Figure 2.
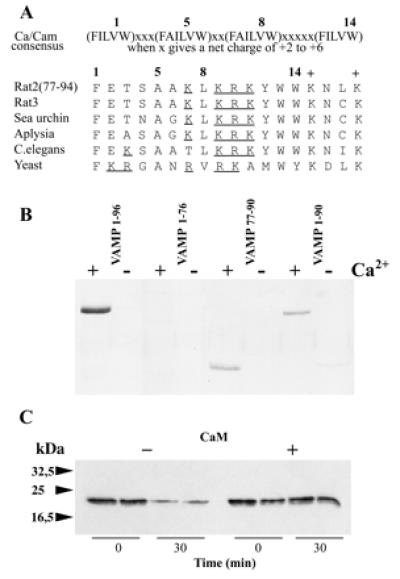
Localization of the calmodulin-binding site to the C-terminal domain of VAMP 2. (A) Residues 77–90 of rat VAMP 2 contain a 1–5-8–14 consensus motif for calcium-dependent calmodulin binding proposed by Rhoads and Friedberg (18). A comparison of VAMP homologues from rat (VAMP 3/cellubrevin), sea urchin (Strongylocentrotus purpuratus) cortical vesicles, aplysia (Aplysia californica), nematode (Caenorhabditis elegans), and yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae Snc1) illustrates evolutionary conservation of this motif. Basic residues within the motif are underlined. Two conserved lysines (+) C-terminal to the motif also contribute to calmodulin interactions (see Results). (B) The binding of GST-fusion proteins containing the sequences VAMP1–96, VAMP1–96 cleaved with TeTx light chain (i.e., VAMP1–76), VAMP77–90, and VAMP1–90 to calmodulin–agarose beads was assayed as in Fig. 1A. (C) Immunoisolated synaptic vesicles from rat brain were incubated with TeTx light chain (300 pM) in buffer containing 1 mM CaCl2, in the presence or absence of calmodulin (15 μM). Duplicate aliquots were removed immediately (0 min) or after a 30-min incubation. Samples were denatured and processed for Western blotting with an antibody directed against the N-terminal region of VAMP 2.
