Figure 2.
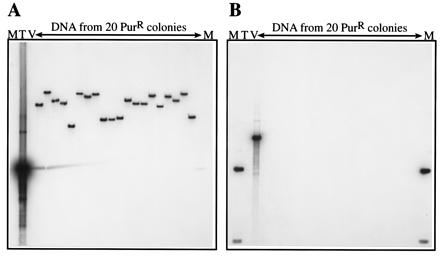
Verification of mini-MAR transposition by DNA hybridization. Genomic DNA from 20 PurR colonies obtained by transformation of M. acetivorans with the delivery plasmid pWM381 was digested with EcoRI (which does not cut within the transposon), electrophoresed, and blotted onto nylon membranes as described in Materials and Methods. The membranes then were examined by hybridization with two probes, one specific for the transposon only (A), the other specific for the delivery vector backbone only (B). Each of the 20 transposon insertions was at a different site within the M. acetivorans genome as shown by the different-sized bands in A. None of the 20 insertions hybridized to the vector probe, indicating that the delivery plasmid backbone was lost in all cases (B). The plasmids that were used as probes also were included in the blot as positive controls for hybridization and as molecular weight markers. pBluescript SK+ (2.9 kbp), which hybridizes only to the vector backbone, was used as a vector-specific probe (V), and pJK4 (1.6 kbp), which hybridizes only to the mini-MAR insert, was used as a transposon-specific probe (T). The 1-kbp ladder (Life Technologies) is shown by M, the hybridizing band in B is 1.6 kbp.
