Fig. 2.
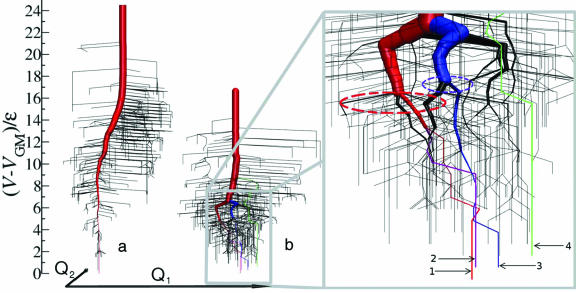
New three-dimensional DGs for Go#x0304; (a) and BLN (b) models where the energy bin ΔV is 0.3ε (19). The paths leading to the global minimum (GM) and the second, third, and fourth lowest minima are highlighted in red, purple, blue, and green, respectively. Roots 1, 2, 3, and 4 of the BLN model terminate at minimum conformations at −53.62ε(GM), −53.53ε, −53.44ε, and −53.14ε, respectively. In the (Q1,Q2) plane, the second, third, and fourth most stable minimum conformations are located at distances of 0.29σ, 2.04σ, and 11.99σ from the GM. Here we have used 500 minima and 636 saddles for the BLN model, and 520 minima and 844 saddles for the Gō model (16). The potential energy function is described by V = (Kr/2)Σi(ri − r0i)2 + (Kθ/2)Σi(θi − θ0i)2 + Σi[A(1 + cosΦi) + B(1 + cos3Φi)] + 4εΣi<j−3S1[(σ/Rij)12 − S2(σ/Rij)6], where S1 = S2 = 1 for BB (attractive) interactions, S1 = 2/3 and S2 = −1 for LL and LB (repulsive) interactions, and S1 = 1 and S2 = 0 for all the other pairs involving N, expressing only excluded volume interactions. Kr = 231.2εσ−2 and Kθ = 20ε/rad2, with the equilibrium bond length r0i = σ and the equilibrium bond angle θ0i = 1.8326 rad. For visual clarity, slightly thicker lines were used for roots 1–4 than the thickness evaluated from the size of superbasins.