theenzymatic reaction was initiated by adding NADH. The reaction was quenched by adding 160 μl of 1 M NaOH, resulting in a pH of 12.2. Quantitative measurements were made 5 min after the addition of NADH to the TNT solution. One unit was defined as the amount of the enzyme that reduced 1 pmol of TNT/μg of protein.