Figure 4.
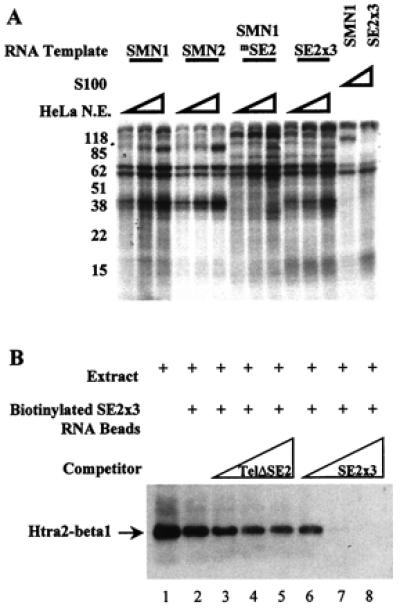
Htra2-β1 binds the SMN exon 7 ESE SE2. (A) Cross-linking of cellular factors to SMN exon 7 RNA. Sense strand RNA corresponding to exon 7 from SMN1, SMN2, SMN1 with the SE2 mutation (SMN1mSE2), or three wild-type copies of SE2 (SE2 × 3), were transcribed and uniformly labeled with all four α-32P NTPs in vitro. Increasing amounts (10, 20, or 30 μg) of splicing competent HeLa nuclear extract or 30 μg of the S100 fraction were reacted with the RNAs under splicing conditions for 15 min before heparin was added (final concentration 2 mg/ml). Samples were UV-irradiated, digested with RNaseA (20 μg) and RNaseT1 (40 units), and resolved by 10% SDS/PAGE. (B) In vitro binding of Htra2-β1 and SMN-derived RNA. C33a cellular extract containing transiently transfected HA-tagged Htra2-β1 (lane 1) binds efficiently to RNA corresponding to three copies of the AG-rich SE2 element (lane 2) when detected by HA-specific antibodies. The RNA-protein interaction of Htra2-β1 and SE2 × 3 RNA was poorly blocked by the addition of increasing amounts of SMN exon 7 RNA that contained the SE2 mutation (lanes 3–5). SE2 × 3:Htra2-β1 binding was efficiently competed by the addition of increasing amounts of RNA corresponding to three wild-type copies of SE2 (lanes 6–8).
