Figure 4.
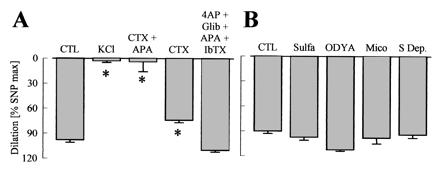
Effects of K+ channel blockade and cytochrome P450 (CYP) inhibition on ACh-induced vasodilator responses in the hindlimb of WT mice. Experiments were performed in presence of diclofenac (10 μmol/liter) and l-NA (300 μmol/liter). (A) CTL = control, potassium channel blockade with charybdotoxin (CTX, 100 nmol/liter), apamin (APA, 100 nmol/liter), 4-aminopyridine, (4AP, 5 mmol/liter), glibenclamide, (Glib, 1 μmol/liter), and iberiotoxin (IbTX, 100 nmol/liter). (B) Inhibition of CYP enzymes with 17-octadecynoic acid (ODYA, 10 μmol/liter), miconazole (Mico, 10 μmol/liter), and sulfaphenazole (Sulfa, 10 μmol/liter) or of arachidonic acid release (S Dep, substrate depletion) by using the combination of the phospholipase A2 inhibitors arachidonyl trifluoromethyl ketone (AACOCF3, 3 μmol/liter) and ONO-RS-082 (10 μmol/liter) with the diacylglycerol-lipase inhibitor THC-80267 (10 μmol/liter). ∗, P < 0.05; n ≥ 4.
