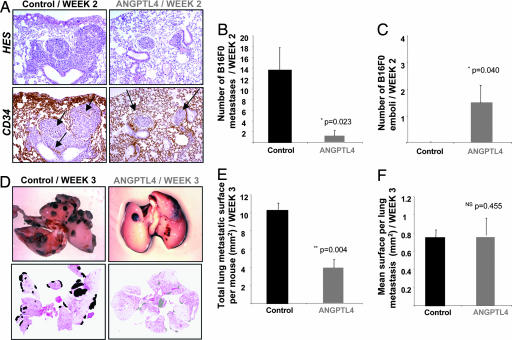
Fig. 3.
In the B16F0 model, ANGPTL4 inhibits extravasation of tumor cells and macrometastases number. B16F0 cells were injected i.v. into C57BL/6 mice 2 weeks after ANGPTL4 electroporation, and mice were killed either 2 or 3 weeks later. At week 2, tumor islets were observed in lungs by staining sections with HES (A Upper) and anti-CD34 (A Lower), allowing discrimination of C57BL/6 micrometastases implanted in the lung parenchyma from intravascular emboli. Left panel, arrows indicate residual vascular walls associated with tumor cell extravasation in control lung. Right panel, arrows show intact vessels enclosing localized nodules (emboli) in lungs from ANGPTL4 mice (A). Quantification of micrometastases invaded the parenchyma of the lung (B) and localized emboli (C). Typical views of lungs presenting macroscopic metastases at week 3 (D Upper). For each mouse, quantification of total metastatic area (E) and mean surface area per macrometastasis (F) was performed by using scanned images of HES-stained lung sections (D Lower).