Figure 3.
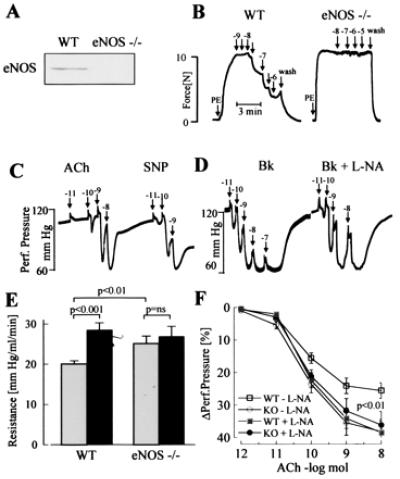
Effects of ACh, SNP, and l-NA on vasodilator responses of eNOS −/− mice. (A) Expression of eNOS in mouse aortic rings from WT and eNOS −/− mice as detected by Western blot analysis. (B) Original tracings showing relaxations of isolated aortic rings from WT and eNOS −/− mice. After constriction with phenylephrine (PE), cumulative dose–response curves to ACh were obtained. Numbers above the arrows indicate the final concentration of the agonist (log mol/liter). Tracings are representative of data obtained in six additional experiments. (C and D) Original tracings showing changes in hindlimb perfusion pressure in eNOS −/− mice upon bolus application of ACh or SNP (C) or bradykinin (Bk) (D) in the presence of diclofenac and presence or absence of l-NA. Numbers above the arrows indicate the dose of the agonist applied as a bolus (log mol). (E) Peripheral resistance of the perfused hindlimb of WT and eNOS −/− mice in the absence (shaded columns) and presence (filled columns) of l-NA. ns, Not significant. (F) Vasodilator responses to bolus applications (100 μl) of ACh in the perfused hindlimb of WT (□,■) and eNOS −/− mice (○,●) in the absence (open symbols) and presence (filled symbols) of l-NA (n ≥ 8).
